[ad_1]

The ransomware saga for organizations around the world continues to unfold as 2023 approaches. ransomware attack on its managed email services.
The Rackspace ransomware attack taught us the importance of good cybersecurity habits. Let’s see what we can learn from the attack and how organizations can protect themselves.
Rackspace ransomware attack
Rackspace users suffered from an outage of the Rackspace Hosted Exchange service. After four days, it became apparent that this was not a typical failure.
Rackspace took to social media on December 6, 2022, posting on Twitter that the outage resulted from a ransomware attack.
The ransomware attack was thought to have initially taken advantage of the ProxyNotShell vulnerability in Microsoft Exchange. Rackspace worked with CrowdStrike to help with the investigation.
As a result, Crowdstrike discovered that the attack used the previously unknown zero-day vulnerability that allowed attackers to bypass the mitigations put in place by ProxyNotShell Rackspace.
Rackspace urges organizations to read information from Crowdstrike
Rackspace’s forensic investigation has determined that the threat actor is a relatively new ransomware group known as PLAY. Additionally, it is believed that the PLAY Group was financially motivated to carry out the attack and was able to gain access to a relatively small amount of customer email data.
The range of the attack
How far did the attackers go? Could they read customer data? Rackspace has about 30,000 customers in its Hosted Exchange environment (about 1% of its customer base).
Of the 30,000 clients in the Hosted Exchange email environment at the time of the attack, forensic investigation determined that the threat actor had accessed a personal storage table (“PST”) of 27 Hosted Exchange customers.
The CrowdStrike investigation found no evidence that the threat actor accessed, obtained, misused, or distributed email or data in PSTs for any of the 27 Hosted Exchange customers.
Risk of zero-day exchange vulnerabilities and stolen credentials
The Rackspace Environment exploit exposed a new critical Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability in Exchange Server, which was initially patched in November 2022. However, many organizations had applied vulnerability mitigations not the fix.
The hacker group Play has developed a new exploit, bypassing the mitigations for ProxyNotShell and launching the ransomware attack on the Rackspace Hosted Exchange environment. Crowdstrike has named the new operating chain combining CVE-2022-41080 And CVE-2022-41082 OWASSRF.
Since the vulnerability was able to bypass the original ProxyNotShell mitigation but does not bypass the patches in the patch, it highlights the need to apply the appropriate patches to the environment rather than relying on the initial mitigations of a vulnerability.
Often attackers combine vulnerabilities, such as ProxyNotShell, with stolen credentials to carry out an attack. While stolen credentials aren’t always necessary, compromised credentials make exploits with valid system access much easier.
Prevent a ransomware attack
Today, organizations can prevent a ransomware attack by implementing security best practice recommendations. Attackers can take advantage of compromised credentials, unpatched systems, lax security around remote access systems, and poorly protected web servers.
Let’s look at the following strategies to prevent the domino effect of a ransomware attack:
- Patch
- Securing Remote Access Systems
- Strengthen password security
Patch
Patching is an essential aspect of preventing a ransomware attack. Unfortunately, as the Rackspace attack shows, attackers often use unpatched vulnerabilities to attack critical systems and launch ransomware attacks. In the case of the Rackspace ransomware attack, hackers could bypass mitigations but would not have been able to bypass fully patched systems.
Securing Remote Access Systems
Unsecured remote access systems are another common attack vector for ransomware groups. Any system available for remote access to legitimate employees is also a target for attackers. For example, organizations have often been attacked using insecure remote desktop servers or VPN connections where weak credentials are involved without multi-factor authentication. Therefore, it is essential to strengthen the security of remote access systems, ensuring that they are fully patched, and users should use strong passwords for authentication as well as multi-factor authentication.
Strengthen password security
Businesses need to think about improving their password security because passwords are often the weakest link in most organizations’ security. Additionally, users often reuse passwords across accounts and choose easily guessed or previously breached passwords, making them an easy target for compromise.
Many companies use Microsoft Active Directory Domain Services as an on-premises identity and access management solution to secure resources. However, Active Directory does not contain native tools that provide modern and effective password policies. Additionally, native Active Directory password policies do not protect against hacked passwords.
tools like Specops password policy enable organizations to meet the challenges of securing passwords against modern attacks. Organizations can use existing group policies to extend password security using Specops Password Policy security options.
