[ad_1]

A critical vulnerability in Ghost CMS’s newsletter subscription system could allow external users to create new newsletters or modify existing ones to contain malicious JavaScript.
Such action could allow hackers to carry out large-scale phishing attacks from normally innocuous sites. Additionally, injecting JavaScript has been shown to allow XSS vulnerabilities that could allow threat actors to gain full access to a site.
Ghost is a free and open source CMS for creating websites, publishing content and sending newsletters, used as a faster and easier alternative to WordPress.
According to Built withGhost is used by around 126,000 websites, most of which are based in the US, UK and Germany.
Targeted remotely
The Cisco Talos team discovered the authentication bypass flaw in October 2022, which they tested and confirmed, impacting Ghost version 5.9.4. However, it probably affects more before and after versions.
The flaw is tracked as CVE-2022-41654 and has a CVSS v3 severity score of 9.6, qualifying it as critical.
Newsletter subscribers (members) are external users with no special privileges on the site, so they are only required to provide an email address and become members without admin approval.
However, Cisco Talos discovered that an exposed API with incorrect inclusion of the “newsletter” relationship could give subscribers access to this subsystem, allowing them to edit or create newsletters.
This includes the system-wide default newsletter that all members are subscribed to by default, essentially giving attackers the power to send whatever content they want to all subscribers.
.png)
A second issue stemming from the same flaw is the ability to inject JavaScript into the newsletter, which Ghost allows by default, assuming only administrators can access this powerful feature.
For example, the Cisco Talos team exploited this flaw to inject an XSS (cross-site scripting) object to create an administrator account, triggered when the administrator attempts to modify the default newsletter.
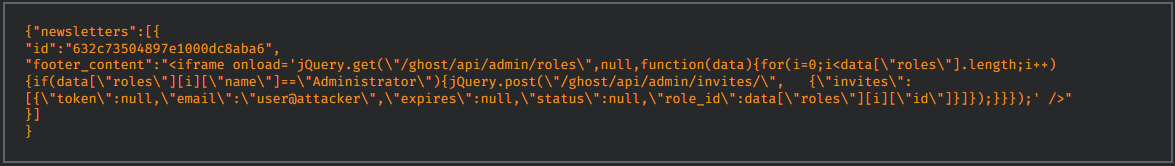
Along with the flaw above, Talos researchers also discovered CVE-2022-41697a medium-severity user enumeration vulnerability in Ghost’s login functionality, allowing an attacker to check whether an email address is associated with a user on the site.
Both vulnerabilities have been patched by Ghost on the latest version of the CMS, so all administrators of websites built on Ghost are recommended to apply the available security update as soon as possible.
[ad_2]
Source link
