[ad_1]

An information-stealing Google Chrome browser extension named “VenomSoftX” is deployed by Windows malware to steal cryptocurrency and clipboard contents when users browse the web.
This Chrome extension is installed by ViperSoftX Windows malware, which acts as a JavaScript-based RAT (Remote Access Trojan) and cryptocurrency hacker.
ViperSoftX has been around since 2020, previously leaked by security researchers Cerberus and Colin Cowieand in a report of Fortinet.
However, in a new report published today by Avastthe researchers provide more details about the malicious browser extension and how the malicious operation has undergone significant development in recent times.
recent activity
Since the start of 2022, Avast has detected and stopped 93,000 ViperSoftX infection attempts against its customers, primarily impacting the United States, Italy, Brazil and India.
.png)
Source: Avast
The main distribution channel of ViperSoftX is torrent files containing laced game cracks and software product activators.
By analyzing hard-coded wallet addresses in samples from ViperSoftX and VenomSoftX, Avast discovered that the two had collectively earned their operators around $130,000 as of November 8, 2022.
This stolen cryptocurrency was obtained by hijacking attempted cryptocurrency transactions on compromised devices and does not include profits from parallel activities.
The downloaded executable is a malware loader that decrypts AES data to create the following five files:
- Log file hiding a ViperSoftX PowerShell payload
- XML file for task scheduler
- VBS file to establish persistence by creating a scheduled task
- Binary application (promised game or software)
- Manifest File
The single line of malicious code hides somewhere down the 5MB log text file and runs to decrypt the payload, the ViperSoftX thief.
The new ViperSoftX variants do not differ much from what has been analyzed in previous yearsincluding theft of cryptocurrency wallet data, execution of arbitrary commands, payload downloads from C2, etc.
A key feature of new ViperSoftX variants is installation of malicious browser extension named VenomSoftX on Chrome-based browsers (Chrome, Brave, Edge, Opera).
Infect Chrome
To remain hidden from victims, the installed extension masquerades as “Google Sheets 2.1”, supposedly a Google productivity app. In May, security researcher Colin Cowie also spotted the extension installed as “Update Manager”.
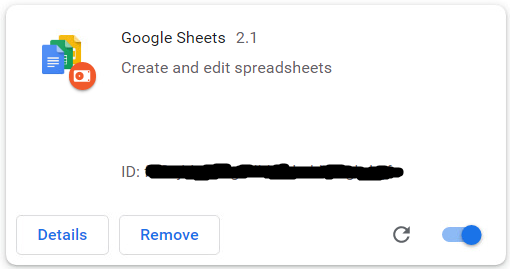
Source: Avast
Although VenomSoftX appears to overlap ViperSoftX’s activity since they both target a victim’s cryptocurrency assets, it performs the theft differently, giving operators a better chance of success.
“VenomSoftX primarily does this (steals crypto) by hooking API requests on a few very popular crypto exchanges that victims visit/have an account with,” Avast explains in the report.
“When a certain API is called, for example, to send money, VenomSoftX forges the request before it is sent to redirect the money to the attacker instead.”
Services targeted by VenomSoftX are Blockchain.com, Binance, Coinbase, Gate.io, and Kucoin, while the extension also monitors the clipboard for adding wallet addresses.
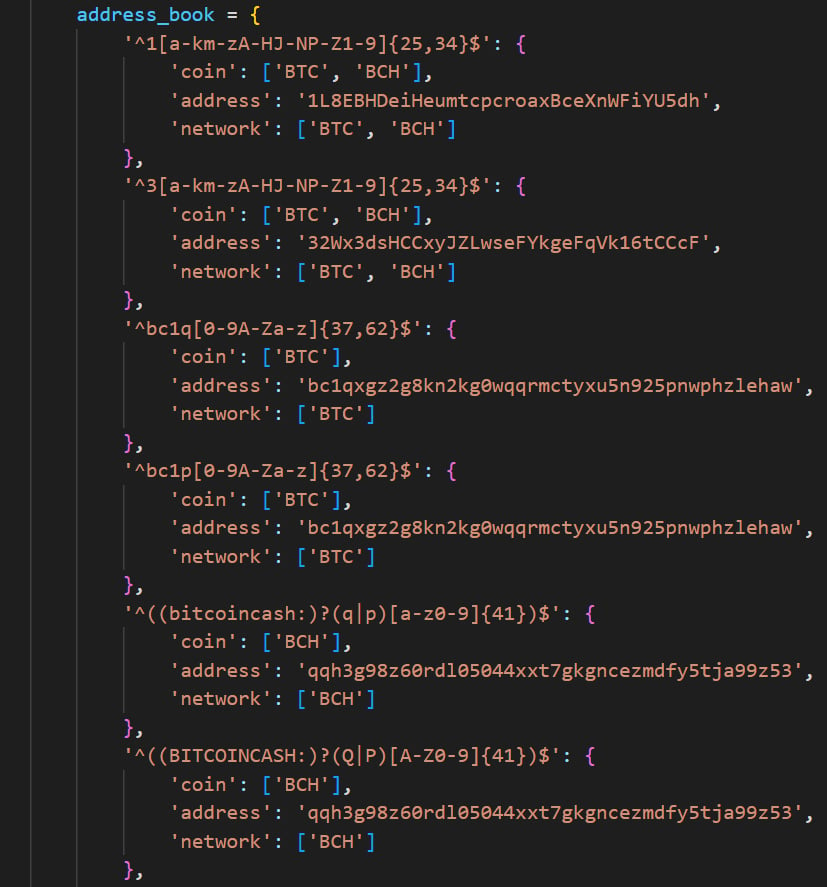
Source: Avast
Additionally, the extension can modify HTML on websites to display a user’s cryptocurrency wallet address while manipulating elements in the background to redirect payments to the threat actor.
To determine the victim’s assets, the VenomSoftX extension also intercepts all API requests to the cryptocurrency services mentioned above. It then sets the trade amount to the maximum available, siphoning off all available funds.
To make matters worse, for Blockchain.info, the extension will also attempt to steal passwords entered on the site.
“This module is about www.blockchain.com and he tries to hang on https://blockchain.info/wallet. It also modifies the password field getter to steal entered passwords,” Avast explains.
“Once the request to the API endpoint is submitted, the wallet address is extracted from the request, combined with the password, and sent to the collector as base64-encoded JSON via MQTT.”
Finally, if a user pastes content into any website, the extension will check if it matches any of the regular expressions shown above and, if so, send the pasted content to the actors of the threat.
As Google Sheets is normally installed in Google Chrome as an application under chrome://apps/ and not as an extension, you can check your browser’s extension page to determine if Google Sheets is installed.
If it is installed as an extension, you should remove it and clear your browser data to ensure the malicious extension is removed.
[ad_2]
Source link
