[ad_1]

Operators of high-yield investment scams known as “pig butchers” have found a way around the defenses of Google Play and Apple’s App Store, official Android app repositories and iOS.
Hog slaughter scams have been happening for a few years. They use fake websites, malicious advertising and social engineering. By adding scam apps to official download platforms, scammers can gain a victim’s trust more easily.
Researchers from cybersecurity firm Sophos claim that scammers target victims on Facebook or Tinder and convince them to download the fraudulent apps and “invest” large sums of money in supposedly real assets.
Sophos has observed such a campaign from a China-based threat group named “ShaZhuPan”, which shows high levels of organization with separate teams dealing with victim interaction, finance, franchising and money laundering.
Approach the victims
Fraudsters appear to be targeting male users on Facebook and Tinder using profiles of women with images stolen from other social media accounts.
The profiles controlled by the scammers were designed to reflect a lavish lifestyle, with photos of high-end restaurants, expensive boutiques and exotic locations.

After gaining the trust of the victims, the scammers say they have an uncle working for a financial analysis company and issue an invitation to trade cryptocurrency through an app on Play Store or App Store. Obviously, the victim is directed to a bogus application.
The scammers walk the victim through their first investment, asking them to create a deposit on the legitimate Binance cryptocurrency exchange platform and then transfer the amount to the fake app.
Applications “Pig butchering”
The malicious apps used in the campaign observed by Sophos are named “Ace Pro” and “MBM_BitScan” on the Apple App Store and “BitScan” on the Play Store.

