[ad_1]

Hackers are deploying new malware named “Frebniss” on Microsoft’s Internet Information Services (IIS) that stealthily executes commands sent via web requests.
Frebniis was discovered by Symantec’s Threat Hunter team, which reported that an unknown malicious actor is currently using it against Taiwan-based targets.
Microsoft IIS is web server software that acts as a web server and web application hosting platform for services such as Outlook on the web for Microsoft Exchange.
In the attacks seen by Symantec, hackers abuse an IIS feature called ‘Failed Request Event Buffering’ (FREB), responsible for collecting request metadata (IP address, HTTP headers, cookies). Its purpose is to help server administrators troubleshoot unexpected HTTP status codes or request processing issues.
The malware injects malicious code into a specific function of a DLL file that controls FREB (“iisfreb.dll”) to allow the attacker to intercept and monitor all HTTP POST requests sent to the ISS server. When the malware detects specific HTTP requests sent by the attacker, it analyzes the request to determine what commands to run on the server.
Symantec says threat actors must first breach an IIS server to compromise the FREB module, but they could not determine the method used to gain initial access.
The injected code is a .NET backdoor that supports proxying and executing C# code without ever touching the disk, making it completely stealthy. It looks for requests to logon.aspx or default.aspx pages with a specific password setting.
A second HTTP parameter, which is a base64-encoded string, instructs Frebniis to communicate and execute commands on other systems through the compromised IIS, potentially reaching protected internal systems that are not exposed to the Internet.
The malware supports the following commands:
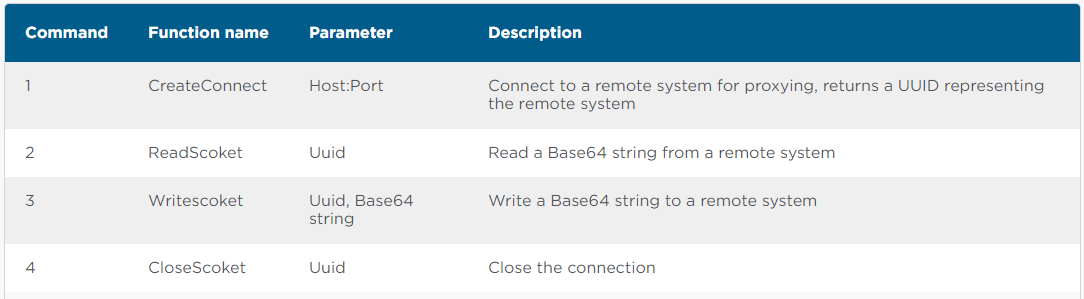
“If an HTTP call to logon.aspx or default.aspx is received without the password parameter, but with the Base64 string, the Base64 string is assumed to be C# code that will be executed directly in memory,” explains The Symantec report.
“The Base64 string is decoded then decrypted (xor 0x08) and should be an XML document with the C# code to be executed in the ‘/doc’ node under the ‘data’ attribute (e.g.
The main advantage of abusing the FREB component for the purposes described is to evade detection by security tools. This unique HTTP backdoor leaves no traces or files and does not create any suspicious processes on the system.
Although the initial path of compromise is unknown, updating your software is generally recommended to minimize the risk of hackers exploiting known vulnerabilities.
Advanced network traffic monitoring tools can also help detect unusual activity by malware such as Frebniis.
In October 2022, Symantec discovered another malware used by the Cranefly hacking group that abused ISS logs to send and receive commands from the C2 server without triggering an alarm.
[ad_2]
Source link
