[ad_1]

Fortra has released an emergency patch to address an actively exploited zero-day vulnerability in the GoAnywhere MFT secure file transfer tool.
The vulnerability allows attackers to obtain remote code execution on vulnerable GoAnywhere MFT instances whose administration console is exposed online.
The company has disclosed (this advisory is only accessible with a free account) over the weekend that the flaw is being exploited in attacks and has provided indicators of compromise for potentially affected customers, including a specific stack trace that would appear in the logs on compromised systems.
“If this stacktrace is in the logs, it’s very likely that this system was the target of an attack,” Fortra said.
Now it has added an update to its customer dashboard labeled as “time sensitive” and urging customers to fix their instances “as soon as possible”.
“This patch (7.1.2) was created as a result of the issue we disclosed in security advisories released last week regarding GoAnywhere MFTaaS. We urgently advise all GoAnywhere MFT customers to apply this patch” , Fortra said.
“Once downloaded, we recommend that you work with your administrators to apply the patch as soon as possible to ensure a full resolution of the identified issue.
“Especially for customers who operate an administration portal exposed to the Internet, we consider this to be an urgent matter.”
You can download the security patch from the “Product Downloads” tab at the top of the GoAnywhere account page after logging in.
Monday, security researcher Florian Hauser also from the IT security consulting firm Code White released a proof-of-concept exploit which could be used to perform unauthenticated remote code execution on unpatched, internet-facing GoAnywhere MFT servers.
Dozens of instances exposed online, mitigation also available
In a Saturday update to its advisory, Fortra explained that “the attack vector for this exploit requires access to the application’s admin console, which in most cases can only be accessed ‘from a private corporate network, via VPN, or by authorization IP addresses (when running in cloud environments, such as Azure or AWS).”
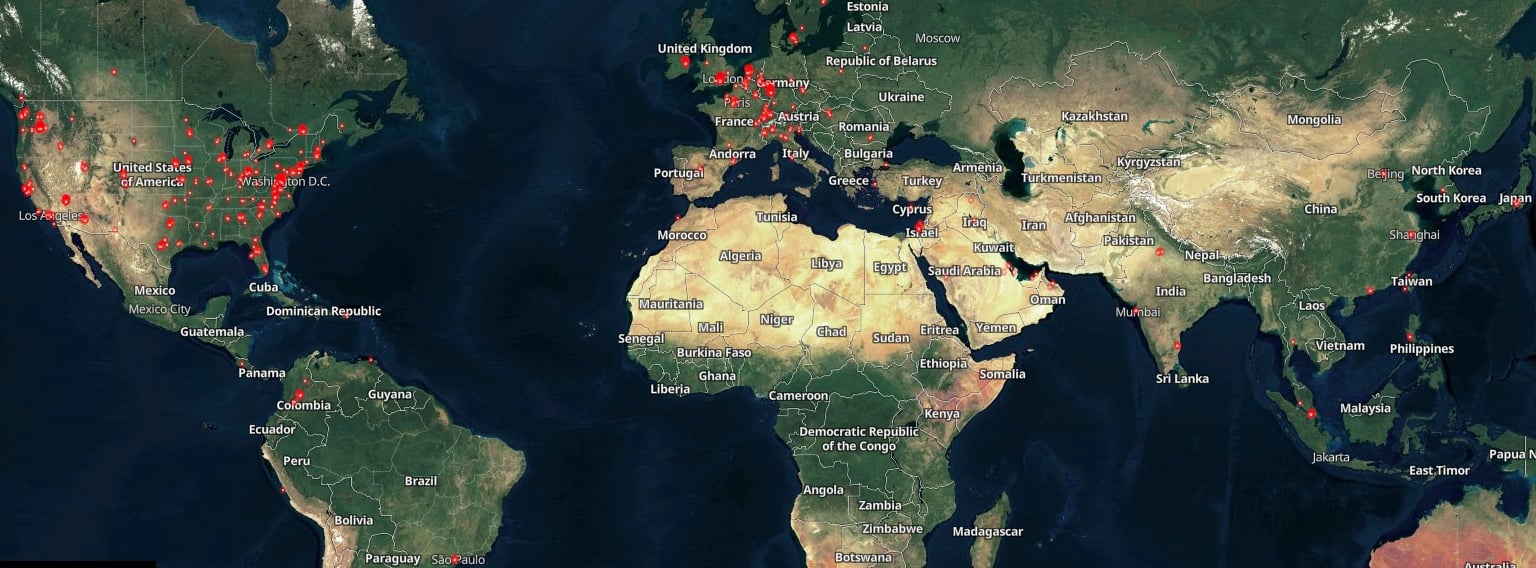
However, a Shodan scan reveals that nearly 1,000 GoAnywhere instances are displayed on the Internet. Despite this, only a little over 140 are accessible on ports 8000 and 8001, those by default used by the vulnerable administration console.
If you cannot immediately apply the GoAnywere MFT emergency security patch, you can follow the company’s mitigation advice which requires implementing access controls to allow access to the interface of administration only from trusted sources or disabling the license service.
To disable the embedded and vulnerable License Server, administrators must comment out or remove the servlet and servlet mapping configurations for the license response servlet in the web.xml file, which would disable the vulnerable endpoint.
After making the changes and saving the modified web.xml file, a reboot is also required to apply the new configuration.
“Because your environment’s data could have been accessed or exported, you should determine if you have stored credentials for other systems in the environment and ensure that those credentials have been revoked” , Fortra added.
“This includes passwords and keys used to access any external systems with which GoAnywhere is integrated.
“Ensure that all credentials have been revoked from these external systems and review relevant access logs related to these systems. This also includes passwords and keys used to encrypt files in the system. “
[ad_2]
Source link
