[ad_1]

Twitter has launched its “Encrypted Direct Messages” feature allowing paid Twitter Blue subscribers to send end-to-end encrypted messages to other users of the platform.
End-to-end encryption (E2EE) uses private and public key pairs to encrypt information sent over the Internet so that only the sender and receiver can read it.
The private decryption key is only stored on the sender’s device and is not shared with anyone else. However, the public encryption key is shared with others who want to send you encrypted data.
As the private decryption key is only stored on the local recipient’s device and never stored elsewhere along the way, such as on the messaging app’s servers, even if someone intercepts the message, they won’t be able to not read it without the decryption key.
End-to-end encrypted DMs on Twitter was a sought after and massively requested feature that was teased and pulled in 2018.
Last November, mobile researcher Jane Manchun Wong REMARK that the source code of Twitter for Android hinted at the implementation of an E2EE system, with Elon Musk anything but confirm the suspicions.
Almost six months later, Twitter today officially announced the availability of an encrypted messages feature on the latest version of the Twitter apps for iOS and Android and on the web platform.
Based on the details of the announcement, which mentions the use of a device-generated private key and a centrally provided public key, Twitter has implemented an asymmetric encryption scheme.
“The public key is automatically saved when a user logs into Twitter on a new device or browser; the private key never leaves the device and is therefore never communicated to Twitter,” a Twitter user explains. support page for functionality.
“In addition to the private-public key pairs, there is one key per conversation that is used to encrypt message content.”
While no specific or technical details like the encryption algorithms employed were disclosed, Twitter has promised to open source its E2EE implementation and publish a detailed whitepaper later in 2023.
Only available to Twitter Blue followers
To the disappointment of many, this new security option will only be available to users who pay for a “verified” badge, with both chat participants having to be Twitter Blue subscribers or affiliated with a verified organization for their messages to be encrypted.
Eligible users’ chat interface now features an “Encrypted Direct Messages” toggle so they can easily switch modes at any time.
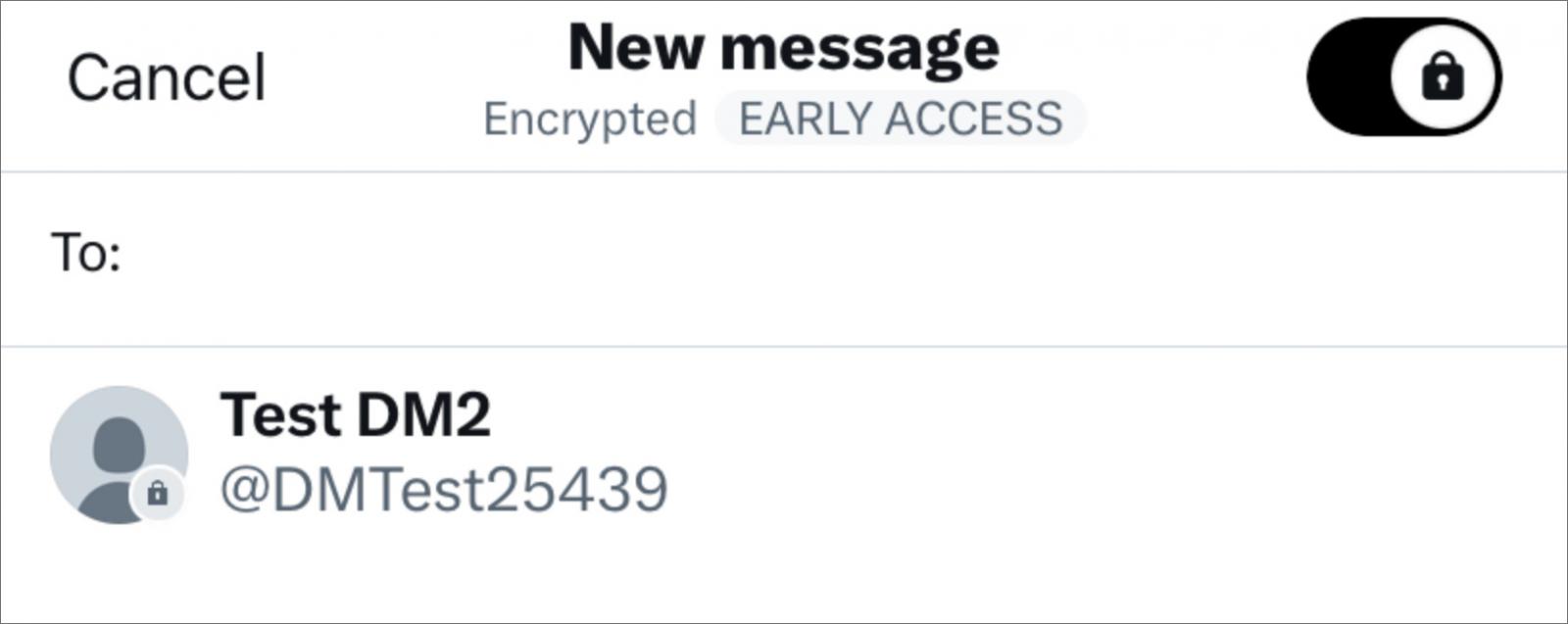
Source: Twitter
Users can resume existing conversations in E2EE mode by entering the previous message exchange, clicking the information icon, and then selecting “Start Encrypted Message”.