The apps allow the victim to initially withdraw small amounts of cryptocurrency, but then lock their accounts when larger sums are involved. However, the initial withdrawal is enough for victims to trust the scheme and continue to invest.
The method used to bypass security checks in mobile app stores is quite simple. For infiltrating the App Store, the ShaZhuPan gang submits an app signed with a valid certificate issued by Apple, a requirement for any code to be accepted into the iOS repository.
Until approval is obtained, the application connects to a benign server and its behavior is legitimate. After passing the exam, the developer changes the domain and the application connects to a malicious server.
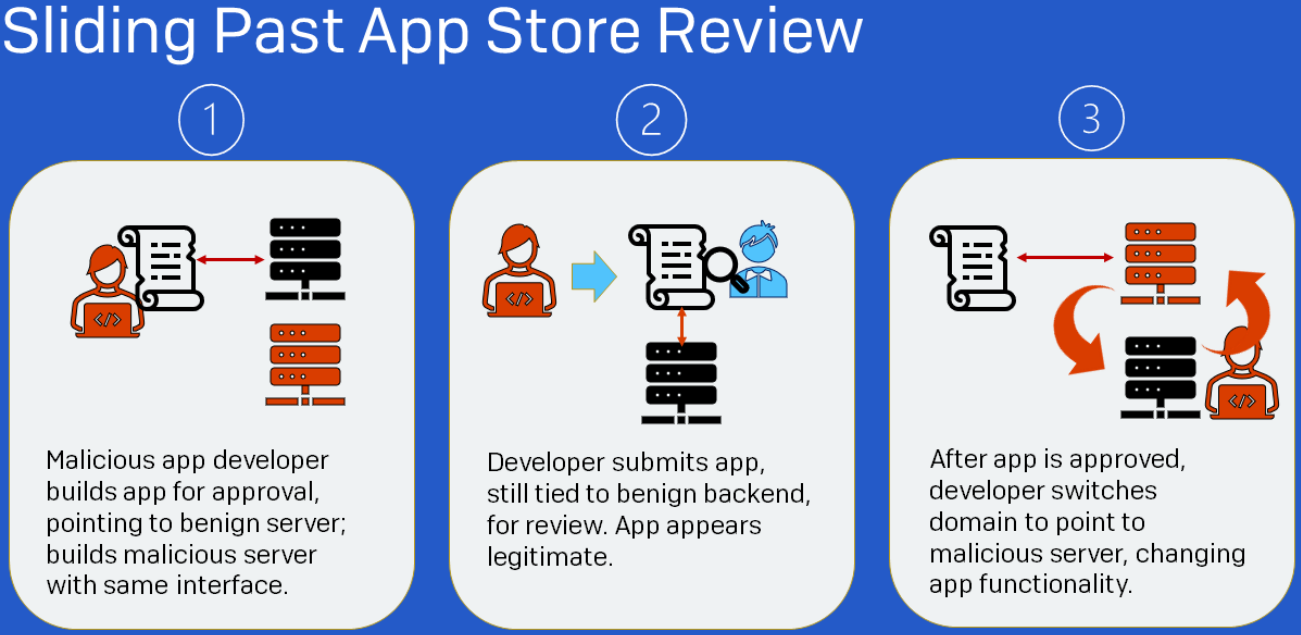
After launching the application, the victim sees a cryptocurrency trading interface delivered by the malicious server. However, everything displayed is fake, except for the user’s repository.
Sophos researchers found that the BitScan apps for Android and iOS have a different vendor name but communicate with the same command-and-control server, from a domain that appears to be impersonating bitFlyer, a software company. legit cryptocurrency exchange in japan.
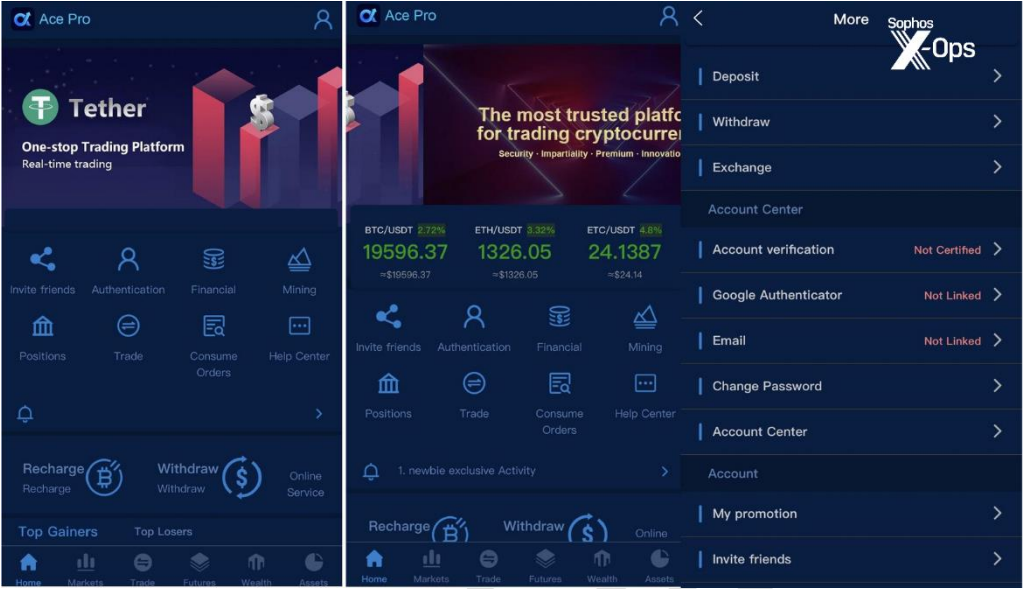
Since these apps are only downloaded by a small number of targeted users, they are not massively flagged for fraud, making it difficult for app store security reviewers to identify them as fraudulent and remove them. .
Don’t get scammed
Hog slaughter scams generate high profits in a short time, so the scammers are motivated to spend time and effort to gain the trust of their victims through thorough communication.
This long engagement, initial withdrawal and the fake apps’ convincing interface makes it difficult for the victim to see through the scam.
Sophos also points out that the emergence of “FinTech” has normalized people’s trust in these software tools and when apps come from official Apple and Google stores, the sense of legitimacy is high.
Before installing any app on your smartphone, it is recommended to check other users’ reviews, privacy policy, developer/publisher details and research company information.
[ad_2]
Source link
