[ad_1]

Google has disclosed more technical details about how Private Compute Core (PCC) works on Android and keeps sensitive user data processed locally on protected devices.
Introduced in Android 12PCC is a secure, isolated, and trusted environment within the operating system where sensor, GPS, microphone, camera, and screen data is stored and processed to provide machine learning capabilities to the user. ‘user.
Examples of these smart features include “Live Caption”, which uses the microphone for voice recognition, “Now Playing”, which recognizes the song, or “Smart Reply”, which suggests replies in messaging apps.
How PCC Works
Ambient and OS-level data processed in this protected “sandbox” can be used to enable smart features on Android devices through the UPS system, but is kept out of reach of remote applications and servers. thereby protecting user privacy.
Isolation of PCC from all other applications is achieved by using the Android Framework API for all data input and output to and from the PCC, facilitated by permissions granted during OS installation.
Only OS updates can change this permission, so no remote app or server login can change this.
BleepingComputer asked Google about the effects of CCP on protecting data from malware that may have compromised an Android device and got the following comment:
“The CCP makes it harder for malware to exploit the operating system. The CCP ensures that device features handle data according to best practices, including not storing it longer than necessary, which which inherently reduces the risk of malware.”
“That said, PCC is designed specifically for user data privacy, not as additional security protection against malware.”
This data sealing includes Google itself, as all processing of user data occurs inside the PCC enclave, locally on the device.
If ML features require this data to interact with external endpoints, Google Private Compute Services will enable an encrypted exchange.
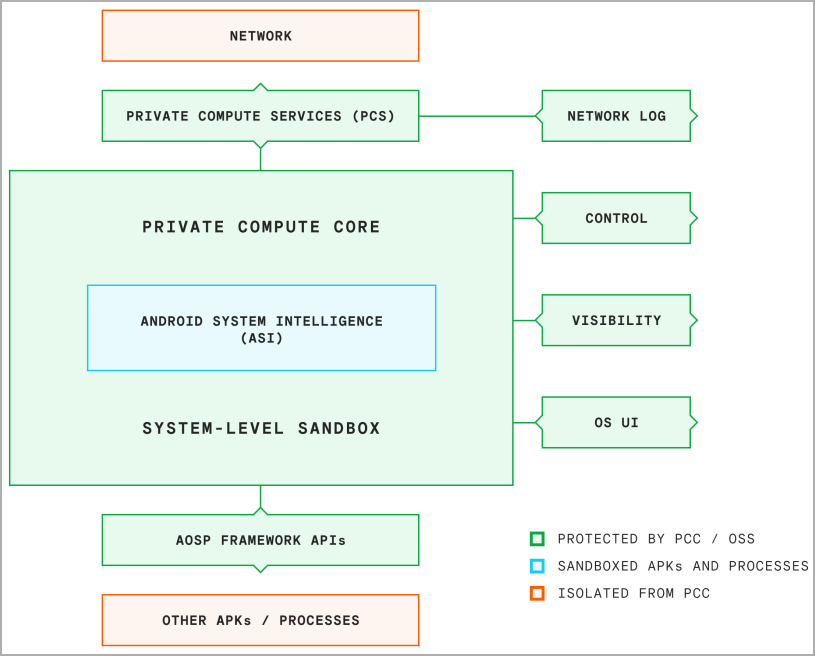
Private Compute Services (PCS) is a set of services that provide a privacy-preserving link between PCC and the cloud.
PCS was recently made open source as part of Google’s ongoing commitment to transparency, and its source code is available at this GitHub repository.
Google says that to improve CCP based on usage statistics, it leverages federated learning and analytics while monitoring the performance of its machine learning models using information retrieval. private.
Federated Analytics and learning enable Google to train ML models without centralized data collection, by running raw data analysis calculations locally on users’ devices.
PCC’s machine learning features stay up-to-date because the system is still part of the Android operating system, so it can continue to evolve independently.
That said, PCC is not beyond the user’s control. For example, if the sensor toggles are disabled, they will stop generating and sending data to the operating system, including the PCC.
