[ad_1]

A new campaign distributing the RomCom backdoor malware impersonates well-known or bogus software websites, tricking users into downloading and launching malicious installers.
The latest campaign was discovered by Trend Microwhich have been tracking RomCom since summer 2022. Researchers report that the threat actors behind the malware have stepped up its evasion using encryption and payload obfuscation and extended the tool’s capabilities by introducing new powerful commands.
Most of the websites used to distribute RomCom to victims relate to remote desktop management applications, which increases the likelihood of attackers using phishing or social engineering to approach their targets.
RomCom linked to Cuba ransomware
The first documented use of RomCom was reported August 2022 by Palo Alto Networks, attributing the attacks to Cuba-affiliated ransomware they named “Tropical Scorpius”. Trend Micro uses “Void Rabisu” to track the same actor.
In October 2022, The Ukrainian CERT-UA reported that the RomCom malware was used in attacks against critical networks in the country.
Another report released almost simultaneously by BlackBerry claimed association with Cuba ransomware but confirmed the attacks in Ukraine while also stating that there were malware victims in the United States, Brazil, and the Philippines.
A later BlackBerry report in November 2022 illustrated how RomCom impersonated legitimate software, including SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor (NPM), KeePass password manager, and PDF Reader Pro.
The current campaign
Trend Micro’s report on RomCom’s latest activity lists several examples of websites used by malware operators between December 2022 and April 2023 that impersonate legitimate software, such as Gimp, Go To Meeting, ChatGPT, WinDirStat, AstraChat, System Ninja, Devolutions’ Remote Desktop Manager, and more.
