[ad_1]

A stealth Remote Access Trojan (RAT) dubbed “SeroXen” has recently gained popularity as cybercriminals start using it for its low detection rates and powerful capabilities.
AT&T reports that the malware is sold under the guise of a legitimate remote access tool for Windows 11 and 10 for $15/month or a single “lifetime” license payment of $60.
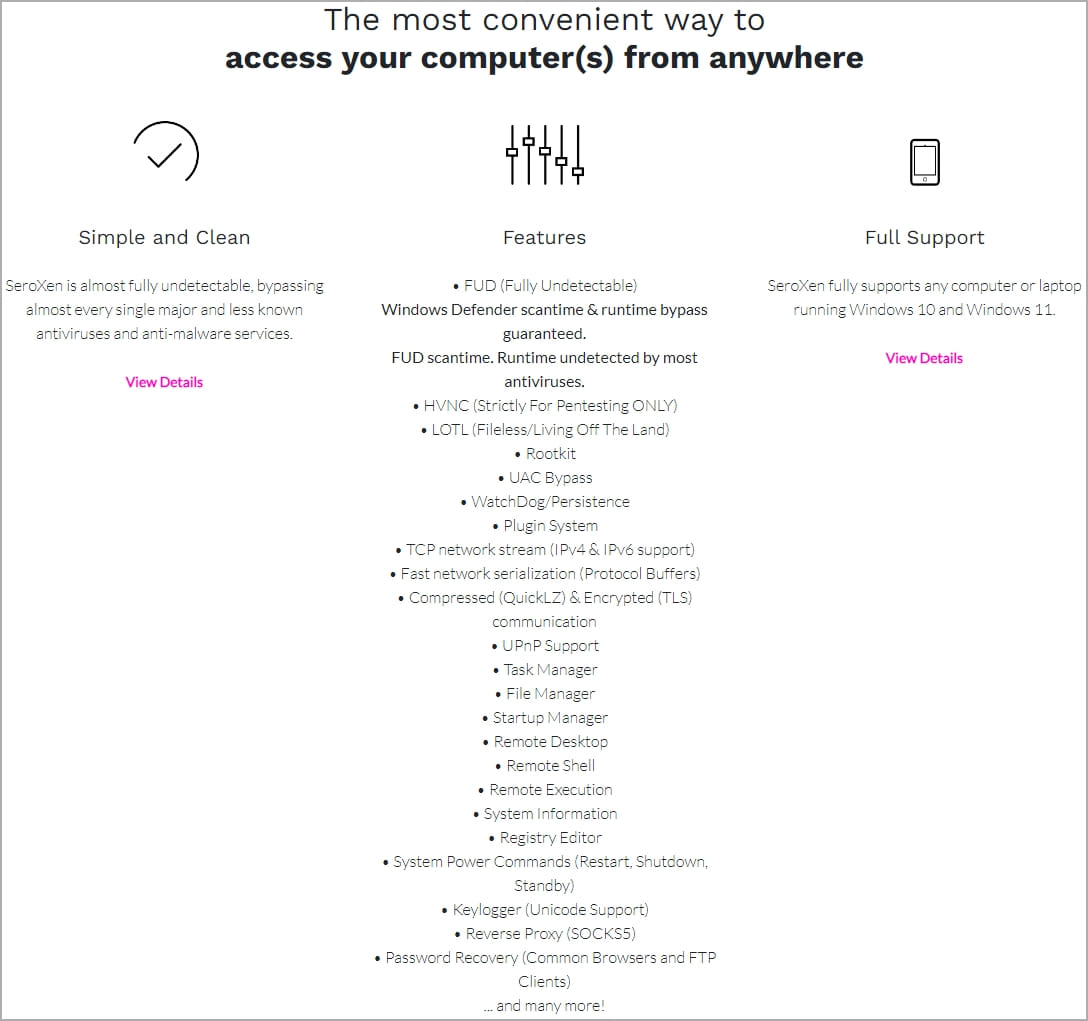
Although marketed as a legitimate program, the Torch systems Cyber intel platform has shown that SeroXen is promoted as a remote access trojan on hacking forums. It’s unclear if those promoting it on the forums are the developers or the shady resellers.