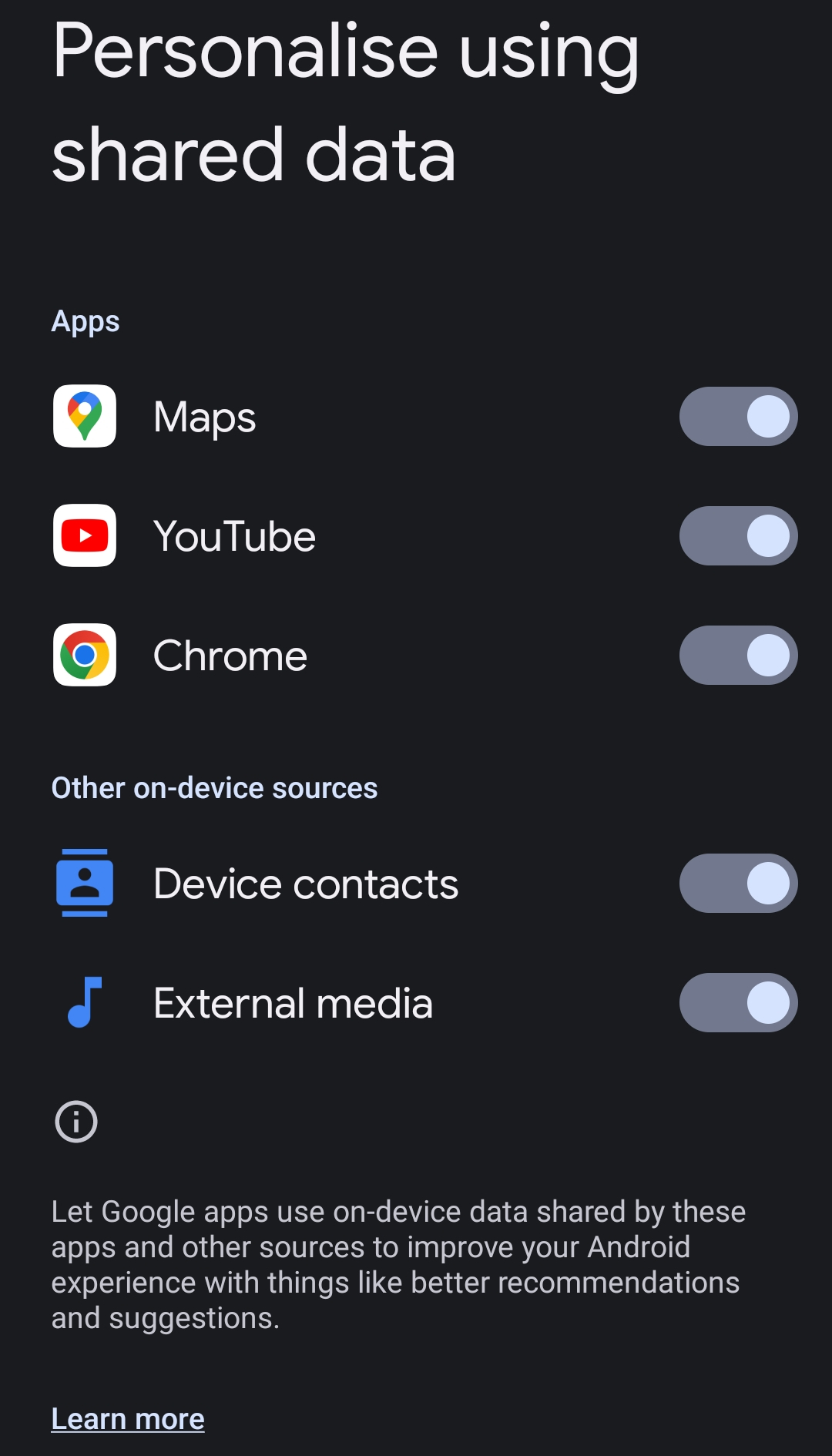
Additionally, users can limit data sharing with PCC by accessing Settings > Google > Personalize using app data and set the toggle to the “off” position for apps that support ML features.
For more details on the operation and functional characteristics of the CCP, Google engineers also published a technical article on Arxiv.org.
[ad_2]
Source link