Some of the malicious sites used during the said period are:
- gllmp.com (offline) – Free and open-source image editor imitation
- gotomeet.us (offline) – Cloud Video Conferencing and Meeting App Imitation
- singularlabs.org (offline) – Imitation PC cleaning tool
- chatgpt4beta.com (online) – AI-powered chatbot platform imitation
- astrachats.com (offline) – Safe Chat Software Imitation
- devolutionrdp.com (online) – Imitation of a remote desktop management tool
- cozy-software.com (offline) – Imitation of a remote desktop management tool
- vectordmanagesoft.com (offline) – Impersonates a remote desktop management tool
- devolrdm.com (online) – Imitation of a remote desktop management tool
- dirwinstat.com (online) – Imitation disk usage viewer and cleanup tool
These bogus sites are promoted via Google ads and highly targeted phishing emails, with most victims based in Eastern Europe.
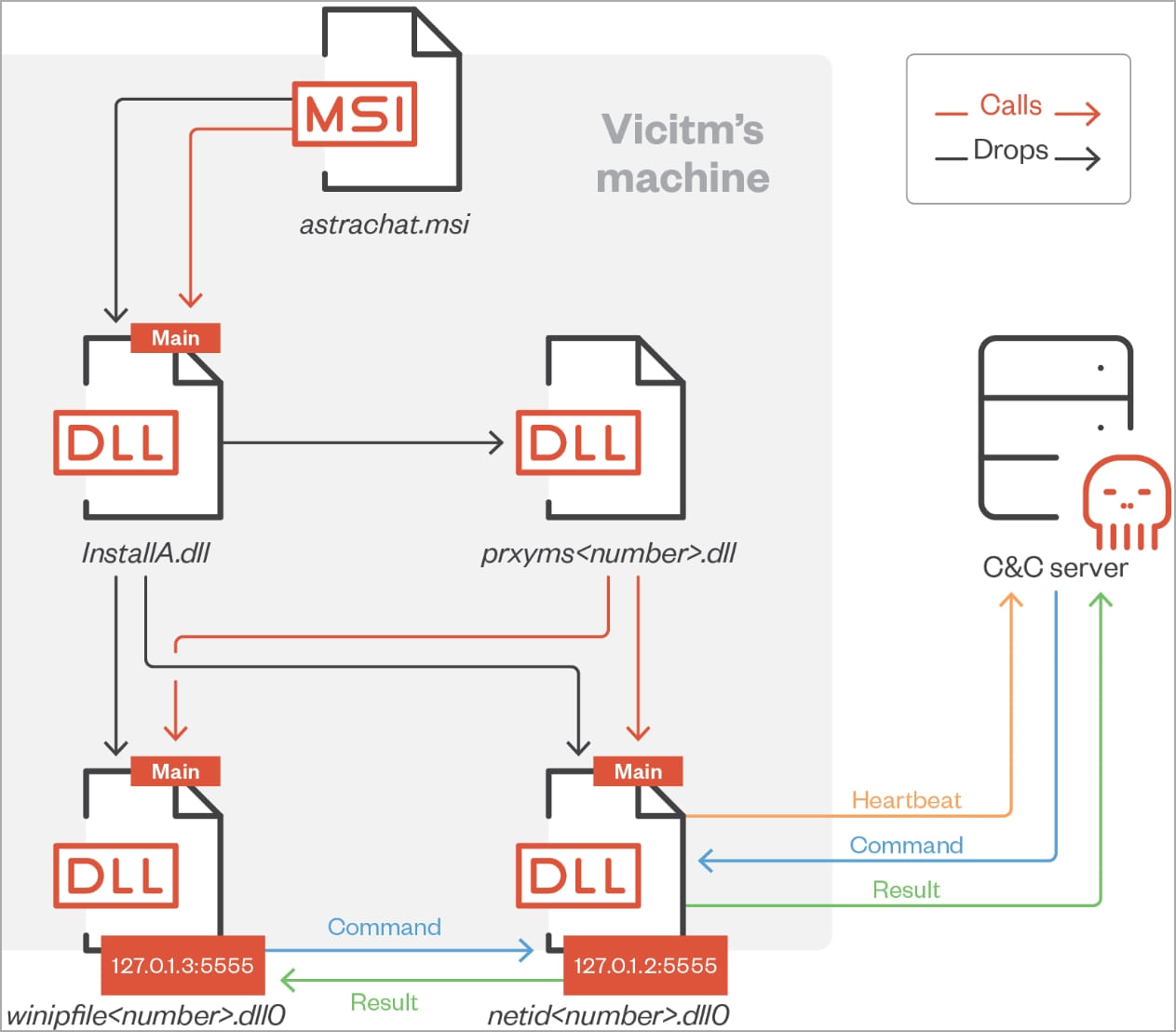
Websites distribute MSI installers that impersonate the promised application but are trojanized with a malicious DLL file (“InstallA.dll”).
This file extracts three other DLLs in the victim’s %PUBLIC%\Libraries folder, which manage command and control server communications and command execution.
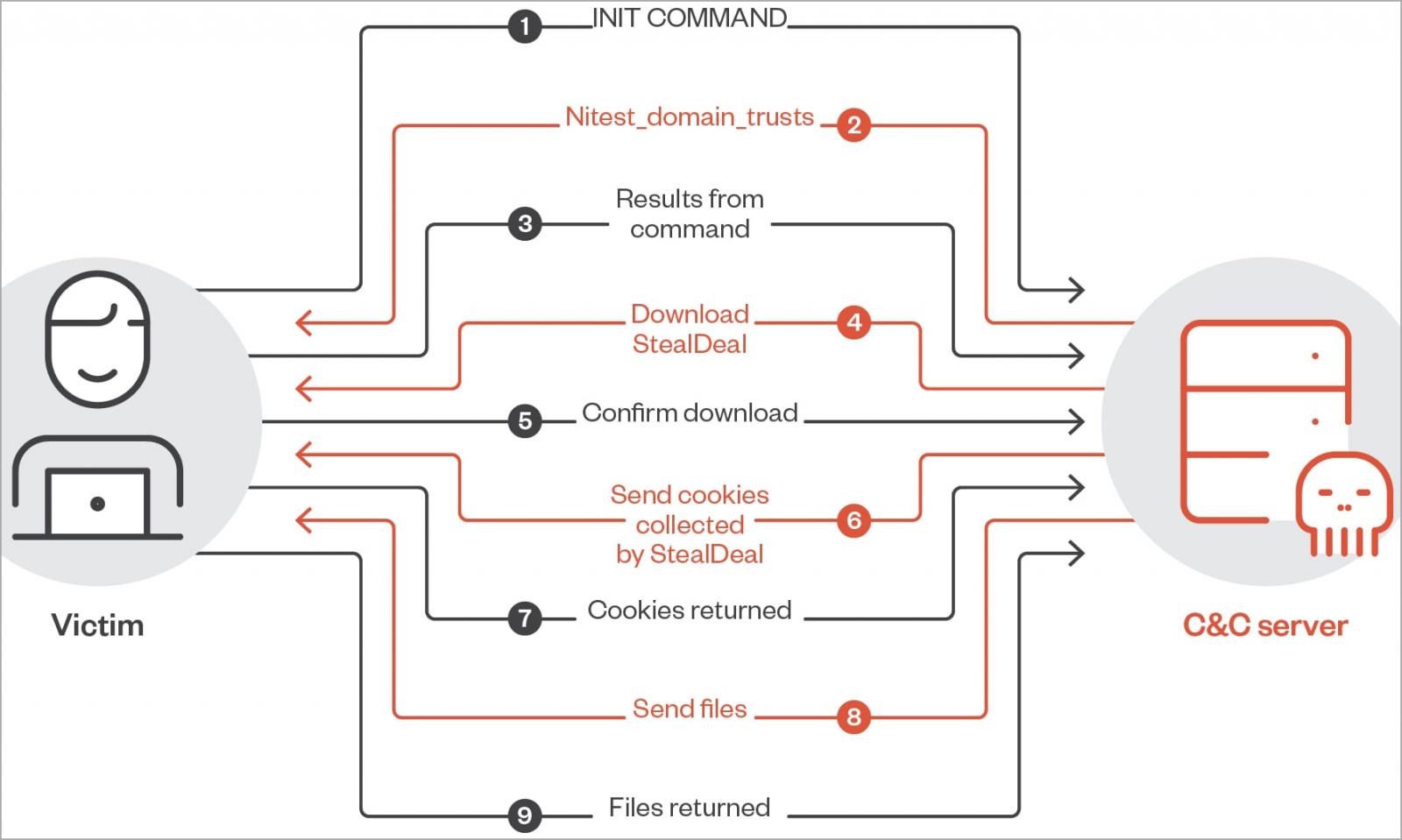
The latest version of the RomCom payload analyzed by Trend Micro shows that its authors have been working on implementing additional malicious commands, with their command count increasing from 20 to 42.
Some of the highlighted commands that can be issued to a RomCom infected device are:
- Start cmd.exe
- Drop a file on the victim’s computer to introduce more payloads.
