[ad_1]

Hackers are actively exploiting a 2018 unpatched authentication bypass vulnerability in exposed TBK DVR (digital video recording) devices.
DVRs are an integral part of security surveillance systems as they record and store video recorded by cameras. The TBK Vision website claims that its products are deployed in banks, government organizations, the retail sector, and more.
As these DVR servers are used to store sensitive security footage, they are usually located on internal networks to prevent unauthorized access to the recorded video. Unfortunately, this makes them attractive to threat actors who can exploit them for initial access to corporate networks and to steal data.
Fortinet’s FortiGard Labs reports that it has recently seen an increase in hacking attempts on TBK DVR devices, with threat actors using a publicly available proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit to target a vulnerability in servers.
The vulnerability is a critical flaw (CVSS v3: 9.8), tracked as CVE-2018-9995which allows attackers to bypass authentication on the device and gain access to the impacted network.
The exploit uses a maliciously crafted HTTP cookie, which vulnerable TBK DVR devices respond to with administrator credentials in the form of JSON data.
“A remote attacker may be able to exploit this flaw to bypass authentication and gain administrative privileges, possibly leading to access to camera video feeds,” reads one. outbreak alert by Fortinet.
The vulnerability affects TBK DVR4104 and TBK DVR4216 and rebrands of these models sold under the Novo, CeNova, QSee, Pulnix, XVR 5-in-1, Securus, Night OWL, DVR Login, HVR Login and MDVR brands.
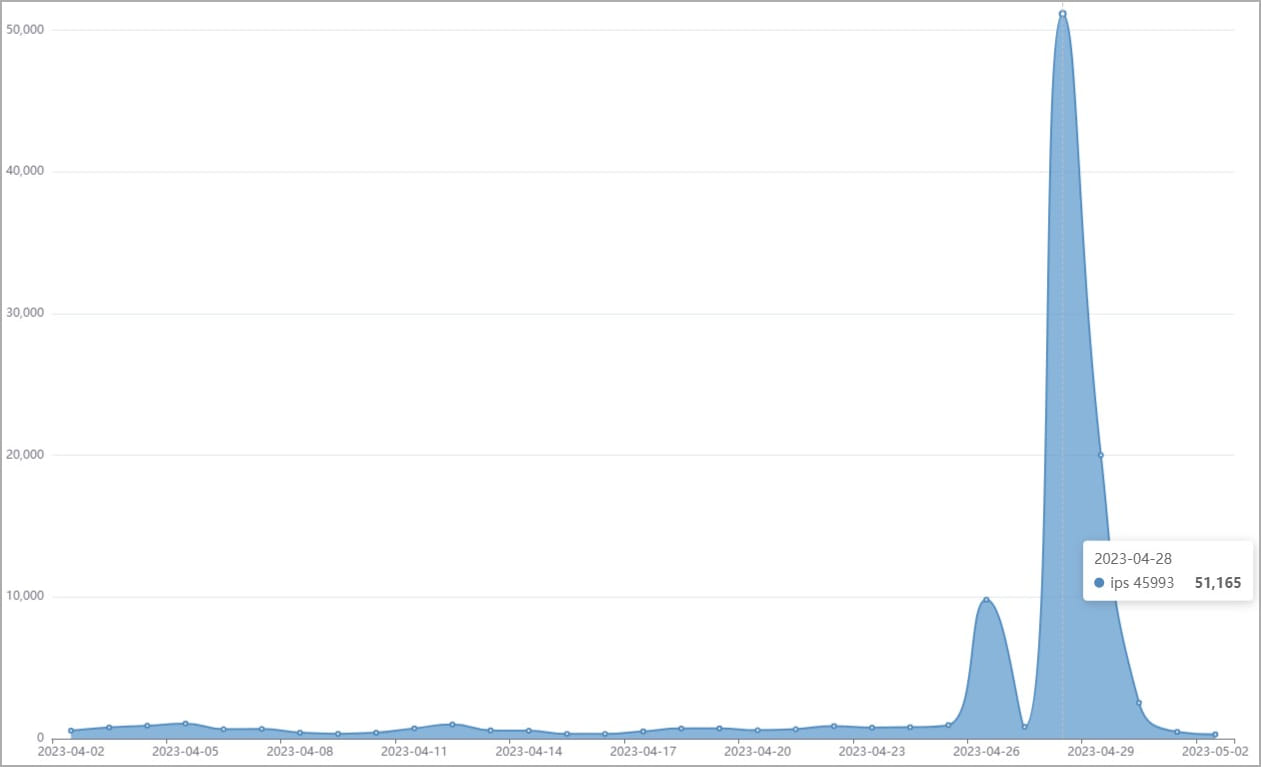
According to Fortinet, as of April 2023, there were over 50,000 attempts to exploit TBK DVR devices using this flaw.
“With tens of thousands of TBK DVRs available under various brands, publicly available PoC code, and ease of exploitation, this vulnerability is an easy target for attackers,” Fortinet said.
“The recent spike in IPS detections shows that network cameras remain a popular target for attackers.”
Unfortunately, Fortinet is not aware of a security update to fix CVE-2018-9995. Therefore, it is advisable to replace vulnerable surveillance systems with new, actively supported models or isolate them from the Internet to prevent unauthorized access.
Another ancient flaw undergoing an “epidemic” of exploitation is CVE-2016-20016 (CVSS v3: 9.8, “critical”), a remote code execution vulnerability affecting MVPower TV-7104HE and TV-7108HE DVRs, allowing attackers to execute unauthenticated commands using malicious HTTP requests .
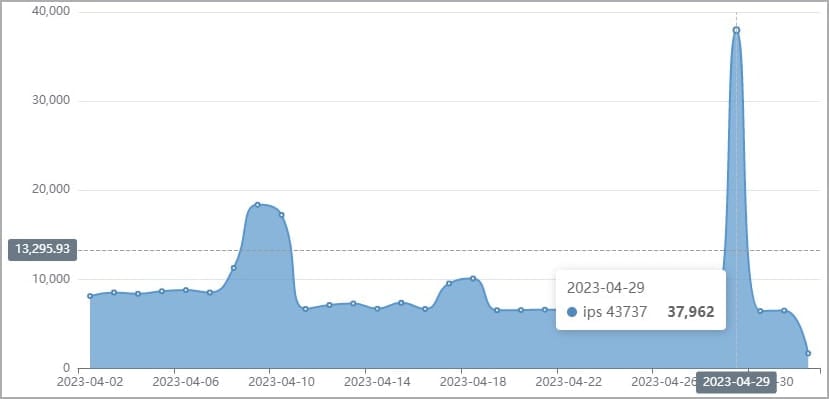
This flaw has been actively exploited in the wild since 2017, but Fortinet has recently seen signs of increased malicious activity taking advantage of it. Also in this case, the vendor did not provide a patch to address the vulnerability.
[ad_2]
Source link
