[ad_1]

Business-targeting Bumblebee malware is distributed via Google Ads and SEO poisoning that promotes popular software such as Zoom, Cisco AnyConnect, ChatGPT, and Citrix Workspace.
Bumblebee is a malware loader discovered in April 2022, which was allegedly developed by the Conti team as a replacement for the BazarLoader backdoor, used to gain initial access to networks and conduct ransomware attacks.
In September 2022, a new version of the malware loader was observed in the wild, with a stealthier attack chain which used the PowerSploit framework for reflexive DLL injection into memory.
Researchers from Secureworks recently uncovered a new campaign using Google ads that promote trojanized versions of popular apps to deliver the malware loader to unsuspecting victims.
Hide in popular apps
One of the campaigns seen by SecureWorks began with a Google advertisement promoting a fake Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility client download page created on February 16, 2023 and hosted on an “appcisco[.]com” domain.
“A chain of infection that started with a malicious Google ad sent the user to this fake download page via a compromised WordPress site,” the report from SecureWorks explains.
This fake landing page promoted an MSI installer containing a trojan named “cisco-anyconnect-4_9_0195.msi” that installs the BumbleBee malware.
Upon execution, a copy of the program’s legitimate installer and a misleadingly named PowerShell script (cisco2.ps1) are copied to the user’s computer.
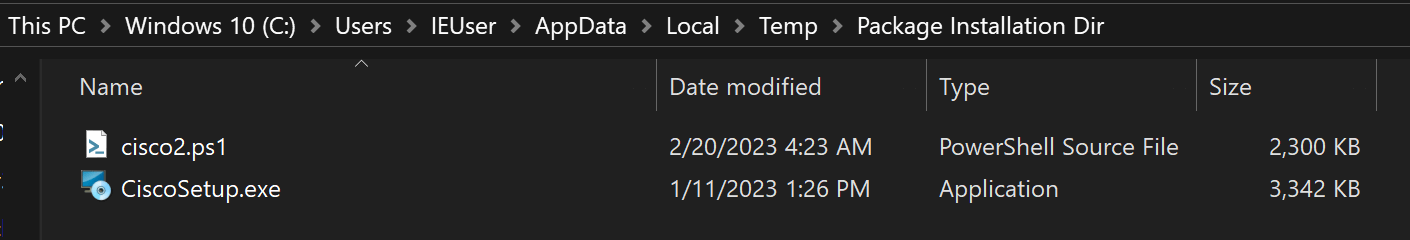
CiscoSetup.exe is the legitimate AnyConnect installer, installing the application on the device to avoid suspicion.
However, the PowerScrip script installs BumbleBee malware and conducts malicious activity on the compromised device.
“The PowerShell script contains a selection of renamed functions copied from the PowerSploit ReflectivePEInjection.ps1 script,” Secureworks explains.
“It also contains an encoded Bumblebee malware payload that it loads reflectively into memory.”
This means that Bumblebee still uses the same post-exploit framework module to load malware into memory without triggering alarms from existing antivirus products.
Secureworks found other software packages with pairs of files with the same name, such as ZoomInstaller.exe and zoom.ps1, ChatGPT.msi and chch.ps1, and CitrixWorkspaceApp.exe and citrix.ps1.
A path to ransomware
Considering that the Trojan software targets professional users, infected devices are candidates for the start of ransomware attacks.
Secureworks took a close look at one of Bumblebee’s recent attacks. They found that the threat actor leveraged their access to the compromised system to move laterally through the network approximately three hours after the initial infection.
The tools the attackers deployed on the hacked environment include the Cobalt Strike penetration testing suite, AnyDesk and DameWare remote access tools, network analysis utilities, an AD database dumper, and a Kerberos credential stealer.
This arsenal creates an attack profile that makes it highly likely that malware operators will want to identify accessible network points, switch to other machines, exfiltrate data, and possibly deploy ransomware.
[ad_2]
Source link
