[ad_1]

Threat actors penetrated the network of a US critical infrastructure organization after exploiting a zero-day RCE vulnerability currently identified as CVE-2023-3519, a critical severity issue in NetScaler ADC and Gateway that Citrix patched this week.
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) says the attack happened in June and the hackers used their access to steal Active Directory data.
Hackers exfiltrated AD data
In an advisory published this week, CISA warns that hackers have exploited the unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE) flaw to implant a web shell on the target’s non-production NetScaler Application Delivery Controller (ADC) appliance.
The backdoor allowed the attacker to discover Active Directory (AD) objects, which include users, groups, applications, and devices on the network, as well as steal AD data.
Because the targeted NetScaler ADC appliance was in a separate environment on the network, attackers were unable to move laterally to a domain controller, CISA said.
CISA has released an advisory with tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) and detection methods to help organizations, especially those in the critical infrastructure segment, determine if their systems have been compromised.
During the initial exploitation phase, the hackers downloaded to the vulnerable appliance a TGZ archive with a generic webshell, a discovery script and a calm binary.
They performed an SMB scan on the subnet and used the webshell to verify and exfiltrate the Active Directory inventory, with particular interest in:
- NetScaler configuration files containing an encrypted password whose key resides on the ADC appliance
- NetScaler decryption keys, which can unlock AD password in configuration file
- The list of users, systems, groups, subnets, organizational units, contacts, partitions, and trusts in Active Directory
The attacker encrypted the discovery data using the OpenSSL library and prepared it for exfiltration to a web-accessible location in compressed form as an archive disguised as a PNG image.
It seems that the hackers tried to cover their tracks by deleting the authorization file, which would prevent administrators from logging in remotely. To regain access, a reboot to single-user mode is required, which may have removed artifacts.
With the threat actors exploiting the vulnerability since this was zero day, NetScaler administrators should install the latest updates released by Citrix without delay to resolve the issue.
Thousands of vulnerable servers exposed
An initial assessment by the Shadowserver Foundation, a non-profit organization aiming to make the internet safer, showed that CVE-2023-3519 likely affects over 11,000 NetScaler ADC and Gateway servers exposed online.
This number increased to 15,000the organization told BleepingComputer today, after refining its query to mark as vulnerable all NetScaler appliances that returned a “last modified” header with a date before July 1.
The new count is also due to improved detection coverage of NetScaler AAA (authentication virtual server) machines. Although it has increased, this number probably represents a conservative estimate, according to the organization.
CISA has also released a set of commands that organizations can use to check for signs of compromise by exploiting CVE-2023-3519.
Stacking commands leading to the root
Citrix patched CVE-2023-3519 on July 18 along with two less severe vulnerabilities. One is a Thoughtful Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) bug with a severity score of 8.3 and tracked as CVE-2023-3466.
Exploitation of this flaw is possible if the victim on the same network as the vulnerable appliance loads a malicious link from an attacker into the browser.
The other is an elevation of privilege to root identified as CVE-2023-3467. It has been assigned a severity score of 8.0 and can be exploited by an attacker with the least privileged role on the NetScaler Command Line Interface (CLI).
Jorren Geurts and Wouter Rijkborst, researchers from cybersecurity firm Resillion, published a detailed technical analysis of the vulnerability, explaining how stacking specific commands in the NetScaler CLI allows any user with read-only permissions to gain root privileges on the system.
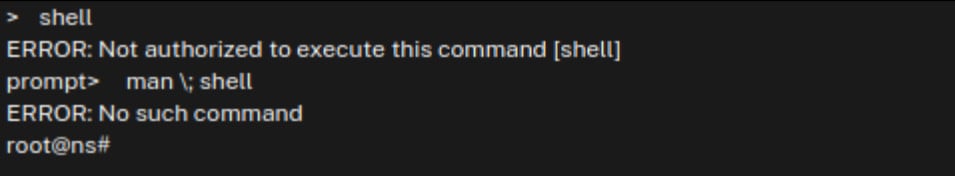
source: Reillion
There is currently no information on these less severe vulnerabilities being exploited in the wild, but threat actors who already have access to the network could exploit them to increase their access to the network.
Recently, The Estée Lauder Companies obtained violated twice in separate attacks from Clop, through the MOVEit zero-day vulnerabilityand the ALPHV/BlackCat ransomware gangs.
It’s still unclear how ALPH/BlackCat got the initial access, but the gang boasted that two weeks after the company hired Microsoft’s DART and Mandiant services to deal with the first incident, they were still on the network.
Threat actors, especially advanced groups, do not always rush to move laterally on the victim network and sometimes they wait silently to find a less noisy method that increases the success of the attack.
[ad_2]
Source link