- Start a process with PID spoofing to make it look legitimate.
- Exfiltrate data from the compromised system.
- Configure a proxy via SSH.
- Update the malware on the device.
- Run AnyDesk on a hidden window.
- Zip a given folder and send it to the attackers server.
These commands already give attackers expanded capabilities, but the cybersecurity firm reports seeing several instances of additional malware payloads being installed through RomCom.
Stealer components downloaded by RomCom on compromised devices include:
- PhotoDirector.dll – A screenshot tool that compresses images into ZIP archives for exfiltration.
- procsys.dll – A web browser cookie thief (Chrome, Firefox, Edge).
- portfolio.exe – A cryptocurrency wallet thief.
- msg.dll – An instant messaging thief.
- FileInfo.dll – An FTP credential stealer who uploads data to an FTP server.
Improved evasion
RomCom authors now use VMProtect software for code protection and anti-VM capabilities. Moreover, it uses encryption for the payload, whose key is not hard-coded but retrieved by an external address.
The malware uses null bytes in its C2 communication to evade detection from network monitoring tools.
Finally, the software downloaded from the malicious websites is signed by apparently legitimate companies supposedly based in the United States and Canada, whose websites are filled with fake or plagiarized content.
RomCom has been associated with ransomware, espionage and warfare, and the exact goals of its operators remain unclear. Either way, it’s a versatile threat that can cause significant damage.
Trend Micro has provided a comprehensive list of indicators of compromise (IoCs) for the last RomCom campaign and Yara Rules to help defenders detect and stop attacks.
[ad_2]
Source link
