[ad_1]

A new phishing campaign targeting Amazon Web Services (AWS) logins is abusing Google ads to introduce phishing sites into Google Search to steal your login credentials.
The campaign was discovered by Sentinel laboratorieswhich analysts observed malicious search results on January 30, 2023. Bad ads ranked second when searching for “aws,” just behind Amazon’s own promoted search result.
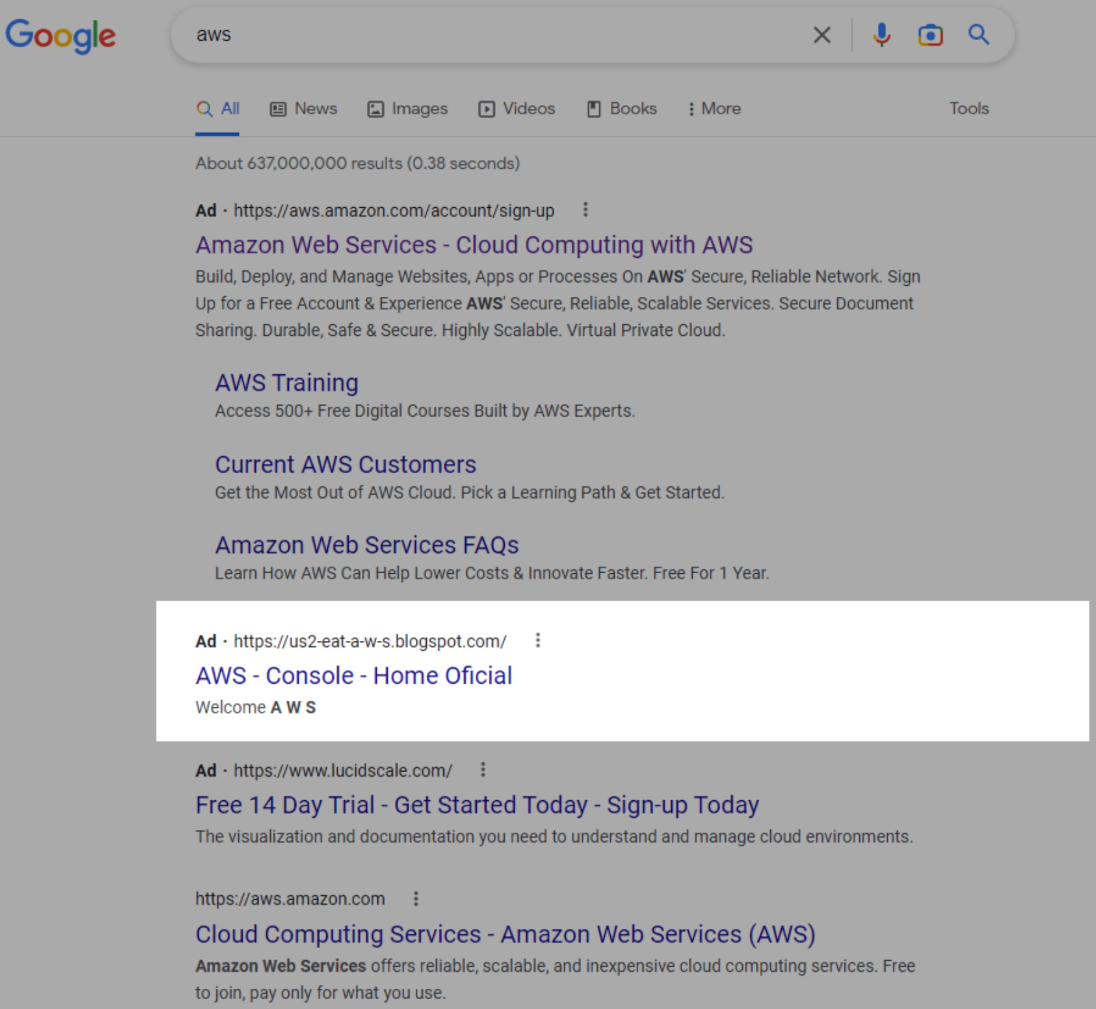
Initially, threat actors linked the ad directly to the phishing page. However, in a later phase, they added a redirect step, which may escape detection by Google’s ad fraud detection systems.
