[ad_1]

Google says it banned 173,000 developer accounts in 2022 to prevent malware operations and fraud rings from infecting Android users’ devices with malicious apps.
The company revealed in its annual “bad apps” report that it also blocked nearly 1.5 million apps linked to various privacy policy violations from reaching the Google Play Store.
The Google Play Commerce security team also blocked fraudulent and abusive transactions that could have resulted in over $2 billion in losses.
“In 2022, we prevented 1.43 million policy-violating apps from being published on Google Play, in part through new and improved security features and policy enhancements, in combination with our continued investments in systems machine learning and application review processes,” Google Security said. crew said.
“We also continued to crack down on malicious developers and fraud rings, banning 173,000 malicious accounts and preventing more than $2 billion in fraudulent and abusive transactions.”
Google has also introduced additional requirements for developers wishing to join the Play Store ecosystem, including identity verification by phone and email. This has led to a drop in the number of accounts used to distribute apps that violate Google Play policies.
Additionally, it has worked with software development kit (SDK) vendors to restrict access to sensitive data and prevent it from being shared, ensuring that more than a million apps on the official Android store have better ” attitude of confidentiality”.
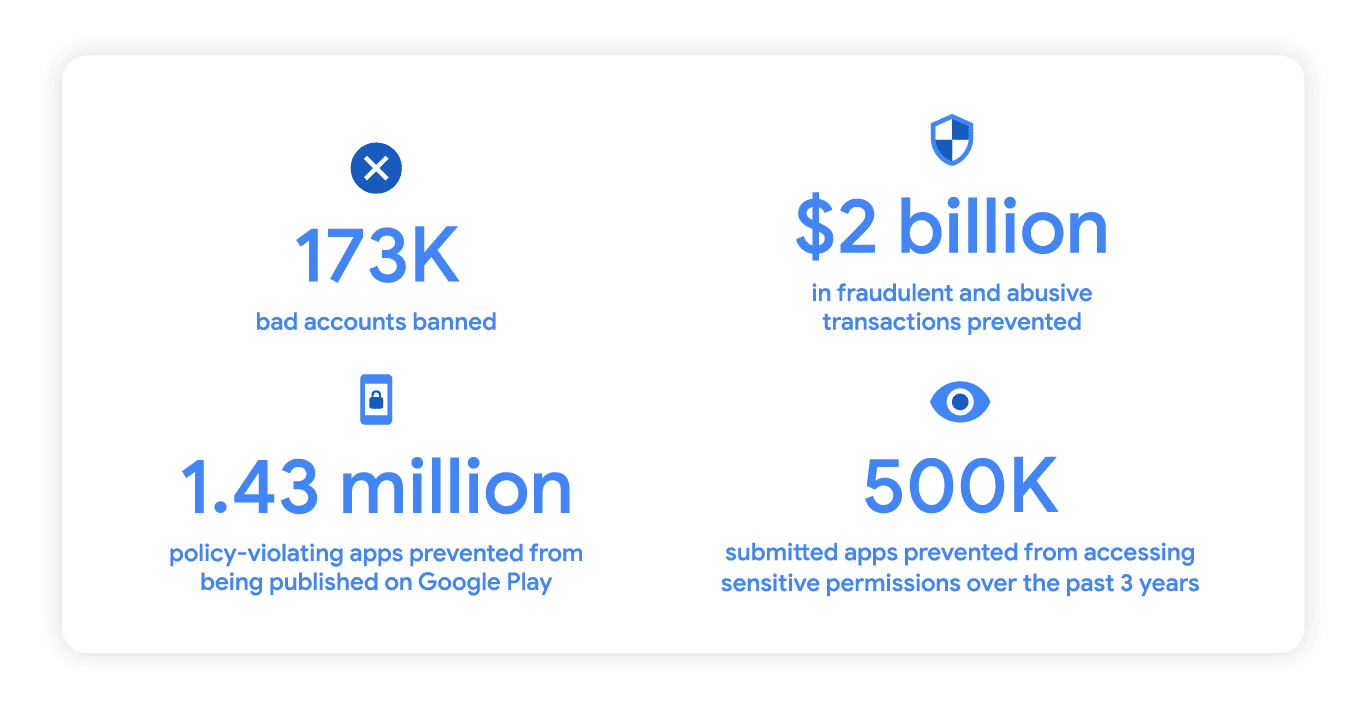
In total, over the past three years, the company says its efforts to further strengthen Android platform protections and policies have prevented approximately 500,000 apps submitted for inclusion in the Google Play Store from requesting and to access sensitive permissions.
Throughout 2021Google blocked 1.2 million apps that violate the rules, banned 190,000 accounts linked to malicious and spammy developers, and closed about 500,000 inactive or abandoned developer accounts.
“As the Android ecosystem grows, it’s critical for us to work closely with the developer community to ensure they have the tools, knowledge, and support needed to build secure and reliable apps. that respect the security and privacy of user data,” Google said.
“We will continue to work closely with SDK vendors to improve app and SDK security, limit how user data is shared, and improve lines of communication with app developers.”
A year ago, Google Play was also updated to include a Data Security Section which details how apps collect, share and secure user data.
More recently, in February 2023, Google revealed that the next major release of the world’s most popular mobile operating system, Android 14 (now in beta), will prevent malware from abusing sensitive permissions by targeting old API levels (Android versions).
[ad_2]
Source link
