[ad_1]

Apache Superset is vulnerable to authentication bypass and remote code execution in default configurations, allowing attackers to potentially access and modify data, harvest credentials, and execute commands.
Apache Superset is an open source data visualization and exploration tool originally developed for Airbnb before becoming a top project at the Apache Software Foundation in 2021.
According to a new report from Horizon3Apache Superset used a default Flask secret key to sign authentication session cookies. Therefore, attackers can use this default key to forge session cookies that allow them to connect with administrator privileges to servers that have not changed the key.
While the Apache Documentation tells administrators to change secret keys, Horizon3 says this dangerous default configuration is currently detectable in about 2,000 Internet-facing servers belonging to universities, companies of various sizes, government organizations, and more.
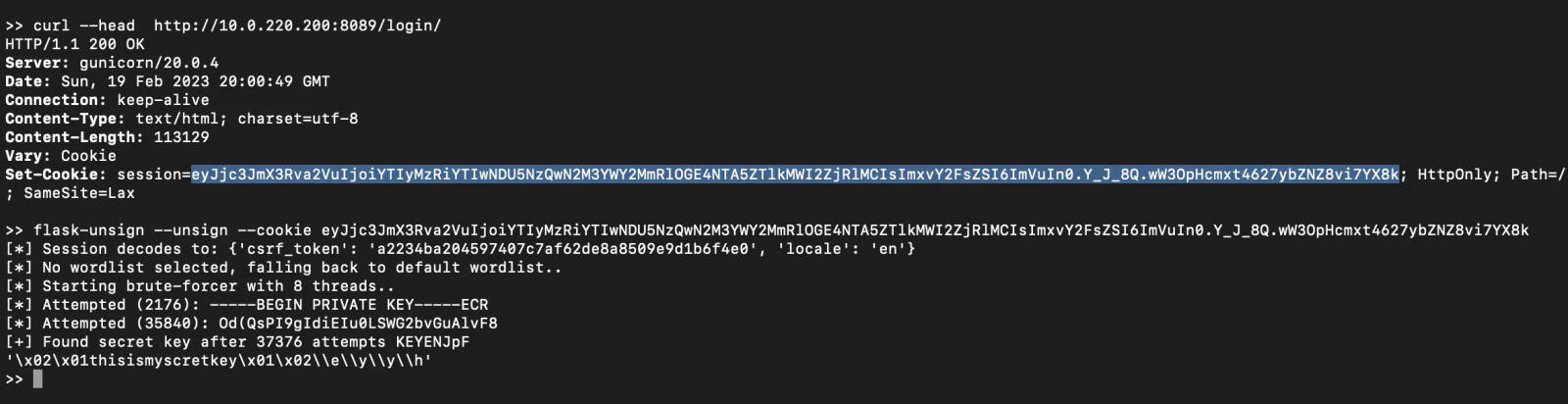
This widely used default Flask secret key is known to attackers who can use vial-unsign and forge their own cookies to gain administrator access on the target, access connected databases, or execute arbitrary SQL statements on the application server.
“We are not disclosing any exploitation methods at this time, although we believe it will be easy for interested attackers to find out,” Horizon3 warns.
It is important to note that if the administrators have changed the default key to a key unknown to the attackers, their installations are not vulnerable to this attack.
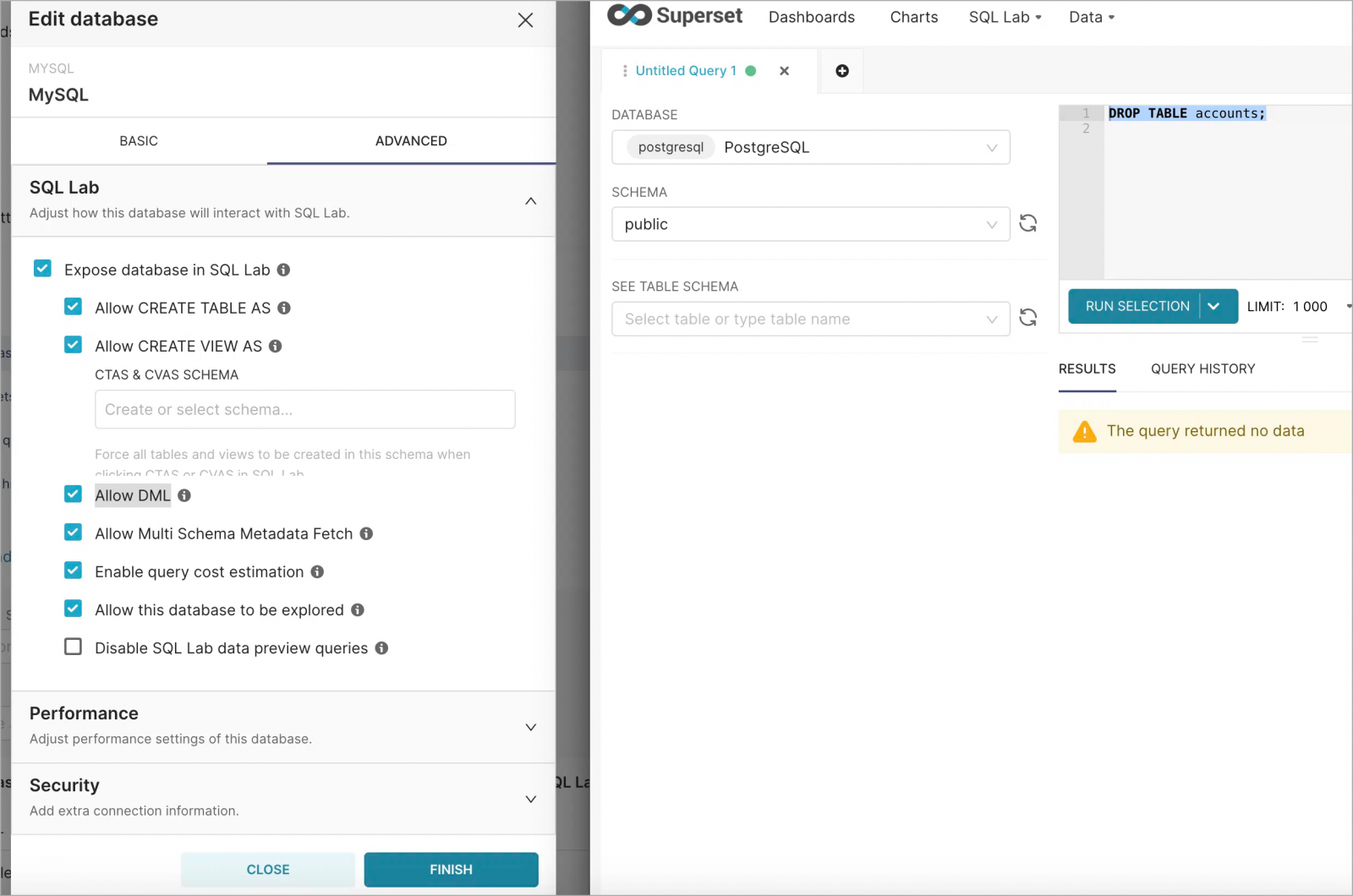
Discovery and impact
The flaw was discovered by the Horizon3 team on October 11, 2021 and reported to the Apache Security team.
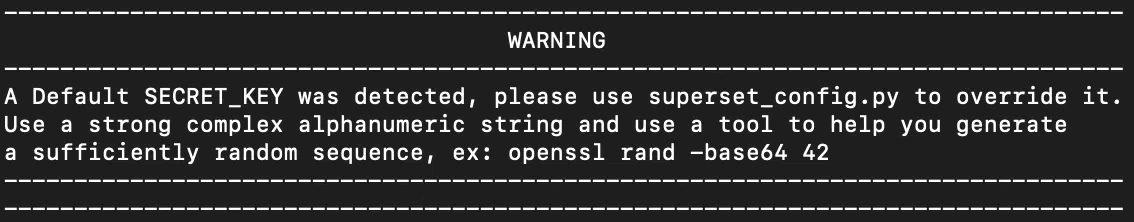
On January 11, 2022, the software developers released version 1.4.1, which changed the default “SECRET_KEY” to a new string, and a warning was added to the logs when the default string was detected on startup .