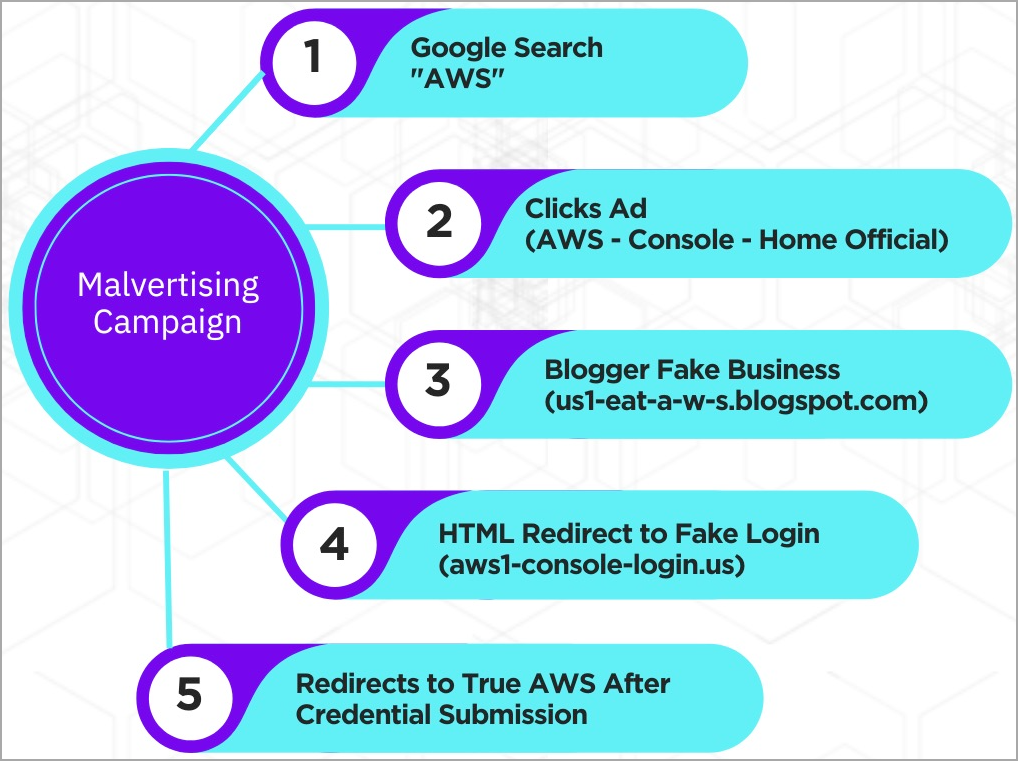
Malicious Google ads direct the victim to a blogger’s website (“us1-eat-aws.blogspot[.]com”) under attackers’ control, which is a copy of a legitimate vegan food blog.
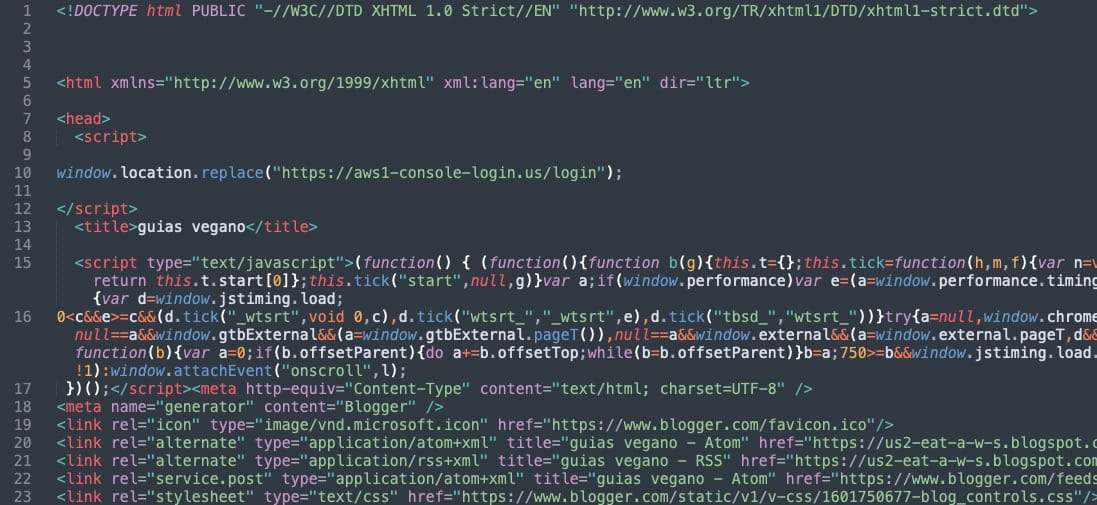
The site uses ‘window.location.replace’ to automatically redirect the victim to a new website that hosts the fake AWS login page, designed to appear genuine.
