[ad_1]

A threat actor named InTheBox is promoting an inventory of 1,894 web injections (phishing window overlays) on Russian cybercrime forums to steal credentials and sensitive data from banking apps, cryptocurrency and e-commerce exchange.
The overlays are compatible with various Android banking malware and mimic apps operated by large organizations used in dozens of countries on almost every continent.
Being available in such large numbers and at a low price allows cybercriminals to focus on other parts of their campaigns, developing the malware, and expanding their attack to other regions.
Typically, mobile banking Trojans check which applications are present on an infected device and extract from the command-and-control server web injections corresponding to the applications of interest.
When the victim launches a target application, the malware automatically loads the overlay which mimics the interface of the legitimate product.
InTheBox provides up-to-date injections for hundreds of apps, researchers at threat intelligence firm Cyble have found.
.png)
According to Cyble’s analysisAs of January 2023, InTheBox lists the following web injection packages, updated as recently as October 2022:
- 814 Alien compatible web injections, ErmacOctopus and MetaDroid for $6,512
- 495 web injections compatible with Cerberus for $3,960
- 585 web injections compatible with Hydra for $4,680
For those who don’t want to buy full packages, InTheBox also sells web injections individually for $30 each. The store also allows users to order custom injections for any malware.
InTheBox’s web injection packages include PNG application icons and an HTML file with JavaScript code that collects victim credentials and other sensitive data.
.png)
In most cases, injections feature a second overlay that asks the user to enter credit card numbers, expiration dates, and CVV numbers.
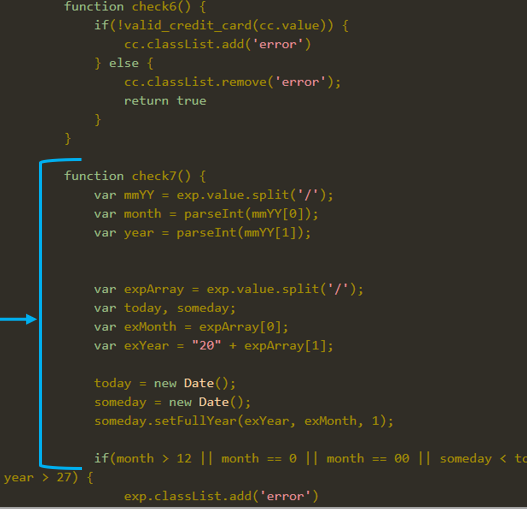
Cyble says InTheBox injections can check the validity of credit card numbers entered by victims using Luhn’s algorithm, which helps Android malware operators filter out invalid data.
.png)
Finally, the stolen data is converted into a string value and sent to a server controlled by the operator of the Android banking Trojan.
InTheBox has been selling web injections for Android malware since February 2020, constantly adding new pages that target more banking and financial apps.
Cyble was able to confirm that InTheBox web injections were used by Android Trojans ‘Coper’ and ‘Alien’ in 2021 and September 2022, respectively, while the most recent campaign took place in January 2023 and targeted Spanish banks.
[ad_2]
Source link
