[ad_1]

The “LearnPress” WordPress online course plugin was vulnerable to several critical-severity flaws, including pre-authorization SQL injection and local file inclusion.
LearnPress is a Learning Management System (LMS) plugin that allows WordPress websites to easily create and sell online courses, lessons, and quizzes, providing visitors with a user-friendly interface without requiring knowledge. in coding on the part of the website developer.
The vulnerabilities of the plugin, used in more than 100,000 active sites, were discovered by PatchStack between November 30 and December 2, 2022, and reported to the software vendor.
The issues were resolved on December 20, 2022, with the release of LearnPress version 4.2.0. However, according to WordPress.org Statisticsonly about 25% have applied the update.
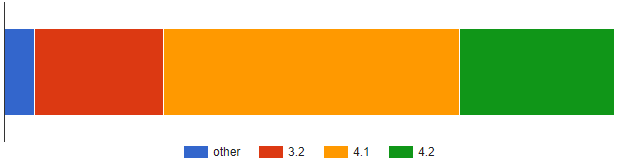
This means that approximately 75,000 websites could be using a vulnerable version of LearnPress, exposing themselves to serious security vulnerabilities, the exploitation of which can have serious repercussions.
Vulnerability details
The first vulnerability discovered by PatchStack is CVE-2022-47615, an unauthenticated local file inclusion (LFI) flaw that allows attackers to view the contents of local files stored on the web server.
This could expose credentials, authorization tokens, and API keys, leading to further compromises.
The vulnerability resides in a piece of code that handles API requests for the website, located in the “list_courses” function, which incorrectly validates certain variables ($template_pagination_path, $template_path and $template_path_item).
An attacker could potentially exploit CVE-2022-47615 by sending a specially crafted API request and using malicious values for all three variables.
The second critical flaw is CVE-2022-45808, an unauthenticated SQL injection that can lead to sensitive information disclosure, data modification, and arbitrary code execution.
The vulnerability resides in a function that handles SQL queries for the website, which fails to properly sanitize and validate the “$filter” variable in the query parameters, allowing an attacker to insert malicious code into it.
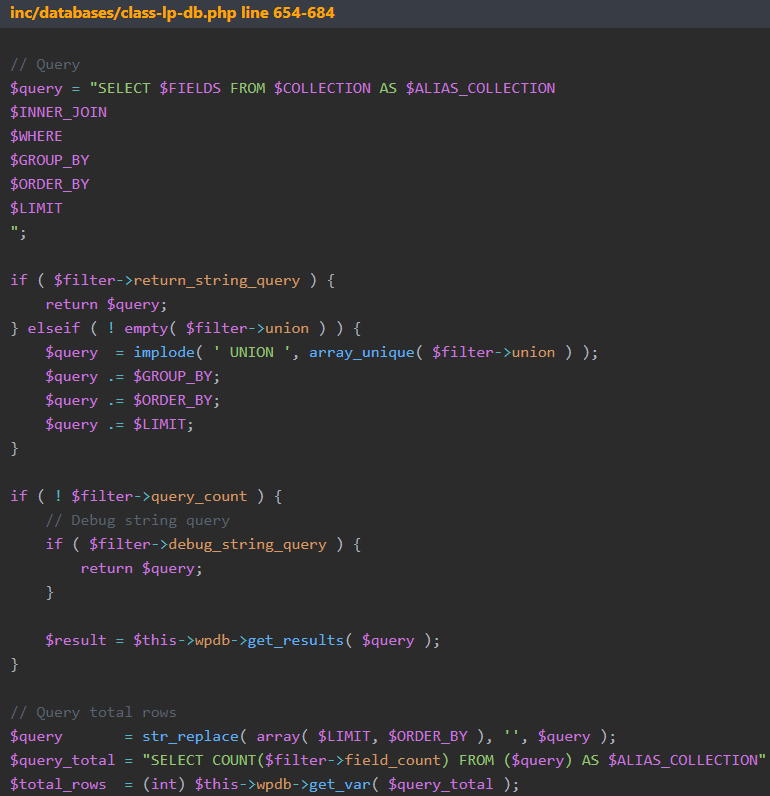
The third flaw impacting older versions of LearnPress is CVE-2022-45820, an authenticated SQL injection flaw in two plugin shortcodes (“learn_press_recent_courses” and “learn_press_featured_courses”) failing to properly validate and sanitize input from the “$args” variable.
PatchStack provided a proof-of-concept exploit showing how a “Contributor” user could trigger SQL injection using a specially crafted shortcode on a written article.
This vulnerability should be performed by a user with the ability to edit or create a new blog post, limiting the risk of a breach.
The vendor addressed the above issues by introducing whitelisting and cleaning up vulnerable variables or removing the ability to include patterns in user input.
Website owners using LearnPress are advised to upgrade to version 4.2.0 or disable the plugin until they can apply the available security update.
[ad_2]
Source link
