[ad_1]

A critical design flaw in the Google Cloud Build service discovered by cloud security firm Orca Security can allow attackers to elevate privileges, providing them with near-full, unauthorized access to Google Artifact Registry code repositories.
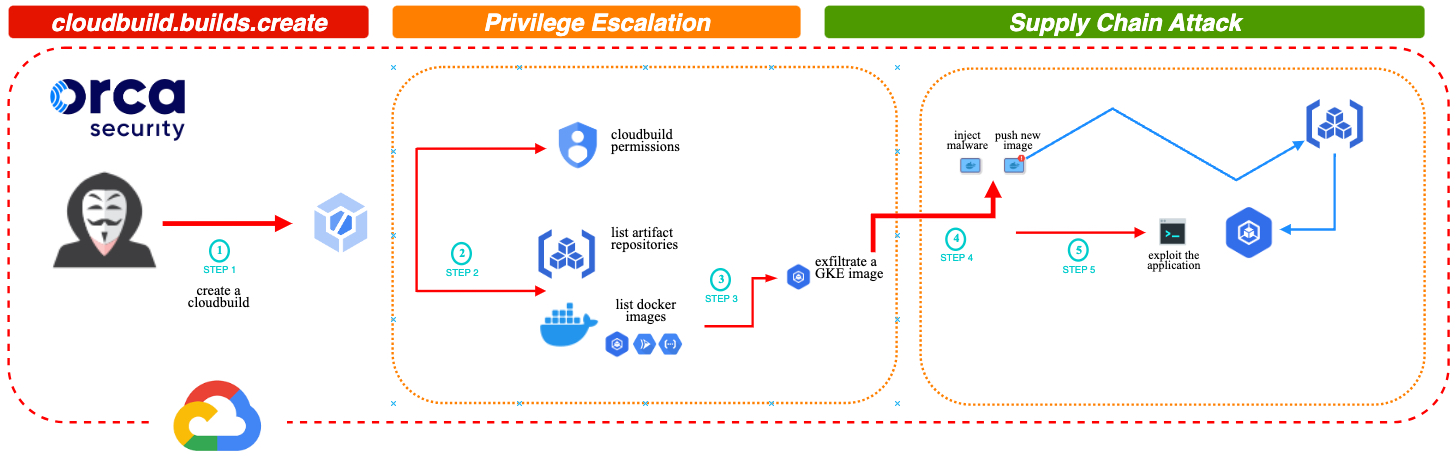
Double Bad.BuildThe flaw could allow threat actors to impersonate the service account for Google Cloud Build’s Managed Continuous Integration and Delivery (CI/CD) service to execute API calls on the artifact registry and take control of application images.
This allows them to inject malicious code, resulting in vulnerable applications and potential supply chain attacks after the malicious applications are deployed in customer environments.
“The potential impact can be diverse and applies to all organizations that use Artifact Registry as a primary or secondary image repository,” said Orca security researcher Roi Nisimi.
“The first immediate impact is the disruption of applications relying on these images. This can lead to DOS, data theft and the spread of malware to users.
“As we have seen with SolarWinds and the recent 3CX and MOVEit supply chain attacks, this can have far-reaching consequences.”
The same vulnerability was observed and reported by Rhino Security Lab here. Yet their method of exploiting this privilege escalation flaw was more complex, involving the use of the GCP API and exfiltrated Cloud Build service account access tokens.
The Orca Security attack leverages the cloudbuild.builds.create permission to elevate privileges and allow attackers to tamper with Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) docker images using artifactregistry and run code inside docker container as root.
After Orca Security reported the issue, the Google security team implemented a partial fix revoking the permission logging.privateLogEntries.list from the default Cloud Build service account, unrelated to Artifact Registry.
Importantly, this measure did not directly address the underlying vulnerability in the artifact registry, leaving the privilege escalation vector and supply chain attack risk intact.
“However, Google’s patch does not revoke the discovered Privilege Escalation (PE) vector. It only limits it – turning it into a design flaw that still leaves organizations vulnerable to the broader chain risk supply,” Nisimi said.
“It is therefore important that organizations pay close attention to the behavior of the default Google Cloud Build service account. Applying the principle of least privilege and implementing detection and response capabilities in the cloud to identify anomalies are part of the recommendations to reduce the risks.”
Google Cloud Build customers are advised to modify the default Cloud Build service account permissions to suit their needs and remove entitlement credentials that violate the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP) to mitigate the risk of privilege escalation.
In April, Google also addressed a Google Cloud Platform (GCP) security vulnerability called GhostToken that allow hackers to hijack any Google Account using malicious OAuth apps.
[ad_2]
Source link
