[ad_1]

A new information-stealing malware named “Mystic Stealer” has been promoted on hacking forums and darknet markets since April 2023, rapidly gaining traction in the cybercrime community.
The malware, leased for $150/month, targets 40 web browsers, 70 browser extensions, 21 cryptocurrency apps, 9 MFA and password management apps, 55 cryptocurrency browser extensions, Steam IDs and Telegram, and more.
Two individual Mystic Stealer reports, published almost simultaneously by Zscaler and Cyfirma, warn of the emergence of the new malware, its sophistication, and what appears to be a surge in sales that is bringing many new online campaigns.
The Rise of Mystic Stealer
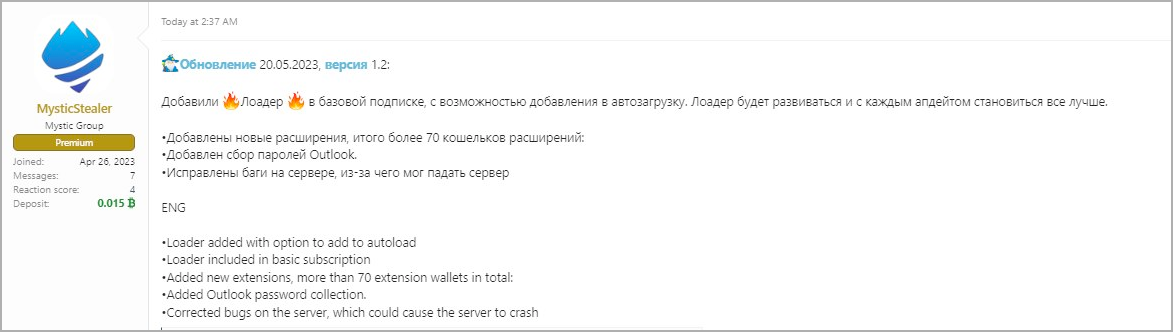
Mystic Stealer launched version 1.0 at the end of April 2023 but quickly upgraded to version 1.2 towards the end of May, indicating active development for the project.

The vendor announced the new malware on several hacking forums, including the WWH-Club, BHF, and XSS, praising it to interested people for the competitive subscription price of $150 per month or $390 per term.
The project also operates a Telegram channel (Mystic Stealer News) where development news, feature requests, and other relevant topics are discussed.
It is reported that the creator of the new malware accepts feedback from established members of the underground hacking community and openly invites them to share suggestions to improve Mystic.
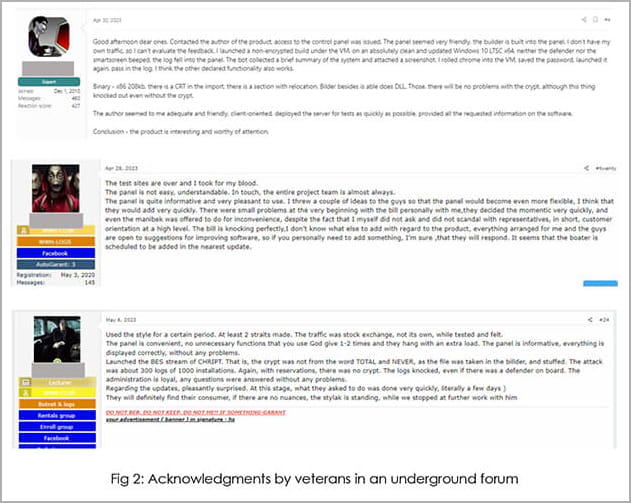
Cyfirma Reports that space veterans have verified the effectiveness of the malware and confirmed that despite its early development state, it is a powerful information stealer.
Technical details
Mystic Stealer can target all versions of Windows, including XP to 11, supporting both 32 and 64 bit operating system architectures.
The malware needs no dependencies, so its footprint on infected systems is minimal, while it operates in memory to avoid detection by antivirus products.
Additionally, Mystic performs several anti-virtualization checks, such as inspecting CPUID details to ensure that it is not running in sandboxed environments.
The author of Mystic added an exclusion for countries in the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) (formerly the Soviet Union), which could point to the origin of the new malware.
Zscaler reports that another restriction set by the creator is to prevent malware from running versions older than a specified date, possibly to minimize the malware’s exposure to security researchers.
As of May 20, 2023, the malware author added loader functionality that allows Mystic to fetch additional payloads from the C2 server.
All communication with the C2 is encrypted using a custom binary protocol over TCP, while all stolen data is sent directly to the server without first storing it on disk.
This is an unusual approach for information-stealing malware, but helps Mystic evade detection.
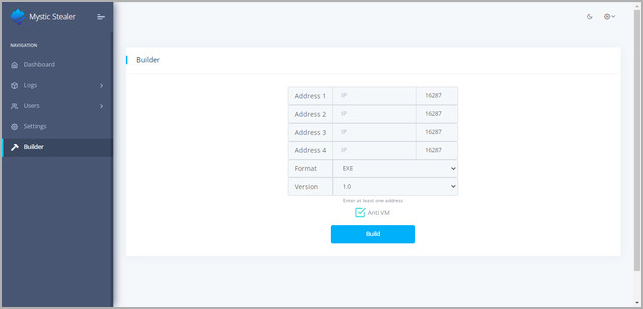
The operator can configure up to four C2 endpoints for resiliency, which are encrypted using a modified algorithm based on XTEA.
flight capabilities
On first run, Mystic gathers operating system and hardware information and takes a screenshot, sending the data to the attacker’s C2 server.
Depending on the instructions it receives, the malware will target more specific data stored in web browsers, apps, etc.
The Zscaler Report gives the full list of targeted apps, which includes popular web browsers, password managers, and cryptocurrency wallet apps.
Notable entries on the list include:
- Google Chrome
- MozillaFirefox
- Microsoft Edge
- Opera
- Vivaldi
- Brave-Navigator
- Binance
- Exodus
- Bitcoin
- Litecoin
- Electrum
- 2FA authentication
- Gauth Authenticator
- EOS Authenticator
- LastPass: free password manager
- Trezor Password Manager
- RoboForm Password Manager
- Dashlane — Password Manager
- NordPass password manager and digital safe
- browser pass
- MYKI Password Manager and Authenticator
Although the future of Mystic Stealer is still under debate, given the volatile nature of illegal MaaS projects, its emergence signals a high risk for users and organizations.
The recent addition of a loader could help Mystic operators drop payloads such as ransomware onto compromised computers. Extreme caution is therefore recommended when downloading software from the Internet.
[ad_2]
Source link
