[ad_1]

The Vice Society ransomware operation switched to using custom ransomware encryption that implements a strong hybrid encryption scheme based on NTRUEncrypt and ChaCha20-Poly1305.
According to cybersecurity firm SentinelOne, which discovered the new strain and named it “PolyVice”, it’s likely that Vice Society purchased it from a vendor that provides similar tools to other ransomware groups.
The Vice Society first emerged in the summer of 2021, when it began stealing data from corporate networks and encrypting devices. Threat actors would then perform double extortion attacks, threatening to release the data if a ransom is not paid.
Historically, Vice Society has used other ransomware operation encryptors in attacks, including Zeppelin, Five Hands, and HelloKitty.
However, that appears to have changed, with Vice Society now using a new encryptor that is believed to be generated by a commodity ransomware builder.
New “PolyVice” encryptor
The new PolyVice strain, however, gives Vice Society attacks a unique signature, appending the “.ViceSociety” extension to locked files and dropping ransom notes named “AllYFilesAE”.
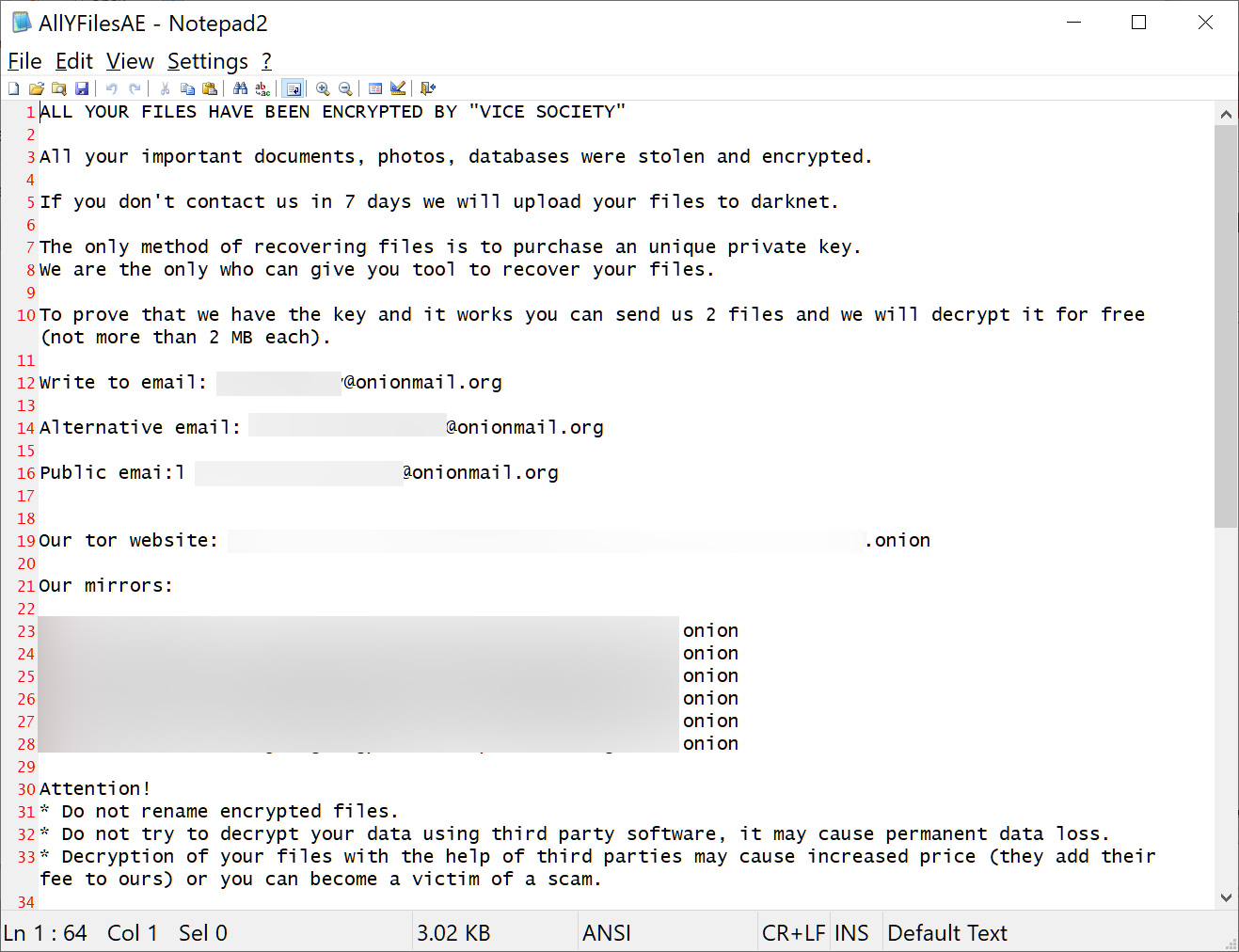
Source: BleepingComputer
The new variant was first seen in the wild on July 13, 2022, but it wasn’t fully embraced by the group until much later.