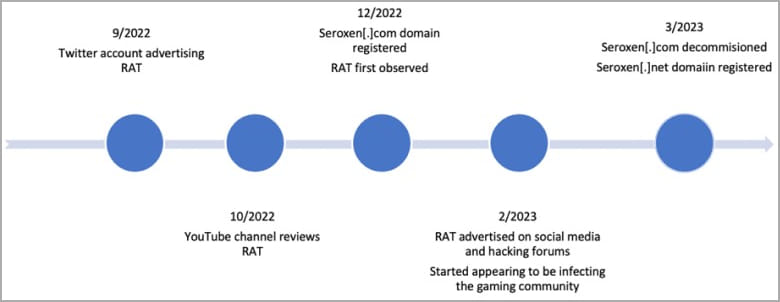
However, the remote access program’s low cost makes it highly accessible to threat actors, with AT&T observing hundreds of samples since its inception in September 2022, with activity recently increasing.
Most of SeroXen’s victims are part of the gaming community, but as the tool’s popularity grows, the scope of targeting could expand to include large corporations and organizations.
Open source building blocks
SeroXen is based on various open source projects, including Quasar RAT, the r77 rootkit, and the NirCmd command line tool.
“Developer SeroXen has found a great combination of free resources to develop a hard-to-detect RAT in static and dynamic analysis,” AT&T comments in the report.
“The use of an elaborate open-source RAT like Quasar, with nearly a decade since its first appearance, provides an advantageous basis for the RAT […] while the combination of NirCMD and the r77 rootkit are logical additions to the mix, as they make the tool more elusive and harder to detect.”
Quasar RAT, which SeroXen uses as its base, is a lightweight remote administration tool first released in 2014. Its latest version, 1.41, includes reverse proxy, remote shell, remote desktop, TLS communication, and a file management system. available via GitHub.
The r77 (Ring 3) rootkit is a open source rootkit which offers fileless persistence, child process hooking, malware embedding, in-memory process injection, and antivirus evasion.
NirCmd is a free utility which performs simple Windows system and device management tasks from the command line.
SeroXen Attacks
AT&T has seen attacks pushing SeroXen through phishing emails or Discord channels, where cybercriminals distribute ZIP archives containing heavily obfuscated batch files.
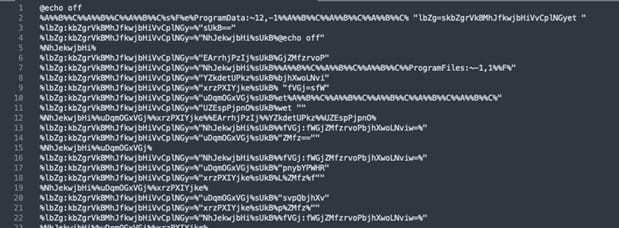
The batch file extracts two binary files from base64-encoded text and loads them into memory using .NET reflection.
The only file touching the disk is a modified version of msconfig.exe, needed to run the malware, and is temporarily stored in the short-lived “C:\Windows\System32\” directory (note the extra space ) which is removed once the program is installed.
This batch file ultimately deploys a payload named “InstallStager.exe”, a variant of the r77 rootkit.
The rootkit is stored in a hidden form in the Windows Registry and is then activated using PowerShell through Task Scheduler, by injecting it into “winlogon.exe”.
