[ad_1]

A crypto theft phishing campaign is underway to bypass multi-factor authentication and access accounts on Coinbase, MetaMask, Crypto.com and KuCoin and steal cryptocurrency.
Threat actors abuse the Microsoft Azure Web Apps service to host a network of phishing sites and lure victims there via phishing messages posing as fake transaction confirmation requests or the detection of suspicious activity.
For example, one of the phishing emails seen in the attacks claimed to be from Coinbase, which says it locked the account due to suspicious activity.
.png)
Source: PIXM
When targets visit the phishing site, they are presented with a chat window purporting to be for “customer support”, controlled by a scammer who leads visitors through a multi-step fraud process.
PIXM has been tracking this campaign since 2021 when the threat group targeted only Coinbase. Recently, PIXM analysts noticed an expansion of the campaign’s targeting scope to include MetaMask, Crypto.com, and KuCoin.
Bypass 2FA
The first phase of the attack in fake crypto exchange phishing sites involves a fake login form followed by a two-factor authentication prompt.
Whatever credentials are entered in this step will always be stolen by threat actors. The page then jumps to a prompt asking for the 2FA code needed to access the account.
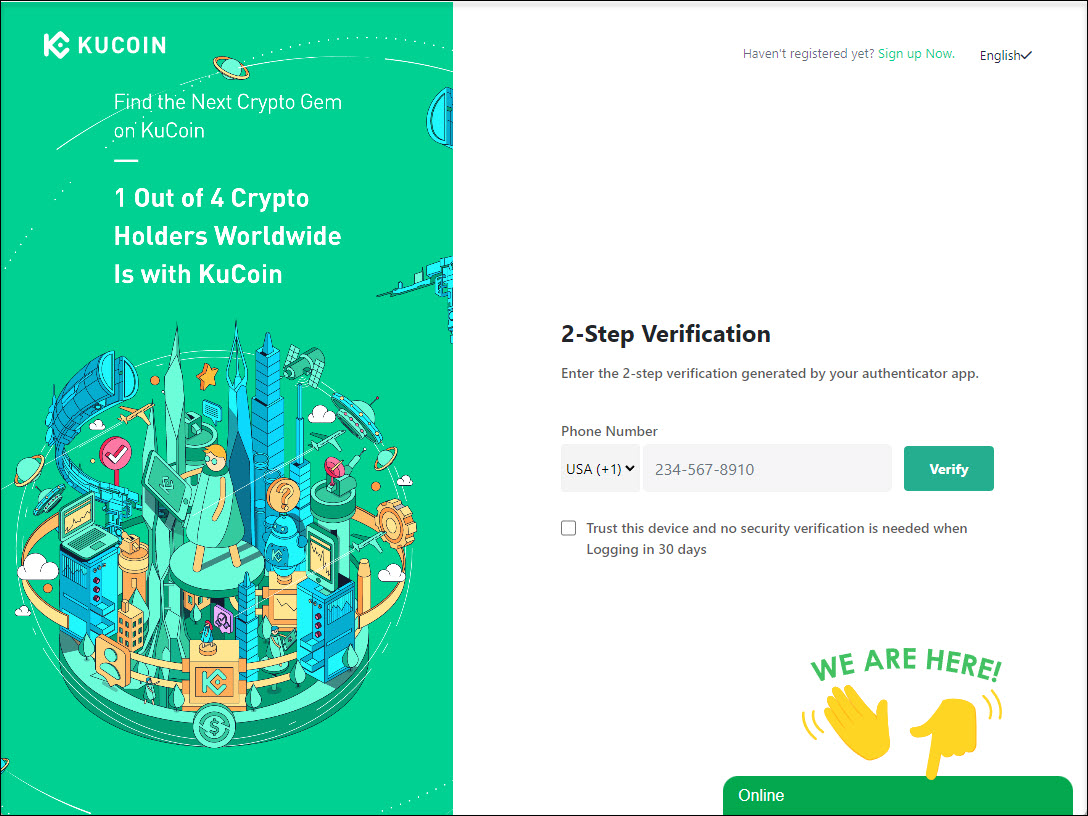
Source: PIXM
The attackers test the credentials entered on the legitimate website, triggering the sending of a 2FA code to the victim, who then enters a valid 2FA on the phishing site.
