[ad_1]

A new information stealer called Stealc has appeared on the dark web and is gaining traction due to aggressive promotion of stealing capabilities and similarities to similar malware like Vidar, Raccoon, Mars and Redline.
Security researchers from cyber threat intelligence firm SEKOIA spotted the new strain in January and noticed that it was starting to gain traction in early February.
New thief for sale
Stealc was advertised on hacking forums by a user called “Plymouth”, who presented the malware as malware with extensive data-stealing capabilities and an easy-to-use admin panel.
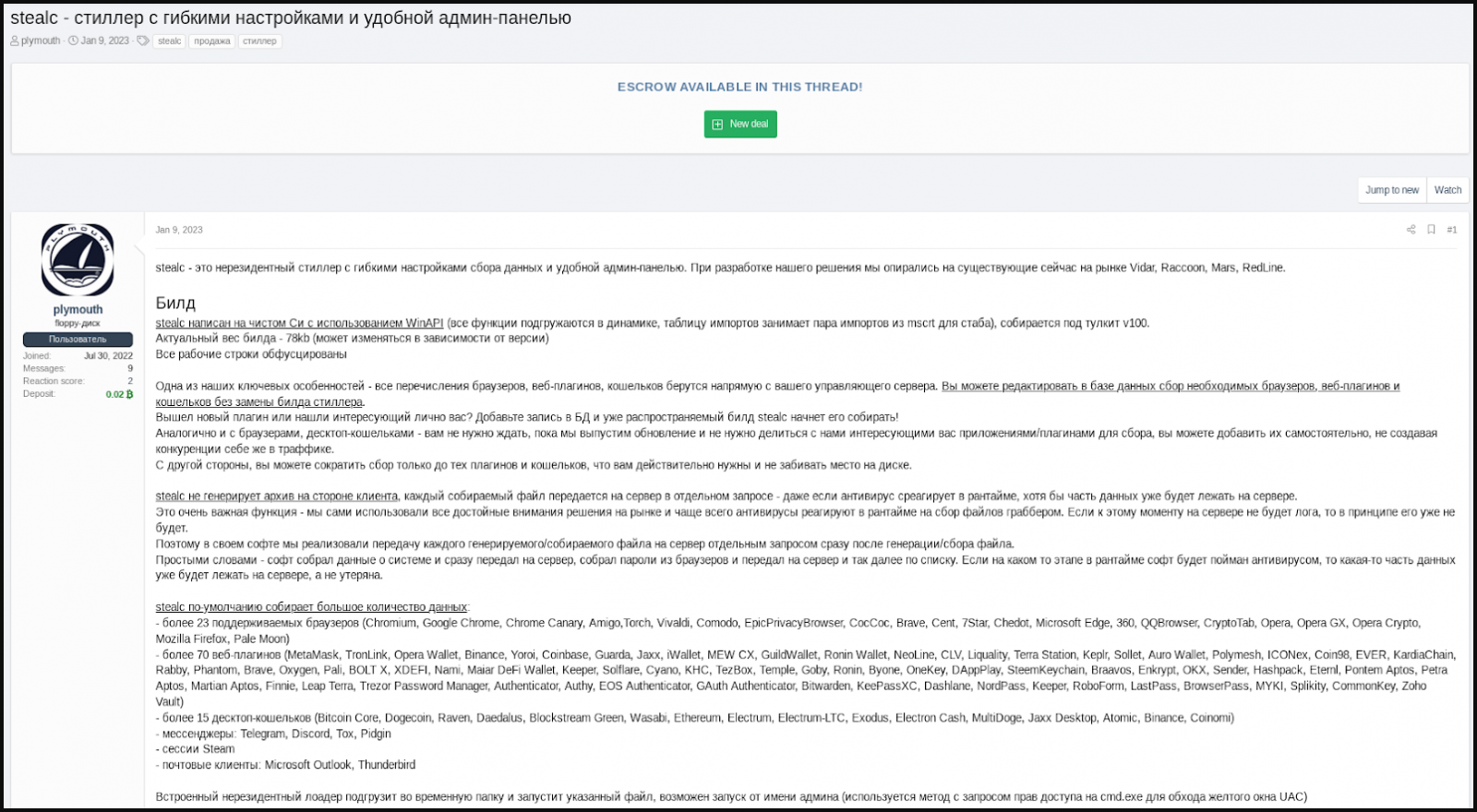
According to the advertiser, besides the typical targeting of web browser data, extensions, and cryptocurrency wallets, Stealc also has a customizable file scraper that can be configured to target all file types that the operator wish to fly.