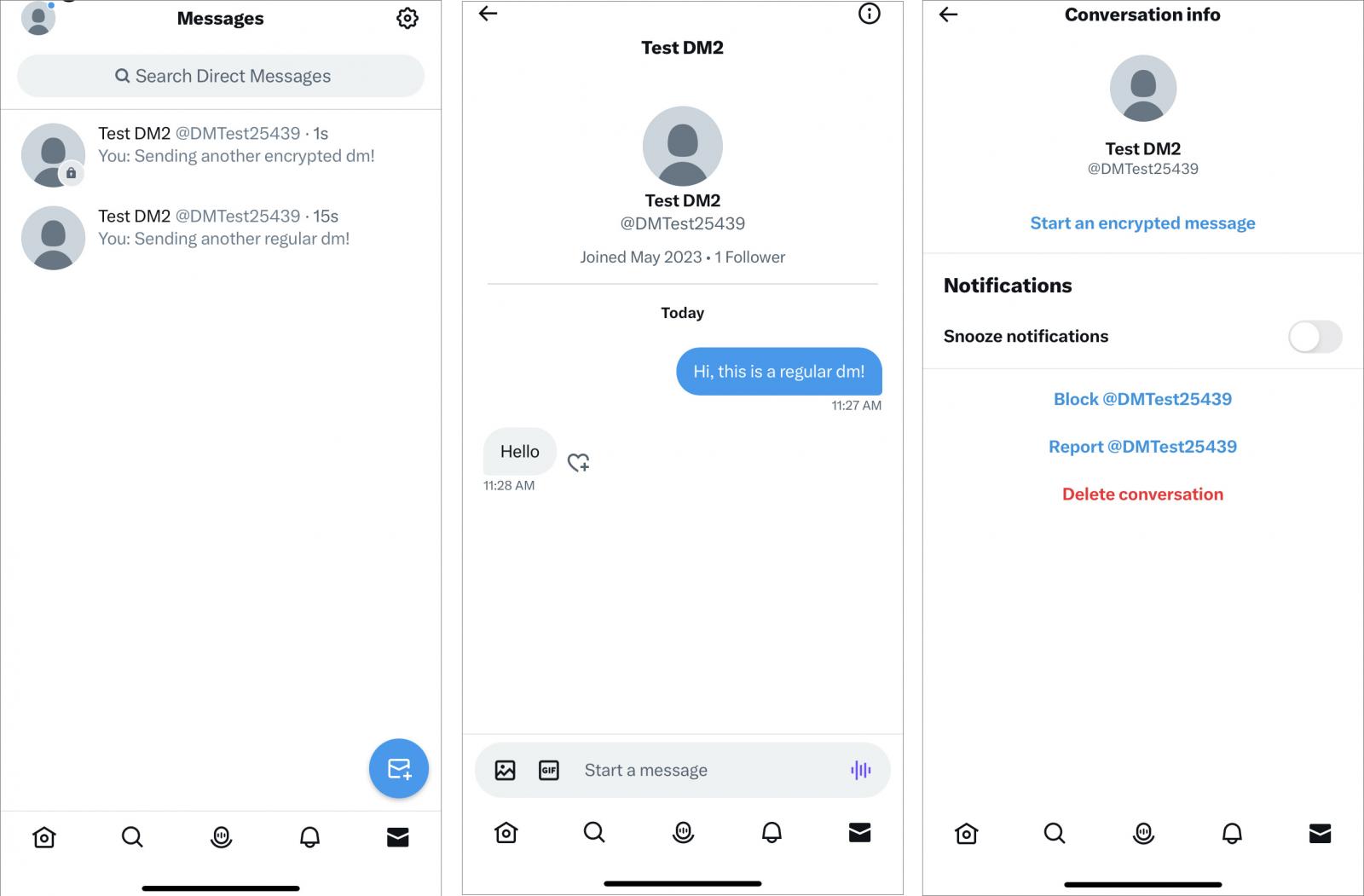
“Free” Twitter users will not be able to use “encrypted direct messages”, by default standard unencrypted communications.
In addition to excluding non-paying users, Twitter also informed of certain limitations, such as the inability to send encrypted messages to groups, support for text and links only (no media), l banning new devices from joining existing encrypted conversations, and only allowing a maximum of 10 registered devices per user.
Twitter also notes that the security of the private key, which remains on the device at all times, is crucial to protecting the integrity of the new E2EE messaging system.
Indeed, if an attacker steals this key, he can use it to decrypt all encrypted messages sent and received by the hacked device.
[ad_2]
Source link