Threat actors then attempt to use the entered 2FA code to log into the victim’s account as long as they act before the time expires.
It should be noted that MetaMask phishing attacks target recovery phrases, rather than credentials or 2FA codes.
Chat with scammers
Regardless of whether a 2FA code works or not, researchers claim that crooks trigger the next stage of attack, which is to launch the chat support on the screen.
This is done by displaying a fake error message stating that the account has been suspended due to suspicious activity and asking the visitor to contact support to resolve the issue.
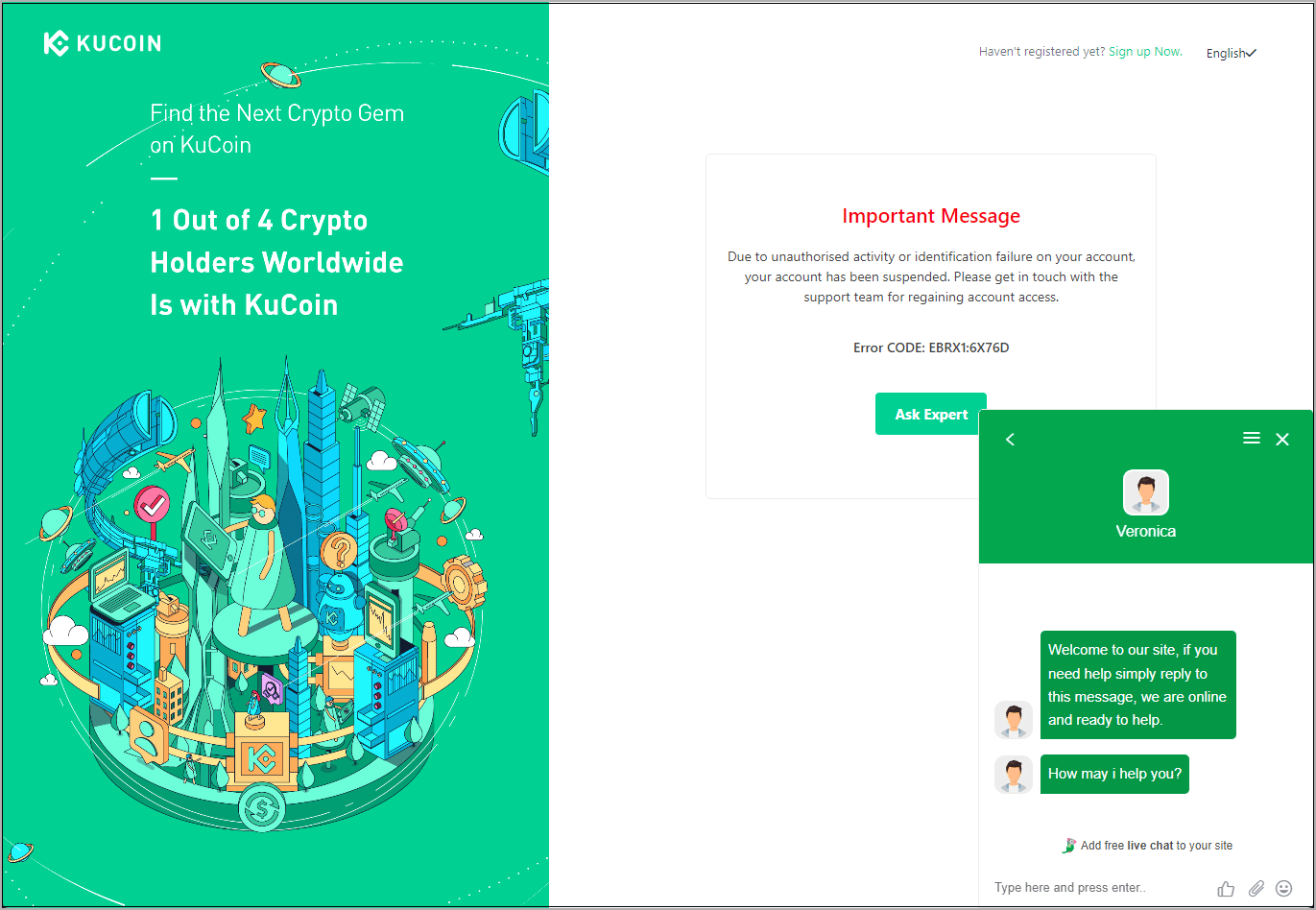
Source: PIXM
In this support chat, the threat actors initiate a conversation with the targeted victim to keep them in case different credentials, recovery phrases or 2FA codes are needed for the threat actors to get together. log in to the account.