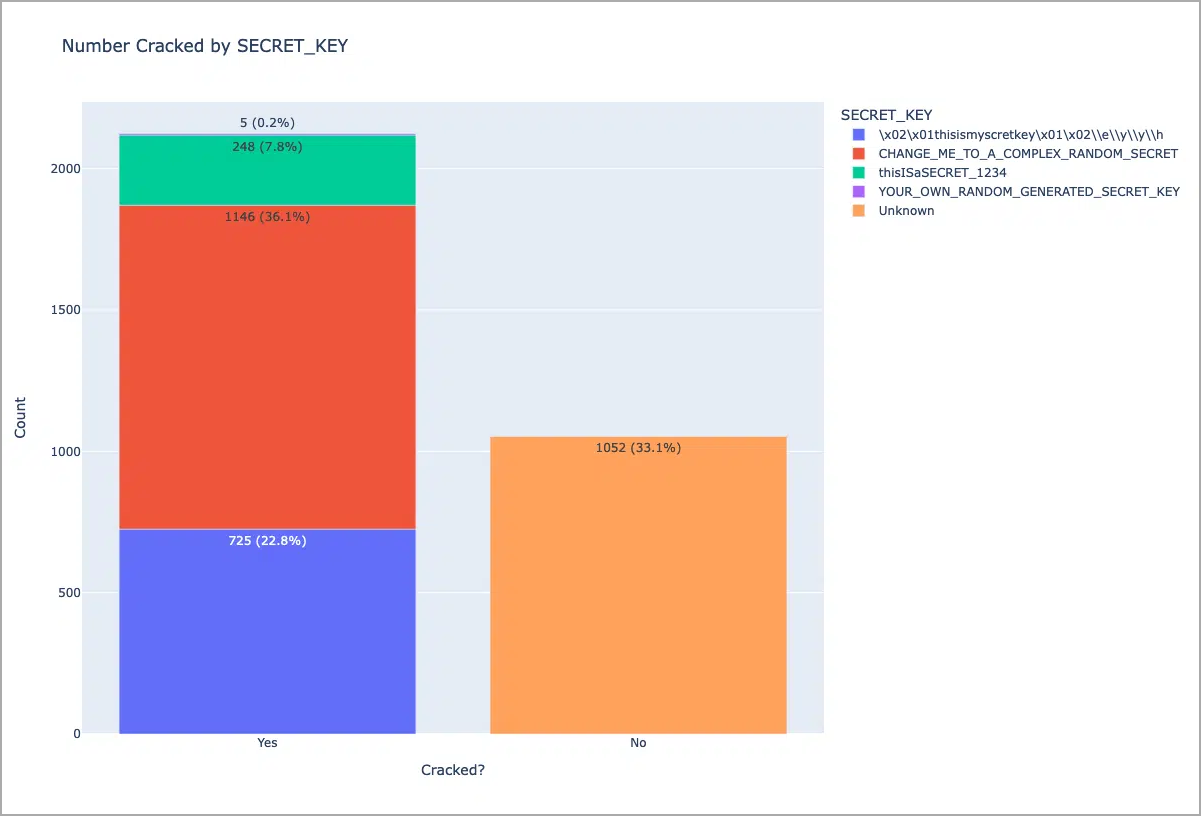
Horizon3 also found two other default keys used in documentation and templates and used Shodan to find instances using these four keys.
At the time, Horizon3 found that around 2,124 (67% of the total) were misconfigured.
Horizon3 contacted Apache again and raised the issues, and in February 2023 researchers began sending out warnings to organizations about the need to change their configuration.
Finally, on April 5, 2023, the Superset team released version 2.1, which does not allow the server to start if it uses a default “SECRET_KEY”.
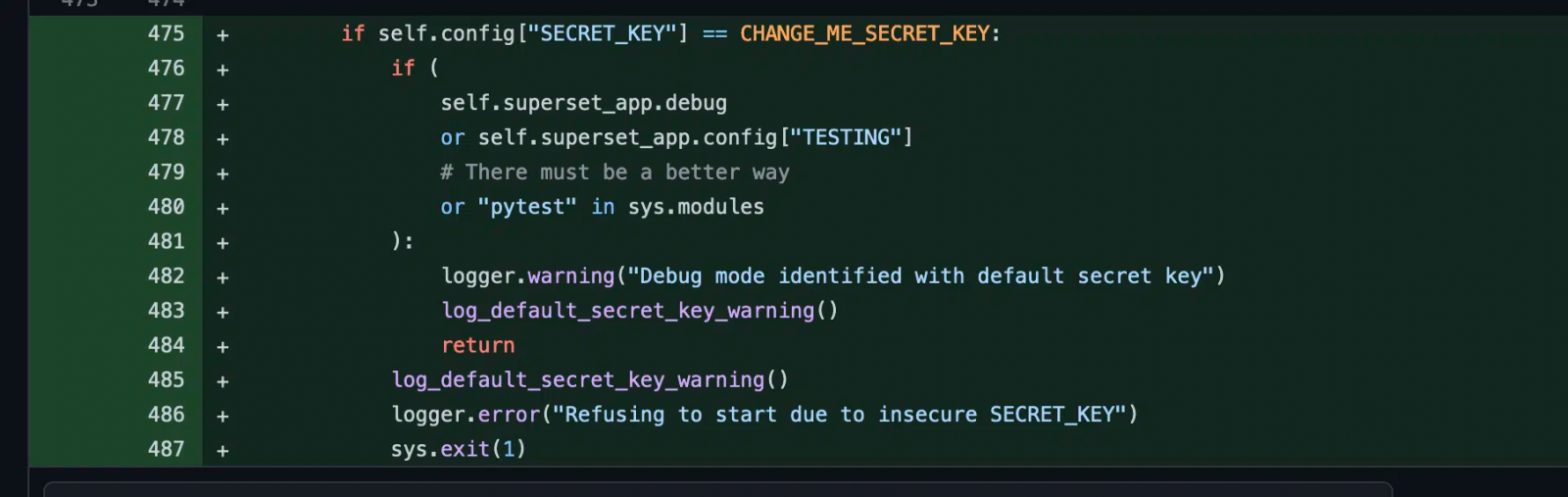
While this drastic fix prevents new risky deployments, it does not fix existing misconfigurations that Horizon3 says are still present in more than 2,000 cases.
The security company shared a script on GitHub that Apache Superset administrators can use to determine if their instance is vulnerable to attacks.
[ad_2]
Source link