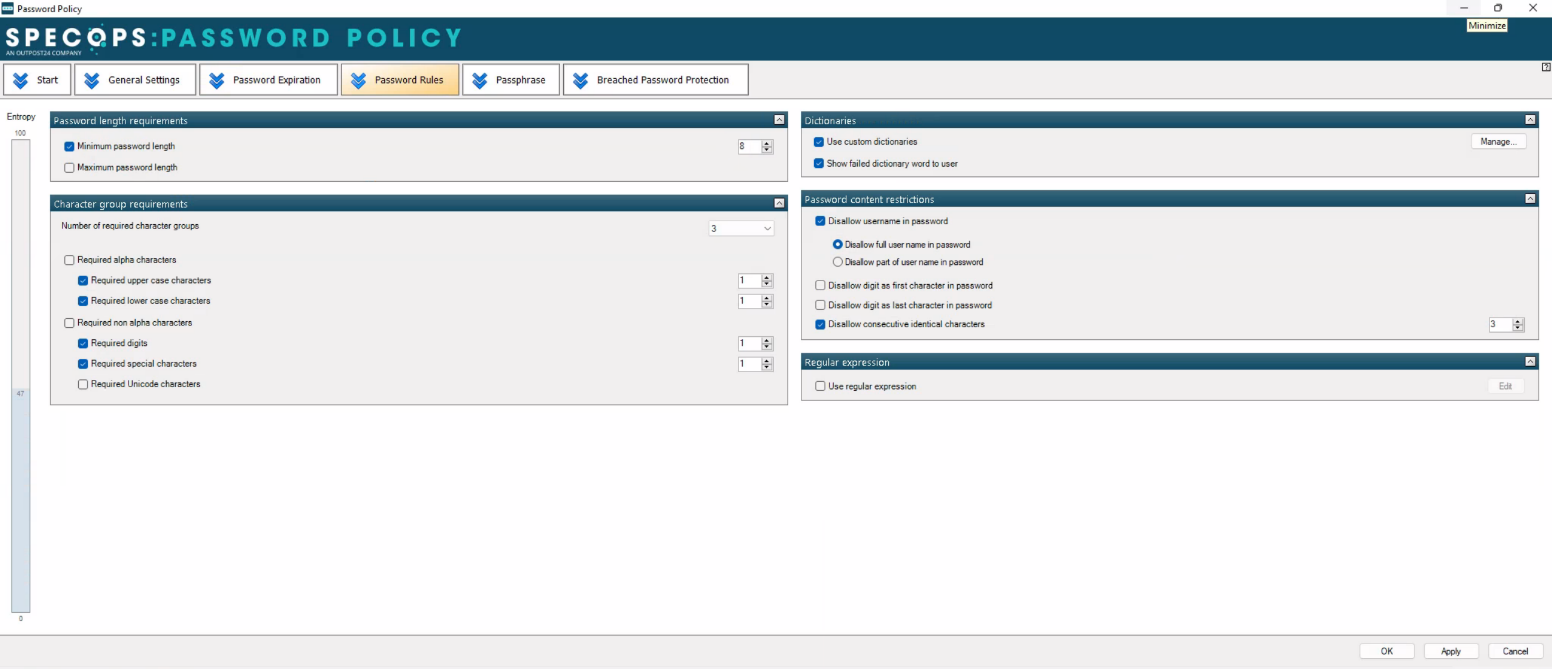
- Block words common to your organization with custom dictionaries
- Prevent the use of over 3 billion compromised passwords with Breached Password Protection
- Find and remove compromised passwords in your environment
- Real-time dynamic feedback when changing password
- Block usernames, display names, specific words, consecutive characters, incremental passwords and reuse part of current password
- Granular GPO-based targeting for any GPO level, computer, user, or group population
Protect against ransomware
Ransomware is a growing concern for organizations around the world, as the fallout and consequences of a ransomware attack are typically severe. Significant cybersecurity attacks can result in lawsuits, regulatory fines, loss of customer trust and damage to brand reputation, as seen with Rackspace Technology.
Therefore, protecting against ransomware attacks and their fallout requires organizations to have a multi-pronged approach to hardening their security, including patching, securing remote access, and increasing security. password security.
Specops password policy is a solution that enables organizations to improve password security for Active Directory accounts and helps protect against hacked and weak passwords
Sponsored and written by Specops software
[ad_2]
Source link