After the initial post, Plymouth began promoting the malware on other hacking forums and private Telegram channels, offering test samples to potential customers.
The vendor has also set up a Telegram channel dedicated to posting changelogs of the new version of Stealc, the most recent being v1.3.0, released on February 11, 2023. The malware is actively being developed, and a new version appears on the channel weekly.
Plymouth also said that Stealc was not developed from scratch, but instead relied on Vidar, Raccoon, Mars and Redline Rogues.
A commonality that researchers have found between Stealc and Vidar, Raccoon and Mars information stealers is that they all download legitimate third-party DLLs (e.g. sqlite3.dll, nss3.dll) to help steal sensitive data.
In a report Now, SEKOIA researchers note that the command and control (C2) communications of one of the samples they analyzed shared similarities with those of the Vidar and Raccoon information thieves.
Researchers have discovered more than 40 C2 servers for Stealc and several dozen samples in the wild, indicating that the new malware has caught the interest of the cybercriminal community.
This popularity can be explained by the fact that customers with access to the administration panel can generate new samples of thieves, which increases the chances of the malware leaking to a wider audience.
Despite the poor business model, SEKOIA believes that Stealc poses a significant threat as it could be adopted by less technical cybercriminals.
Stealc functions
Stealc has added new features since its first release in January, including a C2 URL randomization system, a better search and sorting system for logs (stolen files), and an exclusion for victims in Ukraine.
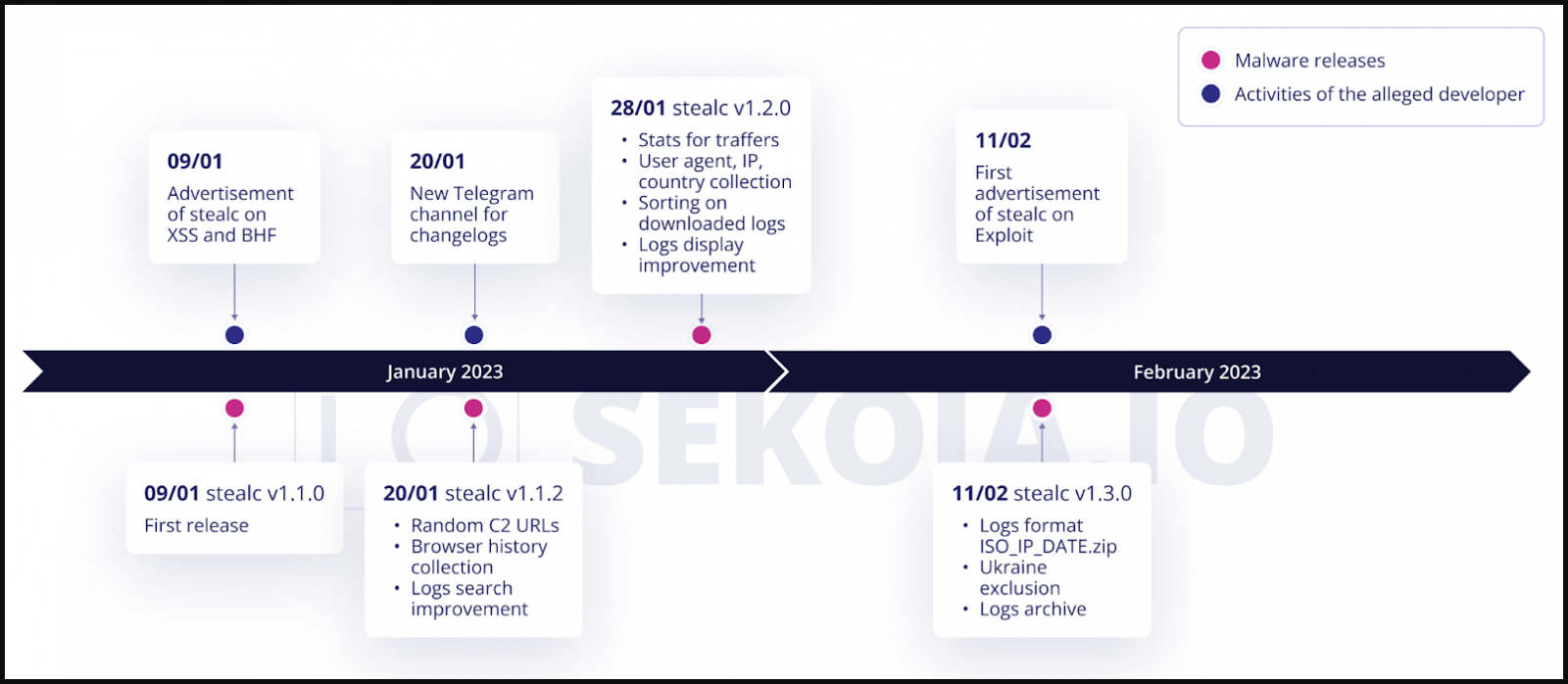
The characteristics that SEKOIA was able to verify by analyzing the captured sample are as follows:
- Light version of only 80 KB
- Use of legitimate third-party DLLs