SentinelOne analysis reveals that PolyVice has many code similarities to Chilly ransomware and SunnyDay ransomware, with 100% matching on functions.
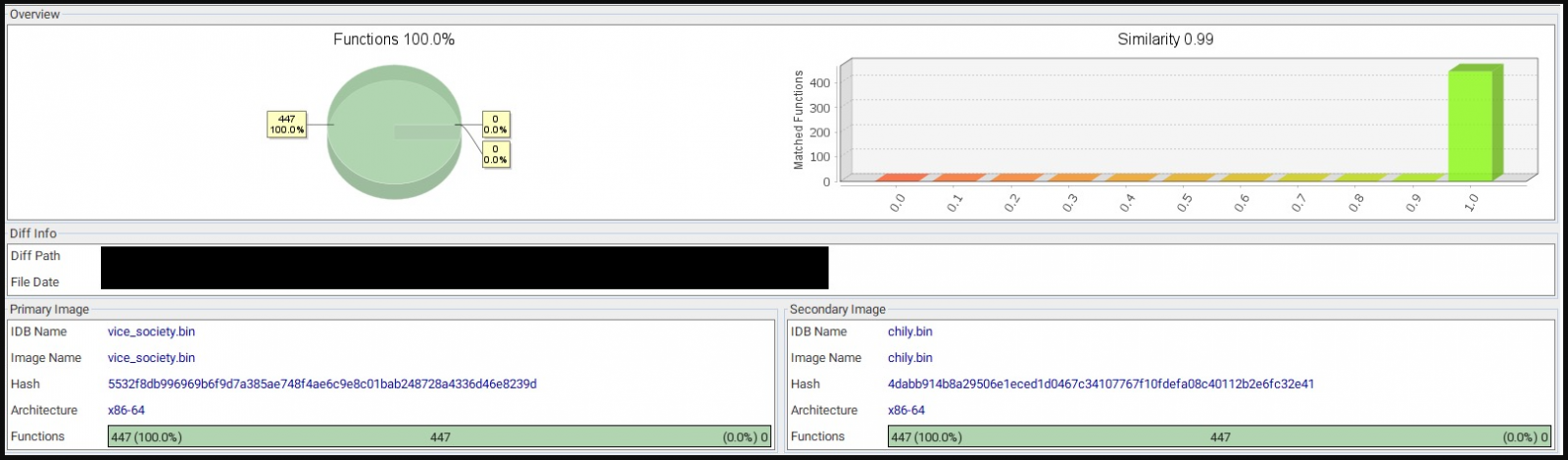
The differences lie in campaign-specific details like file extension, ransom note name, hardcoded master key, desktop background, etc., which support the common hypothesis of the vendor.
“The design of the code suggests that the ransomware developer provides a builder that allows buyers to independently generate any number of lockers/decryptors by binary patching a template payload,” explains SentinelOne in the report.
“This allows buyers to customize their ransomware without revealing any source code. Unlike other known RaaS builders, buyers can build branded payloads, allowing them to run their own RaaS programs.”
Hybrid encryption
PolyVice uses a hybrid encryption scheme combining asymmetric encryption with the NTRUEncrypt algorithm and symmetric encryption with the ChaCha20-Poly1305 algorithm.
