[ad_1]

Exploit code has been released for an actively exploited zero-day vulnerability affecting Internet-exposed GoAnywhere MFT administration consoles.
GoAnywhere MFT is a managed, web-based file transfer tool designed to help organizations securely transfer files with partners and maintain audit logs of who accessed shared files.
Its developer is Fortra (formerly known as HelpSystems), the team behind the much abused Cobalt Strike threat emulation tool.
Monday, security researcher Florian Hauser from IT security consultancy Code White has published the technical details and proof-of-concept exploit code which executes unauthenticated remote code on vulnerable GoAnywhere MFT servers.
“I could provide a job PoC (compare the hash and time of my Tweeter) to my teammates within hours the same day to protect our customers first,” Hauser said.
Fortra states that “The attack vector for this exploit requires access to the application’s admin console, which in most cases can only be accessed from a private corporate network, via VPN or authorized IP addresses (when running in cloud environments, such as Azure or AWS).”
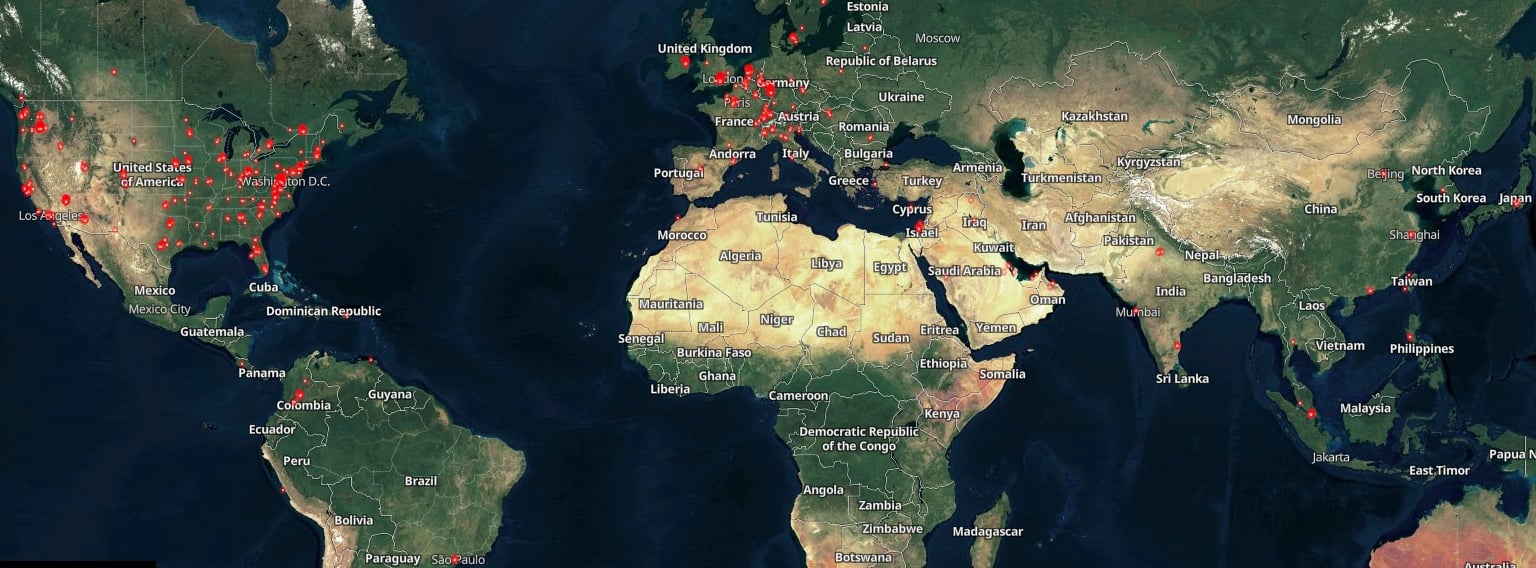
However, a Shodan scan shows that nearly 1,000 GoAnywhere instances are exposed on the Internet, although just over 140 are on ports 8000 and 8001 (those used by the vulnerable administration console).
Attenuation available
The company has not yet publicly acknowledged this remote pre-authentication RCE security flaw exploited in attacks (read the boardyou must create a free account first) and has not released security updates to fix the vulnerability, leaving all exposed installations vulnerable to attack.
However, the private notice provides indicators of compromise, including a specific stack trace that appears in logs on compromised systems.
“If this stacktrace is in the logs, it’s very likely that this system was the target of an attack,” Fortra says.
It also contains mitigation advice that includes implementing access controls to allow access to the GoAnywhere MFT administrative interface only from trusted sources or disabling the license service.
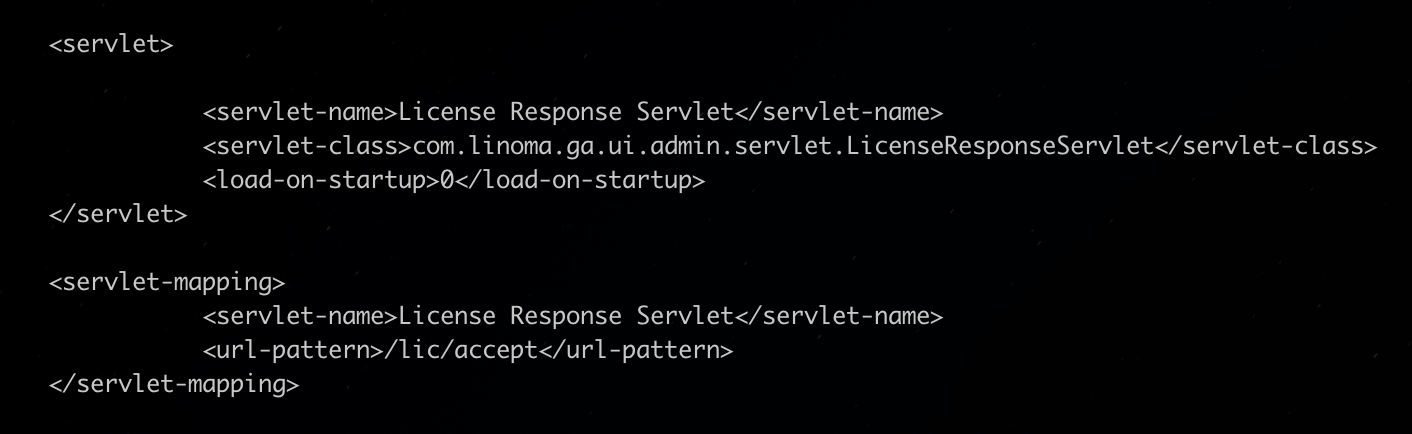
To disable the license server, administrators must comment out or remove the servlet and servlet mapping configuration for the license response servlet in the web.xml file to disable the vulnerable endpoint. A reboot is required to apply the new configuration.
“Because your environment’s data could have been accessed or exported, you should determine if you have stored credentials for other systems in the environment and ensure that those credentials have been revoked” , Fortra added in an update posted on Saturday.
“This includes passwords and keys used to access any external systems with which GoAnywhere is integrated.
“Ensure that all credentials have been revoked from these external systems and review relevant access logs related to these systems. This also includes passwords and keys used to encrypt files in the system. “
Fortra also recommends taking the following post-mitigation actions in environments where there is suspicion or evidence of an attack:
- Rotate your master encryption key.
- Reset credentials – keys and/or passwords – for all trading partners/external systems.
- Examine audit logs and remove any suspicious administrator and/or web user accounts
- Contact support through the https://my.goanywhere.com/ portal, email goanywhere.support@helpsystems.com, or call 402-944-4242 for assistance.
[ad_2]
Source link