- Written in C and abusing Windows API functions
- Most strings are obfuscated with RC4 and base64
- Malware automatically exfiltrates stolen data
- It targets 22 web browsers, 75 plugins and 25 desktop wallets
SEKOIA’s current report does not include all of the data obtained from reverse-engineering Stealc but provides an overview of key steps in its execution.
Once deployed, the malware deobfuscates its chains and performs anti-analysis checks to ensure that it is not running in a virtual environment or sandbox.
Then it dynamically loads WinAPI functions and initiates communication with the C2 server, sending the victim’s hardware ID and build name in the first message, and receiving a configuration in response.
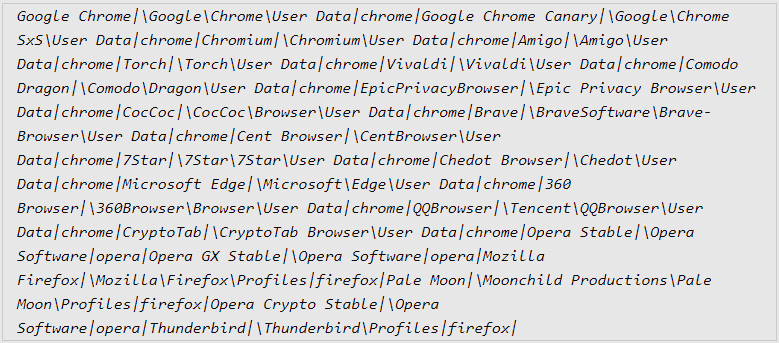
Stealc then collects data from targeted browsers, extensions, and apps, and also runs its custom file scraper if active, and ultimately exfiltrates everything to C2. Once this step is completed, the malware removes itself and the downloaded DLL files from the compromised host to erase the traces of the infection.
For the full list of Stealc capabilities and targeted applications, see the Annex 1 section of the SEKOIA report.
One distribution method observed by researchers is through YouTube videos describing how to install pirated software and a link to a download website.

The researchers say that the software download embeds the Stealc information stealer. Once the installer is executed, the malware begins its routine and communicates with its server.
SEKOIA has shared a wide range of indicators of compromise that companies can use to defend their digital assets as well as YARA And meerkat rules to detect malware based on specific decryption routine, strings and behavior,
Considering the observed distribution method, users are recommended to avoid installing pirated software and download products only from developer’s official website.
[ad_2]
Source link