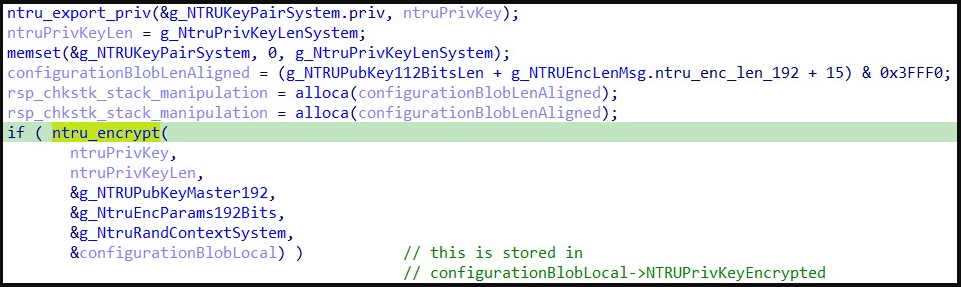
Upon launch, the payload imports a pre-generated 192-bit NTRU public key and then generates a random 112-bit NTRU private key pair on the compromised system that is unique for each victim.
This pair is then used to encrypt ChaCha20-Poly1305 symmetric keys, which are unique to each file. Finally, the NTRU key pair is finally encrypted using the NTRU public key to protect it from recovery attempts.
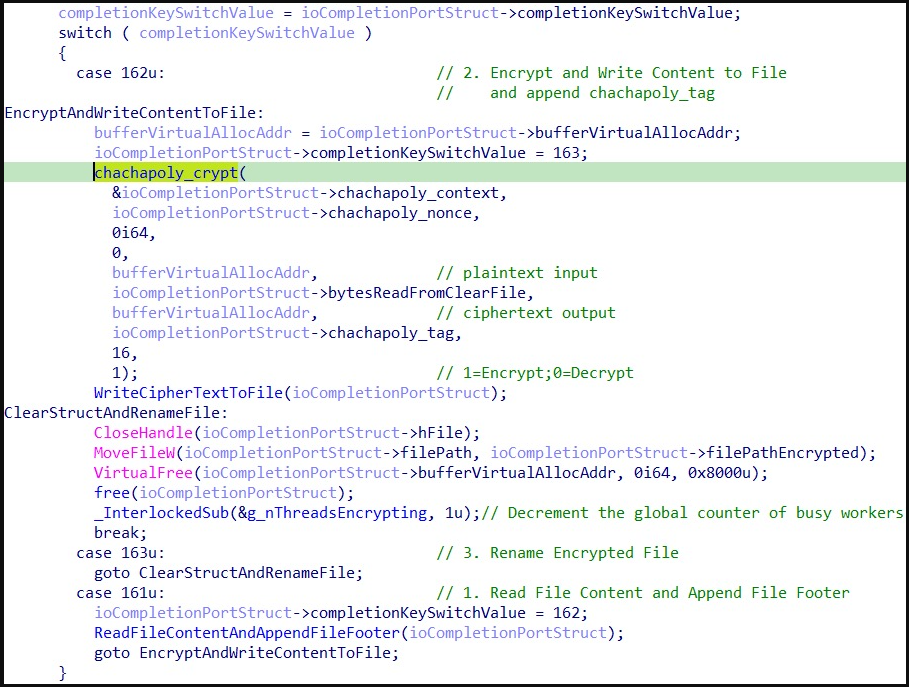
PolyVice ransomware is a 64-bit binary that uses multi-threading for symmetric parallel data encryption, fully utilizing the victim’s CPU to speed up the encryption process.
Additionally, each PolyVice worker reads the contents of the file to determine which speed optimizations can be applied in each case. These optimizations depend on the file size, PolyVice applying intermittent encryption selectively.
- Files under 5MB are fully encrypted.
- Files between 5MB and 100MB are partially encrypted, splitting them into 2.5MB chunks and skipping every second chunk.
- Files larger than 100MB are divided into ten evenly distributed blocks, and 2.5MB of each block is encrypted.
After encryption, each PolyVice worker writes the footer of the file with the information needed for decryption.
All of these characteristics indicate that whoever is developing the new ransomware strains used by Vice Society, Chilly and SunnyDay ransomware is an experienced and skilled malware creator.
In conclusion, SentinelOne’s findings further underscore the outsourcing trend in the space, with ransomware gangs paying specialists to create sophisticated and capable tools.
Depending on the level of availability and cost, these tools can make it easier for unskilled ransomware actors to launch catastrophic attacks and cause significant damage to organizations.
[ad_2]
Source link
