[ad_1]

Cybercrime groups are increasingly running their operations like a business, promoting jobs on the dark web that offer developers and hackers competitive monthly salaries, paid vacations and paid sick days.
In a new Kaspersky reportwhich analyzed 200,000 job postings posted on 155 dark websites between March 2020 and June 2022, hacking groups and APT groups seek to hire primarily software developers (61% of all postings), offering packages very competitive to attract them.
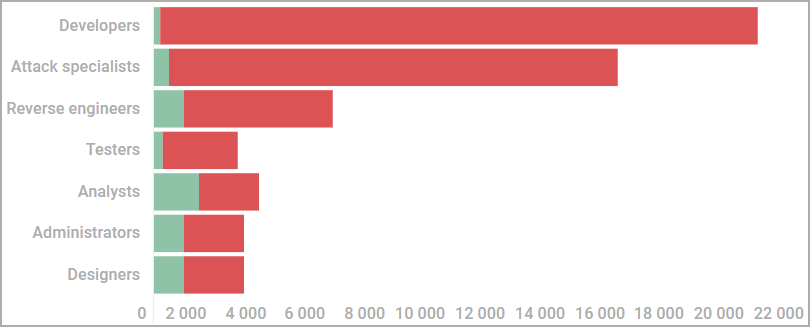
The highest-paying job seen by Kaspersky analysts included a monthly salary of $20,000, while ads for capable attack specialists exceeded $15,000/month.
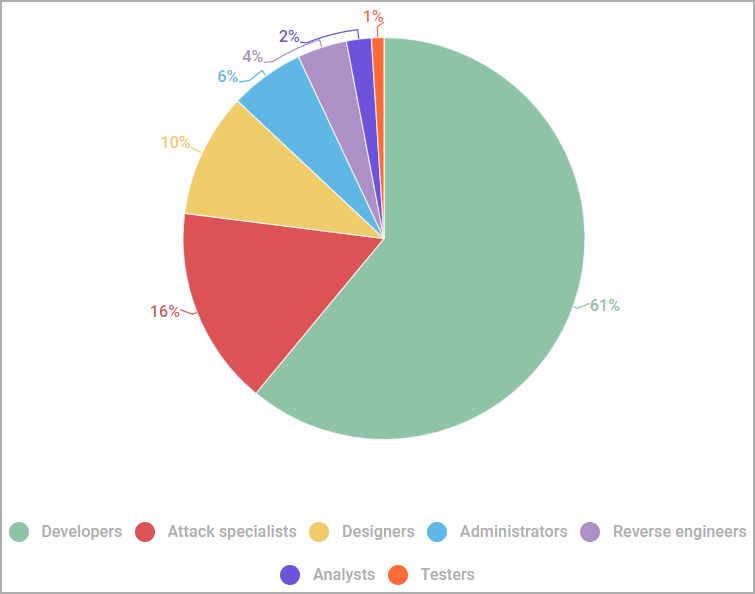
Hacking groups also seek to fill other roles, including data analysts, malware and tool developers, initial compromise actors, reverse engineers, web and e-mail designers. phishing mails, malware testers and IT administrators.
The median salary for IT professionals ranged between $1,300 and $4,000 per month, with designers receiving the lowest amounts and reverse engineers positioned at the higher end of the median salary range.
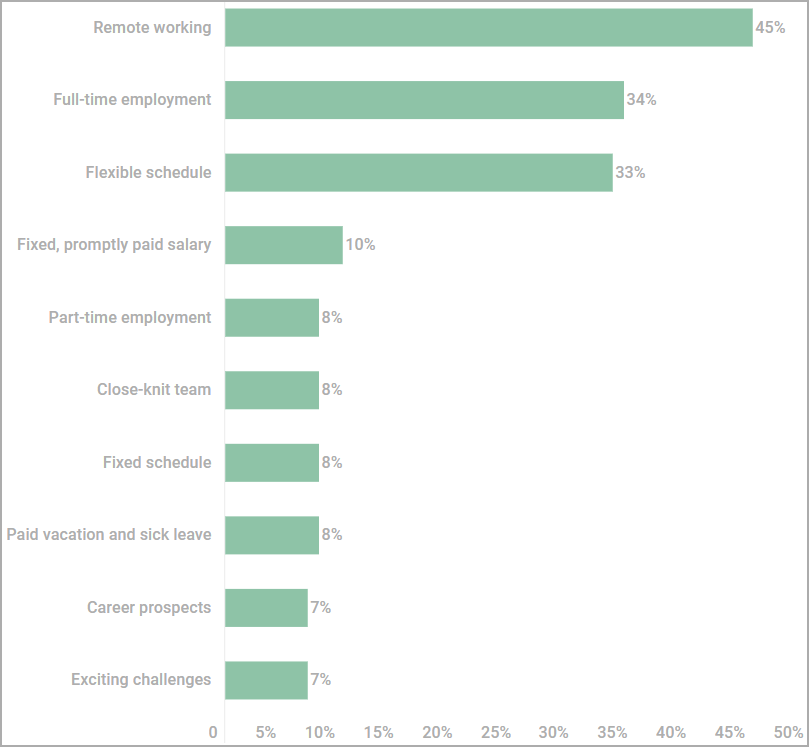
In a third of job postings, recruiters offered candidates full-time employment, and an equal percentage allowed flexible hours.
In some cases (8%), teleworkers would be offered paid holidays and sick leave, which shows that some dark web employers care about making their offers as attractive as possible.
These “employment” packages are quite competitive compared to similar positions in legal labor markets and could attract unemployed professionals or young IT graduates who are struggling to find employment.
“It should be noted that the risks associated with working for a dark web employer always outweigh the benefits,” Kaspersky warns.
“The absence of a legally enforced employment contract absolves employers of liability. A worker could be left unpaid, framed, or embroiled in a fraudulent scheme.”
The highest volume of ads was posted during the first quarter of 2020, coinciding with the massive changes brought to the workforce by the COVID-19 pandemic. A second peak was recorded between Q4 2021 and Q1 2022.
A not-so-typical hiring process
As part of the hiring process, cybercriminal recruiters perform test assignments created to determine a candidate’s skill level in the claimed field.
In some cases, recruiters also review the CV or portfolio provided, and in one in four postings there is an interview session with the job seeker.
In typical examples spotted by Kaspersky, a job posting promised to pay applicants around $300 in BTC for a testing assignment.
Another job posting outlined a multi-step selection process where the candidate would be asked to encrypt a test DLL within 24 hours, rendering it completely undetectable by AVs (maximum of 3 minor AV runtime detections).
As cybercrime businesses embrace business-like operations, we will continue to view the dark web as a recruiting tool for threat actors looking for a stable income.
Some software developers may view these opportunities as a lifeline during difficult times of political unrest, poor economies, or lack of job opportunities in their region.
However, it’s essential to understand the potential risks of working for a dark web employer, ranging from being scammed to being framed, arrested, sued and imprisoned.
[ad_2]
Source link
