[ad_1]

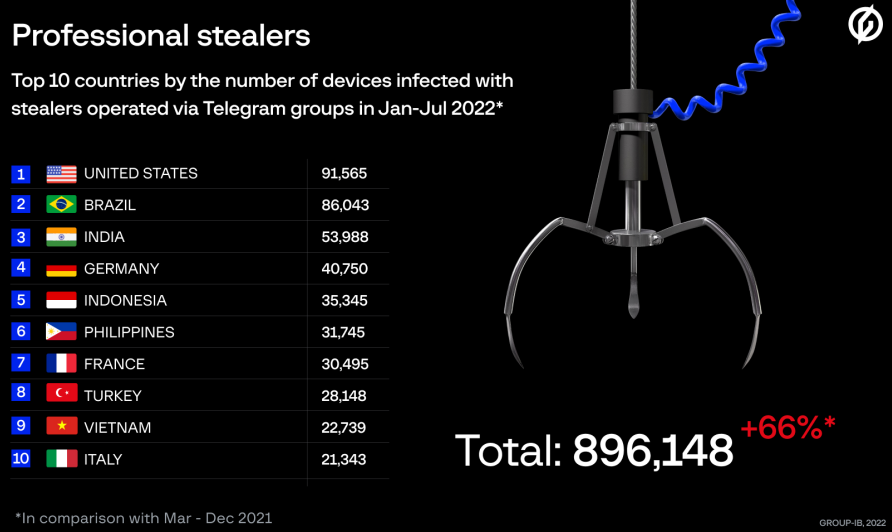
At least 34 separate Russian-speaking cybercriminal groups using information-stealing malware like Raccoon and Redline collectively stole 50,350,000 account passwords from over 896,000 individual infections from January to July 2022.
The stolen credentials included cryptocurrency wallets, Steam, Roblox, Amazon, and PayPal accounts, as well as payment card records.
According to a report by Group-IB, whose analysts tracked these operations globally, most of the victims are based in the United States, Germany, India, Brazil and Indonesia, but the malicious operations targeted 111 countries.
Rise of information thieves
In 2022, the distribution of information-stealing malware has reached unprecedented levels, now involving low-skilled hackers aspiring to make a bigger profit from their illegal activities.
Group-IB says the cybercriminals fueling the growth in the deployment of information thieves are low-level scammers who previously worked as “victim callers” in phishing campaigns known as “Classiscam.”
“The influx of a large number of workers into the popular Classiscam scam, […] at its peak, made up of over a thousand criminal groups and hundreds of thousands of fake websites, led criminals to compete for resources and seek new ways to make a profit,” comments Group-IB.
“The popularity of schemes involving thieves can be explained by the low barrier to entry. Beginners do not need to have advanced technical knowledge because the process is fully automated, and the worker’s only task is to create a file with a thief in the Telegram bot and drive traffic to it.” – Group-IB
Currently, there are 34 active cybercrime groups on Telegram that operate as large-scale information theft gangs, each with around 200 members.
23 of the groups use the Redline thief, eight use Raccoon, and three use their own custom malware.
SEKOIA also noted earlier this week that another information thief named “Aurora” is gain ground on underground forums and has already been adopted by seven prominent threat groups.
The increase in the activity of information thieves is illustrated in statistics compiled by the Group-IB report, which compared a period of 10 months in 2021 to a period of seven months in 2022.
- Passwords stolen: 50,352,518 (up 80%)
- Exfiltrated cookie files: 2,117,626,523 (up 74%)
- Hacked crypto wallets: 113,204 (up 216%)
- Payment cards compromised: 103,150 (up 81%)
.png)
Group-IB also notes that in the first seven months of this year, actors focused on stealing Steam, Epic Games and Roblox accounts, registering a fivefold increase over last year.
Telegram-based operations
Telegram plays a vital role in the operation of these cybergangs, both in organizing their campaigns and in maintaining a functional structure suitable for their data theft activities.
These private Telegram channels offer technical assistance and advice to agents, can serve as data exfiltration points, host important announcements, act as bug reporting portals, and also offer bots that can generate custom builds of software. malware for customers 24/7.
Groups still adhere to hierarchical rules, with “administrators” sitting at the top of the leaderboard, selling access to information-stealing malware to “workers” for a few hundred dollars a month.
The workers are responsible for driving traffic to the malware drop sites, which they do using YouTube videos, BlackSEO, SEO poisoning, laced torrent files, or malicious social media posts.
Users can minimize the risk of infection from information thieves by avoiding downloads from shady locations, checking all downloaded executables with an anti-virus solution before opening them, and keeping their systems up to date.
[ad_2]
Source link
