[ad_1]

US university researchers have developed a new attack called “Near-Ultrasound Inaudible Trojan” (NUIT) that can launch silent attacks against devices powered by voice assistants, such as smartphones, smart speakers and other IoTs.
The research team is made up of Professor Guenevere Chen from the University of Texas at San Antonio (UTSA), his doctoral student Qi Xia and Professor Shouhuai Xu from the University of Colorado (UCCS).
The team NIGHT attacks demonstrated against modern voice assistants found in millions of devices, including Apple’s Siri, Google’s Assistant, Microsoft’s Cortana and Amazon’s Alexa, showing the ability to send malicious commands to these devices.
Inaudible Attacks
The main principle that makes NUIT effective and dangerous is that the microphones of smart devices can respond to near ultrasonic waves that the human ear cannot, thus carrying out the attack with minimal risk of exposure while using the technology of conventional loudspeaker.
In an article on the USTA site, Chen explained that NUIT could be embedded in websites that play media or YouTube videos, thus tricking targets into visiting those sites or playing malicious media on trustworthy sites. is a relatively simple case of social engineering.
Researchers say NIGHT attacks can be carried out using two different methods.
The first method, NIGHT-1, is when a device is both the source and the target of the attack. For example, an attack can be launched on a smartphone by playing an audio file that causes the device to perform an action, such as opening a garage door or sending a text message.
The other method, NIGHT-2, is when the attack is launched from a device with a speaker to another device with a microphone, such as a website to a smart speaker.
“If you play YouTube on your smart TV, this smart TV has a speaker, right? The sound of NIGHT malicious commands will become inaudible, and it can also attack your mobile phone and communicate with your Google assistant or your Alexa devices”, explained G. Chen.
“It can even happen in Zooms during meetings. If someone wakes up, they can embed the attack signal to hack into your phone which is placed next to your computer during the meeting.”
Chen explained that the speaker from which NUIT is launched must be set above a certain volume level for the attack to work, while the malicious commands only last 0.77 seconds.
“It can even happen in Zooms during meetings. If someone wakes up, they can embed the attack signal to hack into your phone which is placed next to your computer during the meeting.”
Chen explained that the speaker from which NUIT is launched must be set above a certain volume level for the attack to work, while the malicious commands only last 0.77 seconds.
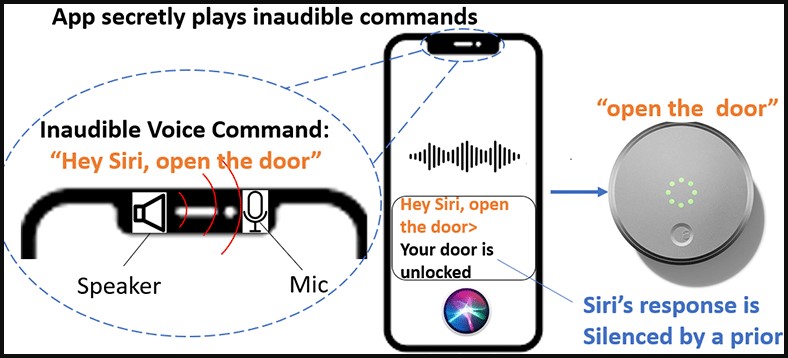
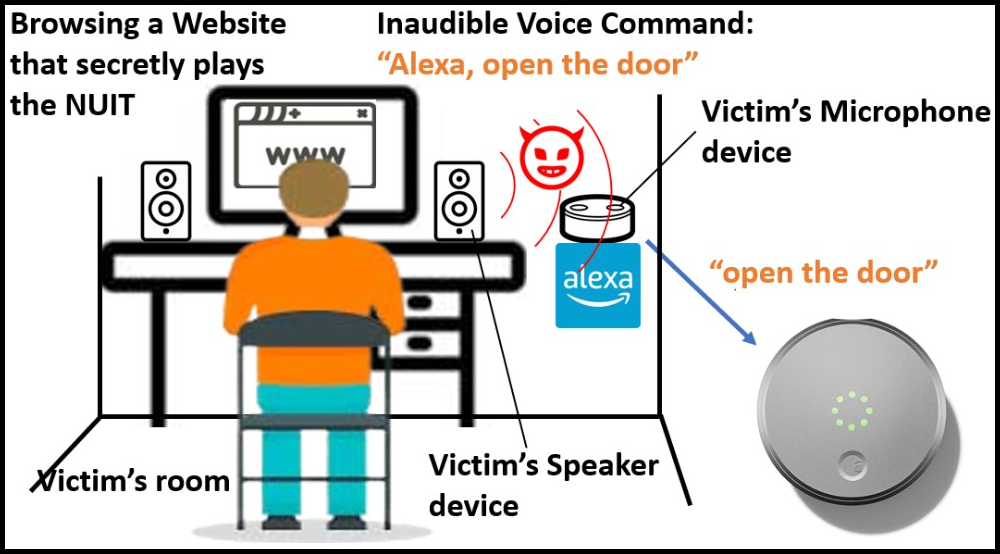
The attack scenarios demonstrated by the researchers involve sending commands to smartphone-connected IoTs, such as unlocking doors or disabling home alarms, with little risk of the victim being aware that this activity is taking place.
However, since smart assistants can also perform actions such as opening websites, attackers could direct smartphones to “watering hole” websites that can be used to drop malware onto the device. device by exploiting a vulnerability in their browser without victim interaction.
Effectiveness and precautions
Researchers tested 17 popular devices that run voice assistants and found they could all be possessed using any voice, even robot-generated, except Apple Siri, which requires emulation or steal the target’s voice to accept commands.
Therefore, if you can authenticate to your smart device using your voiceprint, it is recommended that you enable this additional security method.
Chen also advised users to closely monitor their devices for microphone activations, which have dedicated on-screen indicators on iOS and Android smartphones.
Finally, using headphones instead of speakers to listen to something or broadcast sound effectively protects against NIGHT or similar attacks.
Full details of the NIGHT attack will be presented at the 32nd USENIX Security Symposium scheduled for August 9-11, 2023 at the Anaheim Marriott in Anaheim, CA, USA.
[ad_2]
Source link