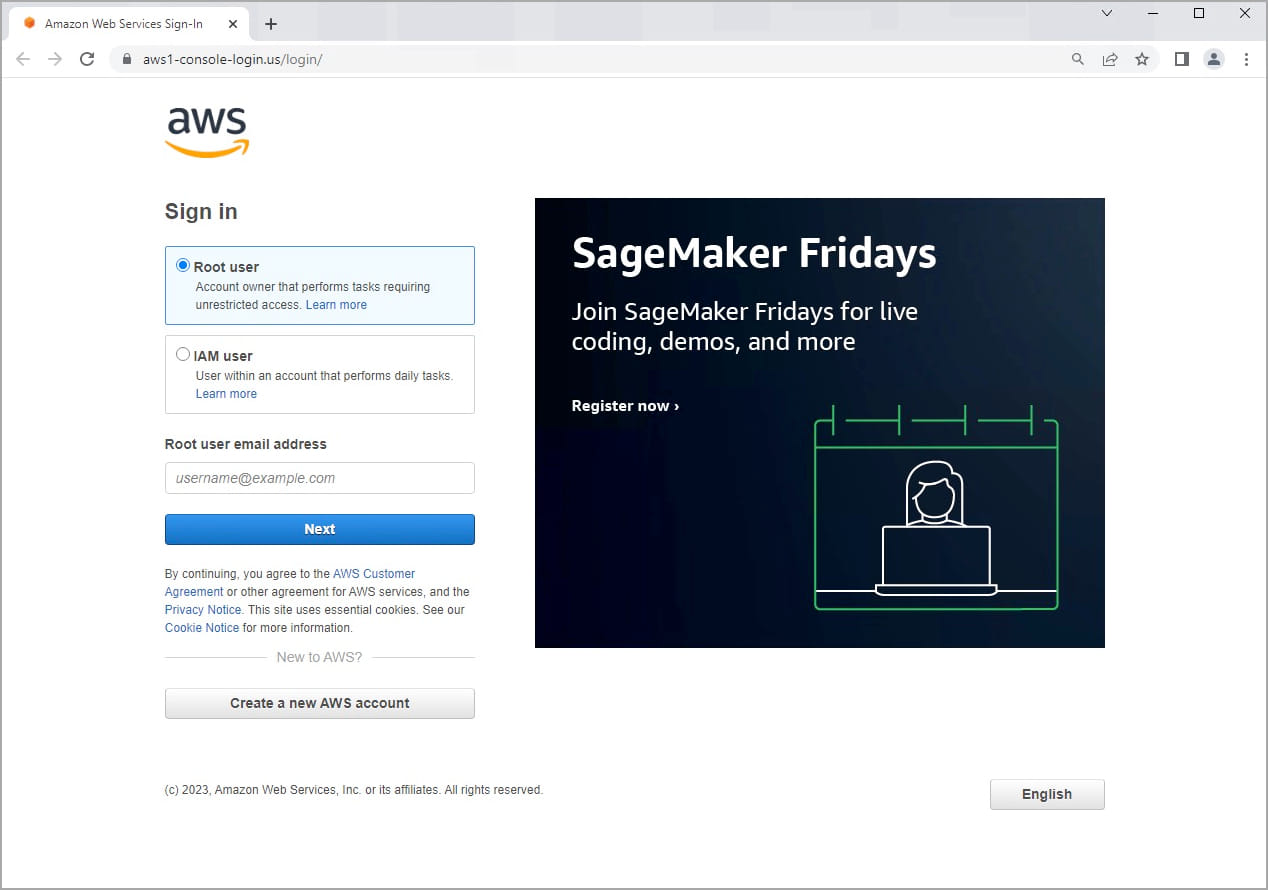
The victim is prompted to select whether they are a root or IAM user, then enter their email address and password. This option helps hackers classify stolen data into two categories of value and usefulness.
