[ad_1]
Biometric authentication is often considered nearly impossible to steal or tamper with, a perfect addition to your cybersecurity arsenal. Although it is difficult for a threat actor to replicate a physical attribute of a specific individual, biometric authentication is not infallible.
In the context of computers, a biometric sample is a physical or behavioral attribute scanned and encoded in data. Not only are there ways to bypass biometric authentication, but not all biometric methods are created equal.
Understand how biometric scans work
Whether physiological or behavioral, the software captures the biological input provided by a user. For example, fingerprint or face scan. The captured image creates a reference data point pattern.
Captured data is now stored in the internal hardware of the device used or in a cloud platform. This data is actually a generated code describing the biometric characteristics of the captured image for the specific biometric technology.
For optimum security, it would be ideal for biometric systems requiring live biometrics to be presented at each access point. Moreover, biometric identification solutions should not be the only step at the point of entry.
Implementing a multi-factor authentication system that combines biometric features such as fingerprint readers with more traditional elements such as 2FA or passwords would provide optimal security.
Increase security with biometrics
In movies, the villain often guesses the password to get in or the action hero uses the fingerprint of someone who is unconscious to gain access. Copying biometric authentication is much more complex. In real life, a stolen or guessed password is much easier to acquire than a person’s fingerprint.
Unless a malicious actor can take a fingerprint from a cup of coffee, print a silicone fingerprint, and gain access to the scanner, they won’t gain quick access to secure data. The amount of effort required is leaps and bounds above what the average striker will spend. In this sense, biometrics is much more secure because you need the physical presence of the individual or an excellent copy of their specific attribute.
Not all biometrics are created equal
Biology is tricky, and so is any biometric authentication. A sweaty hand can mean that a scanner cannot read a fingerprint.
Most biometric authentication systems fall back to a password or PIN. Windows Hello for Business backs up biometrics with a PIN code (linked locally to the device). The main access method is fingerprint, but if that doesn’t work for some reason, enter your PIN to see the desktop.
As an attacker, one could swipe the wrong fingerprint multiple times to access a simpler PIN. Since traditional methods, such as passwords and PINs, provide fallback methods for biometrics, there is a potentially insecure way for the attacker to do so.
So far, fingerprint biometrics has been exclusively mentioned as it is usually the most used method. But, there are different types available, both physical and behavioral. Each method has its pros and cons, and a few are listed below to get an idea of the variety of methods.
Physical biometrics
Most physical biometrics are specific interactions triggered when a second or primary form of authentication is needed. The disadvantage of physical biometrics is that a user must actively participate.
|
Method |
Benefits |
The inconvenients |
|
Digital print |
– Familiar method used on many different devices – Cheap scanning technology – Fast scanning capability |
– Injuries can interfere with a scan – Can be bypassed via fake fingerprints – Reliance on partial fingerprint data reduces accuracy |
|
Facial care |
– Widely used method, especially on phones – Requires minimal interaction – Without contact |
– Lighting affects accuracy – Face props affect accuracy – Potentially circumvented via the image of an individual |
|
Voice |
– Natural communication method – Unique method, difficult to falsify |
– Changes in voice decrease accuracy – Background noise can affect performance – Recordings could potentially be used to circumvent |
|
Retina/Iris |
– Naturally well protected against damage – High level of randomness between individuals |
– Invasive as most scanners require close contact – Low light affects performance – Scanners are more expensive |
|
palm vein |
– Contactless thanks to light scanning – Unique method not affected by hand condition |
– Expensive scanning technology – Some fevers may affect scanning ability |
Behavioral biometrics
One aspect of behavioral biometrics is that they tend to be collected passively. Data collected in the background means that behavioral authentication can be seamlessly added to normal password interaction, providing a second factor without additional user work.
|
Method |
Benefits |
The inconvenients |
|
Using the touch screen |
– Good for mobile devices – Accessible to people who may not use a keyboard |
– Not all devices have a touch screen – The condition of the touchscreen may affect the quality |
|
Typing dynamics |
– Useful for those who mainly work with a keyboard – Familiar input form for many |
– Stronger entry form – Required to enter a certain amount of text input – Not all devices have a keyboard – May not be as accessible as a touchscreen |
|
Mouse activity |
– Less intrusive than using a keyboard – Mainly passive data collection |
– Not all devices have a mouse – May not be as accessible as a touchscreen |
The consequences of compromised biometrics
A stolen password can be changed, but the same cannot be said of a fingerprint. Encoded in the computer is the unique fingerprint distilled into data via an algorithm. As the fingerprint is represented and stored as data, it can be stolen.