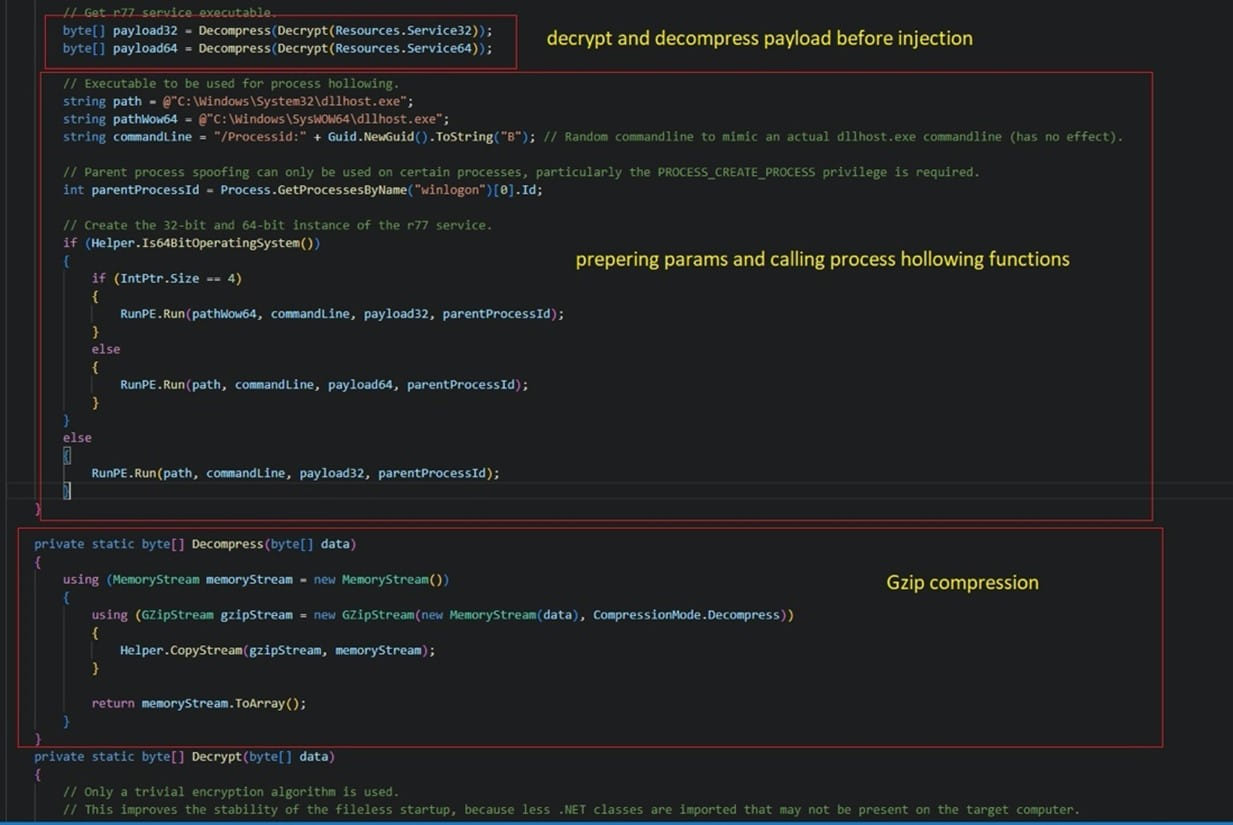
The r77 rootkit injects the SeroXen RAT into system memory, ensuring that it remains undetected and now provides remote access to the device.
Once the remote access malware is launched, it establishes communication with the command and control server and waits for commands issued by attackers.
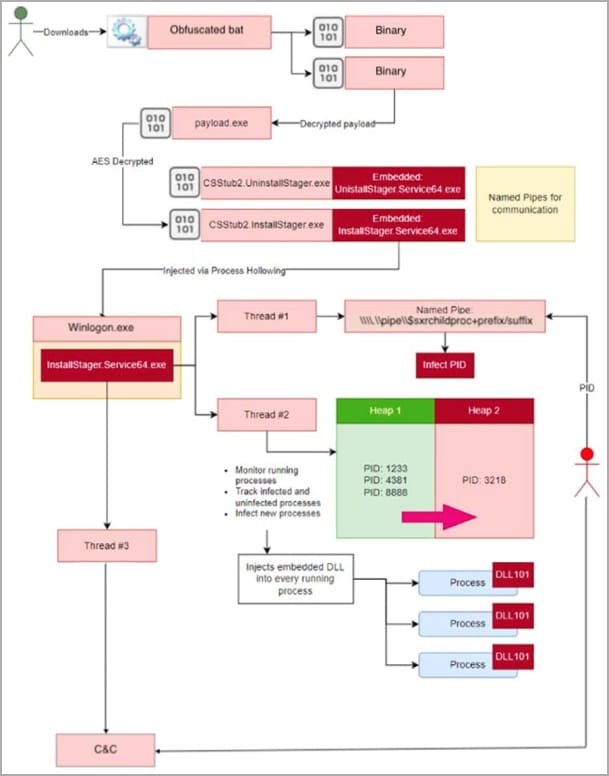
Analysts found that SeroXen uses the same TLS certificate as QuasarRAT and has most of the features of the original project, including TCP network stream support, efficient network serialization, and QuickLZ compression.
AT&T is concerned that the growing popularity of SeroXen will attract hackers interested in targeting large organizations rather than focusing on gamers and has released indicators of compromise for use by network defenders.
[ad_2]
Source link