“They will prompt the user to enter their username, password, and 2-factor authentication code directly in the chat,” says the new PIXM Report.
“The criminal will then pass this directly to a browser on their machine and try again to access the user’s account.”
For successfully hacked accounts, the victim is still in contact with customer support in case they need to confirm fund transfers while scammers empty their wallets.
However, for accounts they cannot hack via support chat, threat actors switch to an alternate method to authenticate their device as “trustworthy” to the cryptocurrency platform.
Remote trickery
To overcome the authenticated device hurdle, the attackers convince the victim to download and install the “TeamViewer” remote access application.
Then the crooks ask the victims to log into their cryptocurrency wallet or exchange accounts, and while they do this the threat actors add a random character in the password field to cause a connection failure.
The attacker then asks the victim to paste the password into the TeamViewer chat, uses the password (minus the randomness) to log into their device, and then enters the device confirmation link sent to the victim to authenticate their device as trusted.
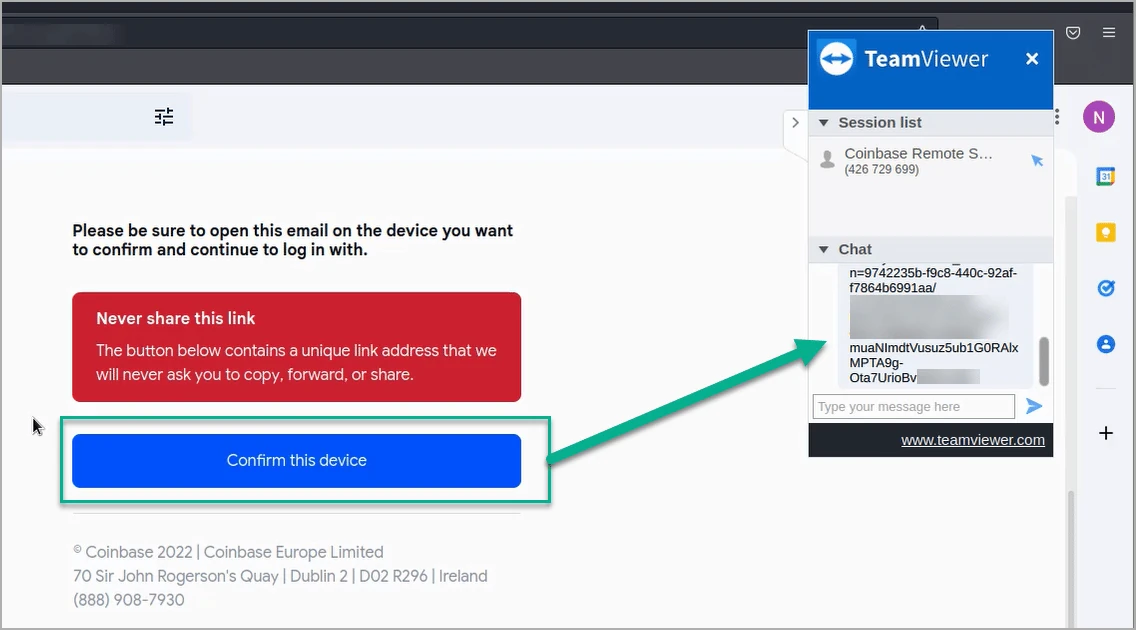
Source: PIXM
Once they gain access to the account or wallet, threat actors drain it of all funds while keeping the victim engaged in the support chat.
To avoid being scammed in such attacks, it is essential to always pay attention to the sender’s email address and the URLs sent.
If these URLs do not match the cryptocurrency platform, you should immediately treat the email as suspicious and delete it.
Unfortunately, if you fall for one of these scams, there is nothing a crypto exchange can do to recover your funds once they are transmitted from your wallet.
[ad_2]
Source link