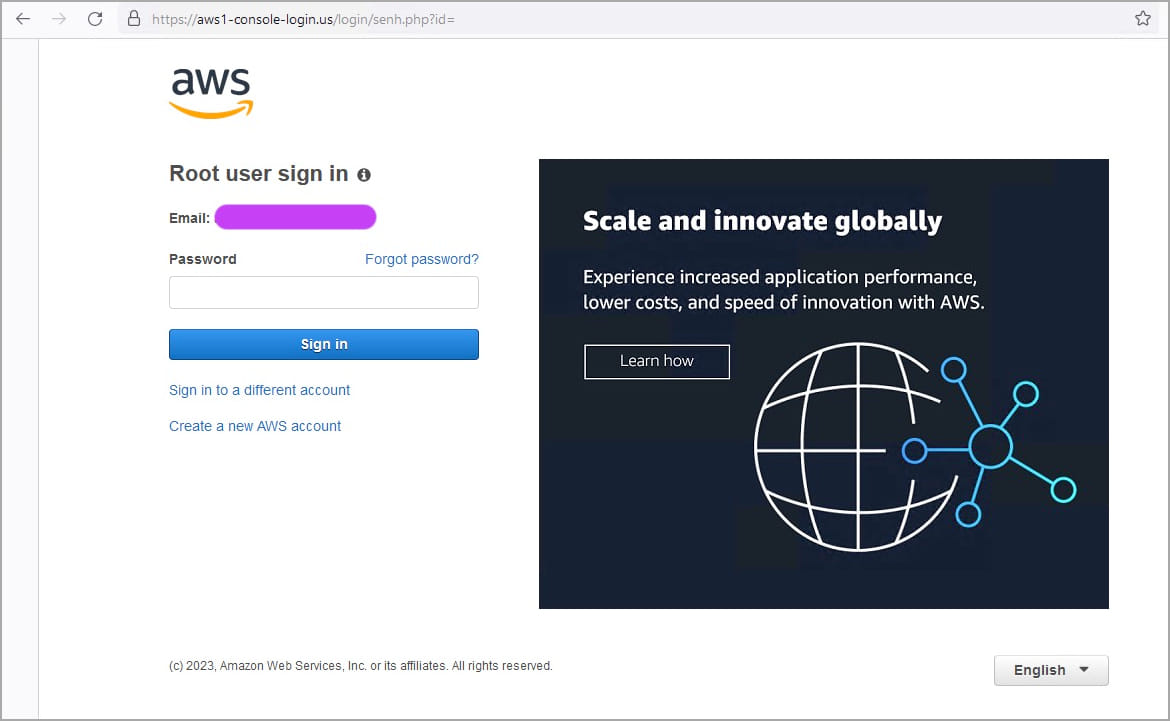
The phishing domains seen by Sentinel Labs are:
- aws1-console-login[.]We
- aws2-console-login[.]X Y Z
- aws1-ec2-console[.]com
- aws1-us-west[.]Information
An interesting feature of phishing pages is that their author has included a JavaScript function to disable right clicks, middle mouse buttons or keyboard shortcuts.
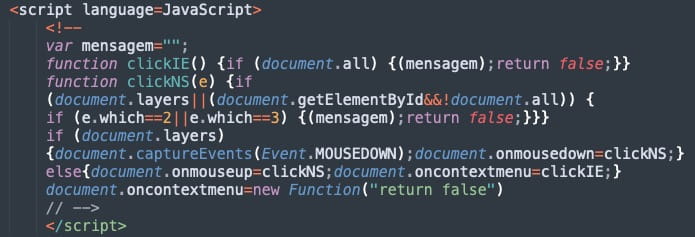
Sentinel Labs says this is likely a mechanism to prevent users from leaving the page, either on purpose or by mistake.
The security firm reports seeing Portuguese used as the language in comments and variables in JavaScript code, while the root page of the blogger’s domain mimics a Brazilian dessert company. Finally, the Whois details used to register the domains point to a Brazilian person.
Sentinel Labs reported the abuse to CloudFlare, which protected phishing sites, and the internet company quickly shut down the account. However, malicious Google Ads remain, even if the sites they link to are no longer online.
Google Ads has recently been heavily abused by cyber criminals of all kinds, serving as an alternative method to reach potential victims.
These ads have recently been used to phishing password manager accountsrealizing initial network compromise for deploying ransomware, and distributing malware masquerade legitimate software tools.
Last week, Sentinel Labs discovered a campaign that uses virtual technology with Google Ads to spread malware that makes it more difficult for antivirus tools to detect.
[ad_2]
Source link
