[ad_1]

Microsoft said today that security vulnerabilities affecting an abandoned web server since 2005 have been used to target and compromise organizations in the energy industry.
As cybersecurity firm Recorded Future revealed in a report in April, state-backed Chinese hacking groups (including one identified as RedEcho) have targeted several Indian power grid operators, compromising an Indian national security system. emergency response and the subsidiary of a multinational logistics company.
The attackers gained access to the internal networks of the hacked entities through cameras exposed to the Internet on their networks as command and control servers.
“In addition to the targeting of power grid assets, we also identified the compromise of a national emergency response system and the Indian branch of a multinational logistics company by the same group of threat activities” , said Recorded Future. said.
“To achieve this, the group likely compromised and co-opted internet-connected DVR/IP camera devices for command and control (C2) of Shadowpad malware infections, as well as using the open-source tool . FastReverseProxy“
Attacks related to Boa web server vulnerabilities
While Recorded Future did not elaborate on the attack vector, Microsoft said today that attackers exploited a vulnerable component of the Boa web server, a software solution discontinued since 2015 that is still used by IoT devices (routers to the cameras).
Boa being one of the components used to connect and access IoT device management consoles, greatly increases the risk of critical infrastructure breaches through vulnerable and internet-exposed devices running the vulnerable web server.
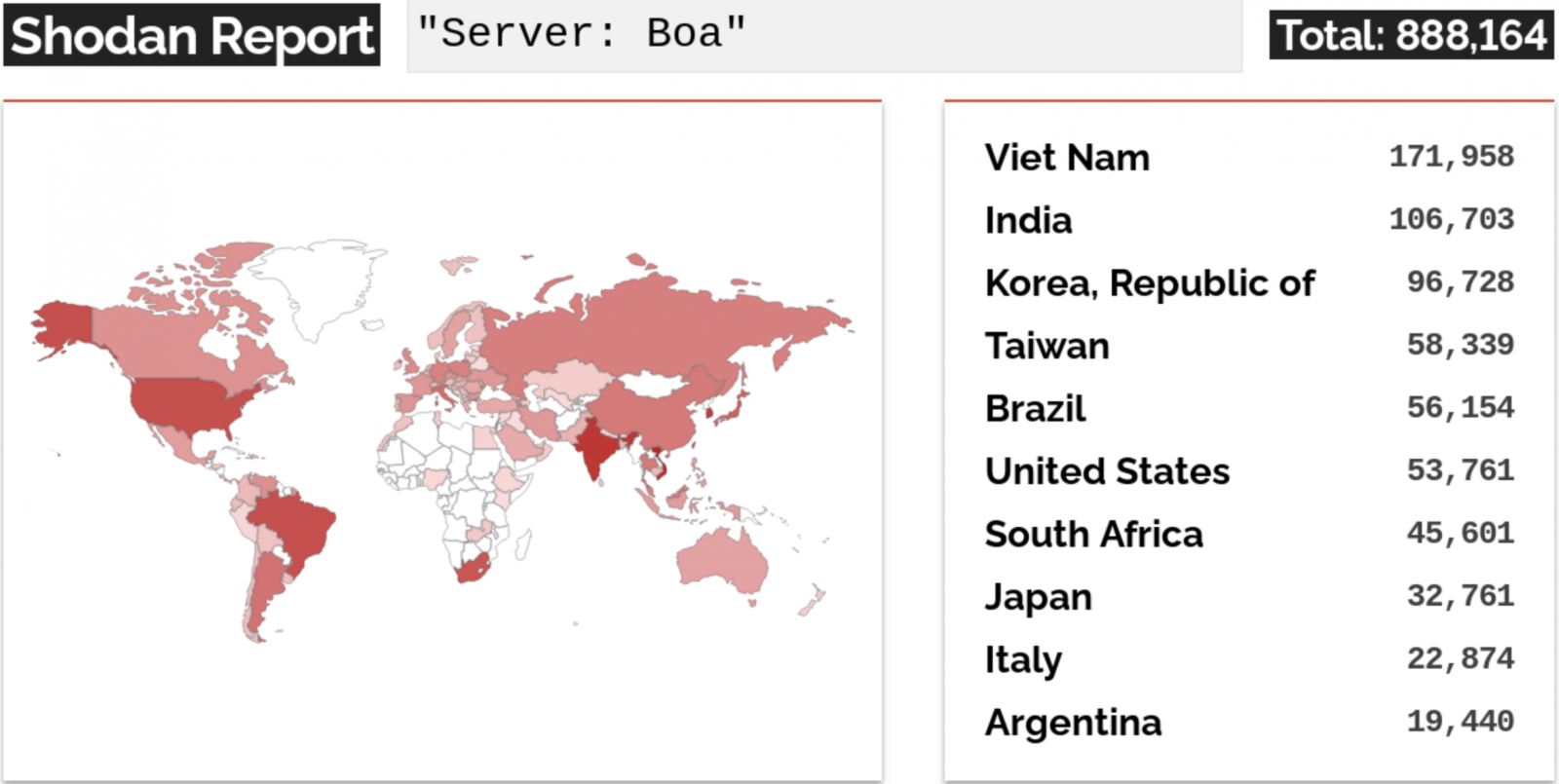
The Microsoft Security Threat Intelligence team said today that Boa servers are ubiquitous in IoT devices, primarily due to the web server’s inclusion in popular software development kits (SDKs).
According to data from the Microsoft Defender Threat Intelligence Platform, more than one million Internet-exposed Boa server components were detected online worldwide in a single week.
.png)
“The Boa servers are affected by several known vulnerabilities, including arbitrary file access (CVE-2017-9833) and disclosure of information (CVE-2021-33558),” Microsoft researchers said.
“Microsoft continues to see attackers attempting to exploit Boa vulnerabilities beyond the published reporting period, indicating that it is still being targeted as an attack vector.”
Attackers can exploit these security flaws without requiring authentication to execute code remotely after stealing credentials by accessing files containing sensitive information on the targeted server.
Tata Power Breached Using Boa Web Server Vulnerabilities
In one of the most recent attacks exploiting these vulnerabilities seen by Microsoft, Hive ransomware hacked into India’s largest integrated power company, Tata Power, last month.
“The attack detailed in the Recorded Future report was one of many attempted intrusions on India’s critical infrastructure since 2020, with the most recent attack on confirmed IT assets as of October 2022,” Redmond said.
“Microsoft assesses that the Boa servers were running on the IP addresses on the list of IOCs published by Recorded Future at the time of the report’s publication and that the power grid attack targeted exposed IoT devices running Boa.”
Tata Power revealed a cyberattack on its “IT infrastructure impacting some of its IT systems” in a stock deposit on Oct. 14 without sharing any additional details regarding the threat actors behind the incident.
The Hive ransomware gang then released data they claimed to have stolen from the Tata Power networks, indicating that the ransom negotiations had failed.
[ad_2]
Source link