Once stolen, a person’s fingerprints cannot be altered, just like a retinal scan or palm geometry. This means that the stolen biometric data is permanently compromised. The consequences of compromised biometrics mean that data can never be recovered once stolen.
Overlay passwords and biometrics for increased security
Since most biometric data is part of multi-factor authentication and is often backed by specific passwords, how does an organization secure its data? Layering biometric authentication with a strong password policy will ensure that more than compromised biometrics are needed to access secure resources.
As stated earlier, if a PIN is available as a fallback method, it’s likely much faster to crack than a really strong password depending on the length and complexity requirements. In the case of Windows Hello for Business, an attacker would need access to a specific physical device. But, if an additional authentication metric of a password were added, it would make an attacker’s job exponentially more difficult.
All of this implies that without the requirement of a password, a biometric authentication method is not sufficient.
Strengthen security with Specops password policy and Specops uReset
Biometrics alone cannot fully secure a system, because relying on an insecure password provides a gateway for a malicious actor to access it. Not to mention, the cost of migrating to this model is more than the average IT security budget allows.
However, there are tools to strengthen password security that don’t require a system overhaul. Specops password policy integrates with Active Directory to deliver targeted policies containing flexible rule sets to conform to your organization’s needs.
With the Breached Password Protection add-on, ensure that no previously stolen passwords are used. Plus, keep your users safe and aware of needed adjustments to their passwords when changing passwords with the built-in password requirement screen at Windows logon.
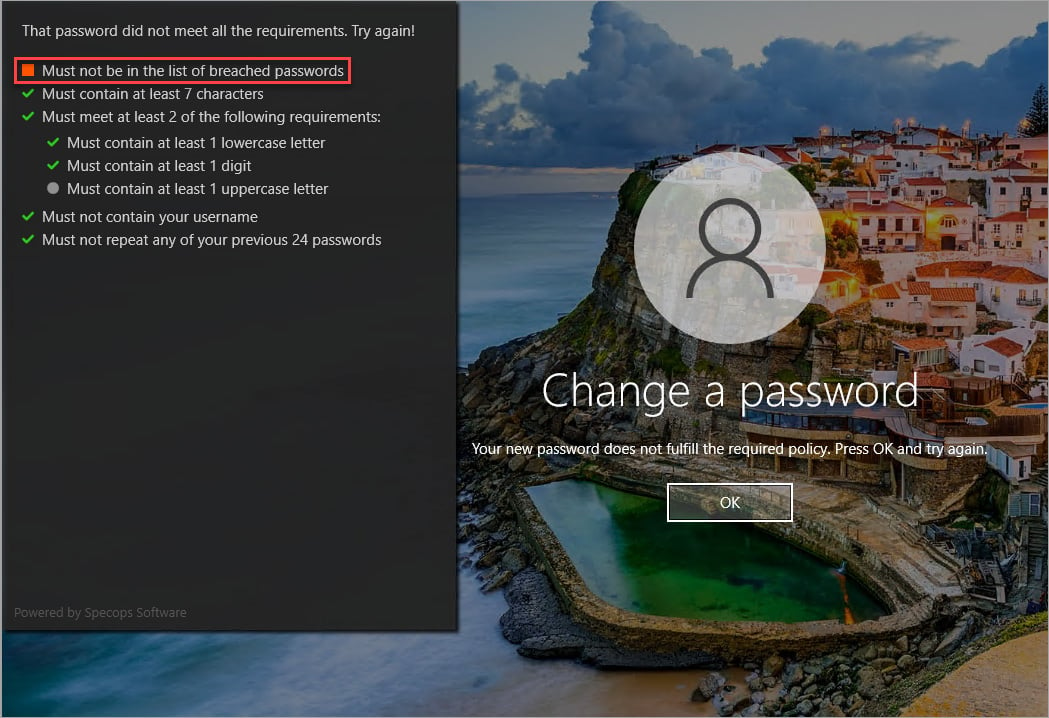
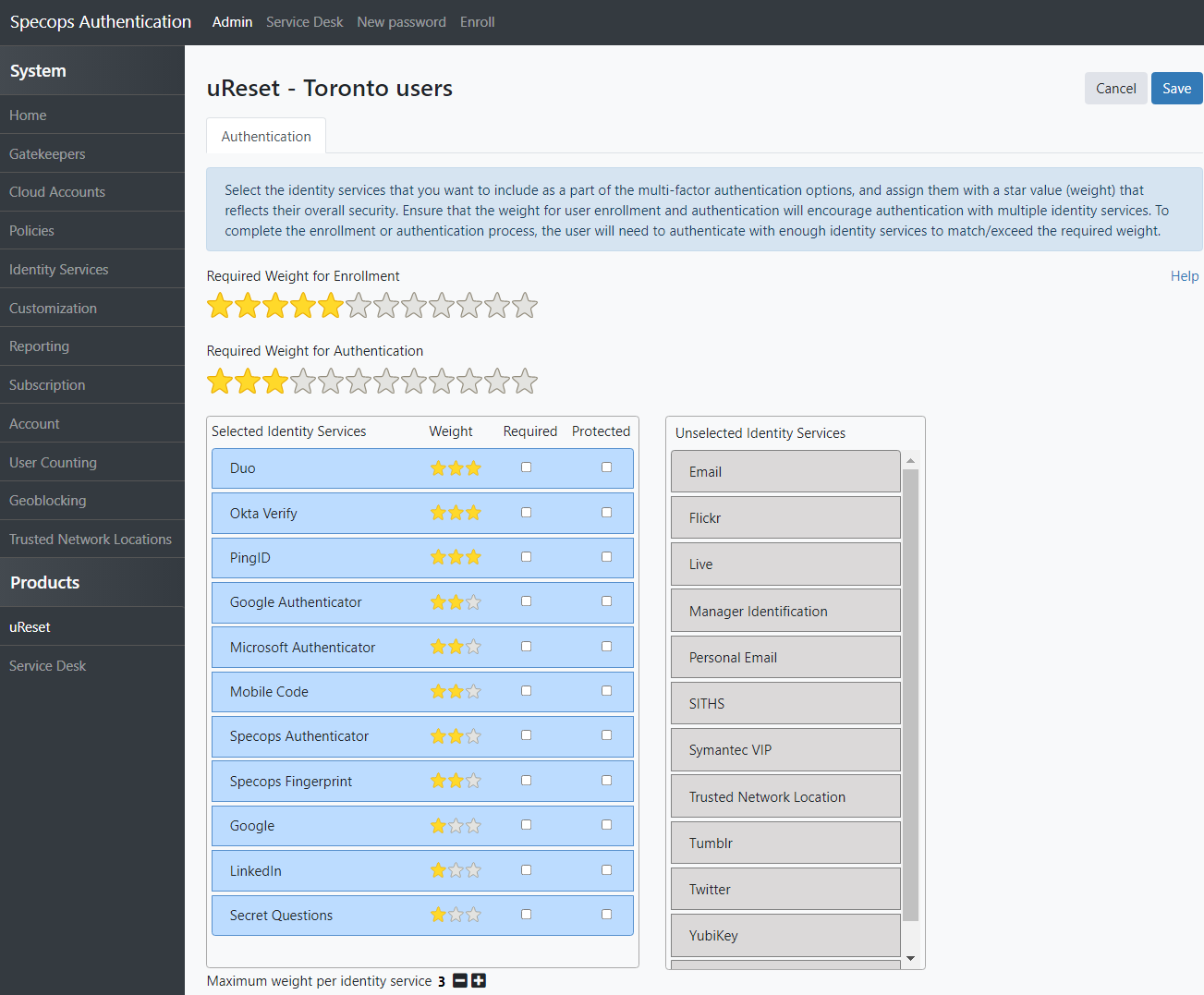
There may come a time when a user needs to reset a lost password, and to make this process easier and more secure,uReset Specifications offers multiple weighted authentication providers. Not all methods are considered equally safe, so layer several to ensure a user can get back to work quickly.
Given the importance that passwords still play with biometric authentication, a flexible reset process is needed to ensure that a locked account doesn’t get in the way of your users. This is especially true for the home user and hybrid offices to avoid constant help desk calls!
Stronger together, biometrics and passwords
As powerful as biometrics are, more than enough to properly secure access to resources. Moreover, the risk of theft of biometric data is much more durable than a password.
Therefore, layering biometrics with strong passwords guarantees a high probability of security.
With Specops password policy And uReset Specificationsgive your users the best possible experience by protecting them with flexible policies while ensuring that even if they are locked out, they will enter through a variety of authenticated methods while reducing help desk calls.
Sponsored and written by Specops software
[ad_2]
Source link
